
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing permeable rock, rock fractures or unconsolidated materials.

The water table is the upper surface of the zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with water. It can also be simply explained as the depth below which the ground is saturated.

A submersible pump is a device which has a hermetically sealed motor close-coupled to the pump body. The whole assembly is submerged in the fluid to be pumped. The main advantage of this type of pump is that it prevents pump cavitation, a problem associated with a high elevation difference between the pump and the fluid surface. Submersible pumps push fluid to the surface, rather than jet pumps, which create a vacuum and rely upon atmospheric pressure. Submersibles use pressurized fluid from the surface to drive a hydraulic motor downhole, rather than an electric motor, and are used in heavy oil applications with heated water as the motive fluid.

Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock become completely saturated with water is called the water table. Groundwater is recharged from the surface; it may discharge from the surface naturally at springs and seeps, and can form oases or wetlands. Groundwater is also often withdrawn for agricultural, municipal, and industrial use by constructing and operating extraction wells. The study of the distribution and movement of groundwater is hydrogeology, also called groundwater hydrology.

Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies, usually as a result of human activities, in such a manner that negatively affects its legitimate uses. Water pollution reduces the ability of the body of water to provide the ecosystem services that it would otherwise provide. Water bodies include for example lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and groundwater. Water pollution results when contaminants are introduced into these water bodies. For example, releasing inadequately treated wastewater into natural waters can lead to degradation of these aquatic ecosystems. All plants and organisms living in or being exposed to polluted water bodies can be impacted. The effects can damage individual species and impact the natural biological communities they are part of. Water pollution can also lead to water-borne diseases for people using polluted water for drinking, bathing, washing or irrigation.

Retaining walls are relatively rigid walls used for supporting soil laterally so that it can be retained at different levels on the two sides. Retaining walls are structures designed to restrain soil to a slope that it would not naturally keep to. They are used to bound soils between two different elevations often in areas of terrain possessing undesirable slopes or in areas where the landscape needs to be shaped severely and engineered for more specific purposes like hillside farming or roadway overpasses. A retaining wall that retains soil on the backside and water on the frontside is called a seawall or a bulkhead.

Wastewater treatment is a process used to remove contaminants from wastewater and convert it into an effluent that can be returned to the water cycle. Once returned to the water cycle, the effluent creates an acceptable impact on the environment or is reused for various purposes. The treatment process takes place in a wastewater treatment plant. There are several kinds of wastewater which are treated at the appropriate type of wastewater treatment plant. For domestic wastewater, the treatment plant is called a sewage treatment plant. For industrial wastewater, treatment either takes place in a separate industrial wastewater treatment plant, or in a sewage treatment plant. Further types of wastewater treatment plants include agricultural wastewater treatment plants and leachate treatment plants.
In the oil industry, waterflooding or water injection is where water is injected into the oil reservoir, to maintain the pressure, or to drive oil towards the wells, and thereby increase production. Water injection wells may be located on- and offshore, to increase oil recovery from an existing reservoir.
An aquifer test is conducted to evaluate an aquifer by "stimulating" the aquifer through constant pumping, and observing the aquifer's "response" (drawdown) in observation wells. Aquifer testing is a common tool that hydrogeologists use to characterize a system of aquifers, aquitards and flow system boundaries.

Agricultural wastewater treatment is a farm management agenda for controlling pollution from confined animal operations and from surface runoff that may be contaminated by chemicals in fertilizer, pesticides, animal slurry, crop residues or irrigation water. Agricultural wastewater treatment is required for continuous confined animal operations like milk and egg production. It may be performed in plants using mechanized treatment units similar to those used for industrial wastewater. Where land is available for ponds, settling basins and facultative lagoons may have lower operational costs for seasonal use conditions from breeding or harvest cycles. Animal slurries are usually treated by containment in anaerobic lagoons before disposal by spray or trickle application to grassland. Constructed wetlands are sometimes used to facilitate treatment of animal wastes.

In geotechnical engineering, a caisson is a watertight retaining structure used, for example, to work on the foundations of a bridge pier, for the construction of a concrete dam, or for the repair of ships. Caissons are constructed in such a way that the water can be pumped out, keeping the work environment dry. When piers are being built using an open caisson, and it is not practical to reach suitable soil, friction pilings may be driven to form a suitable sub-foundation. These piles are connected by a foundation pad upon which the column pier is erected.
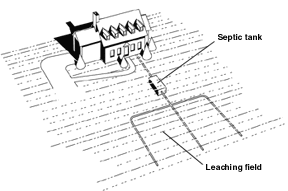
Septic drain fields, also called leach fields or leach drains, are subsurface wastewater disposal facilities used to remove contaminants and impurities from the liquid that emerges after anaerobic digestion in a septic tank. Organic materials in the liquid are catabolized by a microbial ecosystem.

A ground source heat pump is a heating/cooling system for buildings that uses a type of heat pump to transfer heat to or from the ground, taking advantage of the relative constancy of temperatures of the earth through the seasons. Ground source heat pumps (GSHPs) – or geothermal heat pump (GHP) as they are commonly termed in North America – are among the most energy-efficient technologies for providing HVAC and water heating using far less energy than can be achieved by burning a fuel in a boiler/furnace) or by use of resistive electric heaters.
Overdrafting is the process of extracting groundwater beyond the equilibrium yield of the aquifer. Groundwater is the fresh water that can be found underground; it is also one of the largest sources. Groundwater depletion can be comparable to "money in a bank", The primary cause of groundwater depletion is pumping or the excessive pulling up of groundwater from underground aquifers.
Groundwater models are computer models of groundwater flow systems, and are used by hydrogeologists. Groundwater models are used to simulate and predict aquifer conditions.

A well is an excavation or structure created in the ground by digging, driving, or drilling to access liquid resources, usually water. The oldest and most common kind of well is a water well, to access groundwater in underground aquifers. The well water is drawn up by a pump, or using containers, such as buckets, that are raised mechanically or by hand. Water can also be injected back into the aquifer through the well. Wells were first constructed at least eight thousand years ago and historically vary in construction from a simple scoop in the sediment of a dry watercourse to the qanats of Iran, and the stepwells and sakiehs of India. Placing a lining in the well shaft helps create stability, and linings of wood or wickerwork date back at least as far as the Iron Age.

River Bank filtration is a type of filtration that works by passing water to be purified for use as drinking water through the banks of a river or lake. It is then drawn off by extraction wells some distance away from the water body. The process may directly yield drinkable water, or be a relatively uncomplicated way of pre-treating water for further purification.
Dewatering is the removal of water from solid material or soil by wet classification, centrifugation, filtration, or similar solid-liquid separation processes, such as removal of residual liquid from a filter cake by a filter press as part of various industrial processes.

Stormwater harvesting or stormwater reuse is the collection, accumulation, treatment or purification, and storage of stormwater for its eventual reuse. While rainwater harvesting collects precipitation primarily from rooftops, stormwater harvesting deals with collection of runoff from creeks, gullies, ephemeral streams, and other ground conveyances. It can also include catchment areas from developed surfaces, such as roads or parking lots, or other urban environments such as parks, gardens and playing fields.

Groundwater pollution occurs when pollutants are released to the ground and make their way into groundwater. This type of water pollution can also occur naturally due to the presence of a minor and unwanted constituent, contaminant, or impurity in the groundwater, in which case it is more likely referred to as contamination rather than pollution. Pollution can occur from on-site sanitation systems, landfills, effluent from wastewater treatment plants, leaking sewers, petrol filling stations or from over application of fertilizers in agriculture. Pollution can also occur from naturally occurring contaminants, such as arsenic or fluoride. Using polluted groundwater causes hazards to public health through poisoning or the spread of disease.














