Related Research Articles

Cash flow, in general, refers to payments made into or out of a business, project, or financial product. It can also refer more specifically to a real or virtual movement of money.

This aims to be a complete article list of economics topics:

The historical cost of an asset at the time it is acquired or created is the value of the costs incurred in acquiring or creating the asset, comprising the consideration paid to acquire or create the asset plus transaction costs. Historical cost accounting involves reporting assets and liabilities at their historical costs, which are not updated for changes in the items' values. Consequently, the amounts reported for these balance sheet items often differ from their current economic or market values.
In accounting, fixed capital is any kind of real, physical asset that is used repeatedly in the production of a product. In economics, fixed capital is a type of capital good that as a real, physical asset is used as a means of production which is durable or isn't fully consumed in a single time period. It contrasts with circulating capital such as raw materials, operating expenses etc.
In accounting, book value is the value of an asset according to its balance sheet account balance. For assets, the value is based on the original cost of the asset less any depreciation, amortization or impairment costs made against the asset. Traditionally, a company's book value is its total assets minus intangible assets and liabilities. However, in practice, depending on the source of the calculation, book value may variably include goodwill, intangible assets, or both. The value inherent in its workforce, part of the intellectual capital of a company, is always ignored. When intangible assets and goodwill are explicitly excluded, the metric is often specified to be tangible book value.

In accountancy, depreciation is a term that refers to two aspects of the same concept: first, an actual reduction in the fair value of an asset, such as the decrease in value of factory equipment each year as it is used and wears, and second, the allocation in accounting statements of the original cost of the assets to periods in which the assets are used.

An income statement or profit and loss account is one of the financial statements of a company and shows the company's revenues and expenses during a particular period.
In financial accounting, free cash flow (FCF) or free cash flow to firm (FCFF) is the amount by which a business's operating cash flow exceeds its working capital needs and expenditures on fixed assets. It is that portion of cash flow that can be extracted from a company and distributed to creditors and securities holders without causing issues in its operations. As such, it is an indicator of a company's financial flexibility and is of interest to holders of the company's equity, debt, preferred stock and convertible securities, as well as potential lenders and investors.
In economics and finance, the profit rate is the relative profitability of an investment project, a capitalist enterprise or a whole capitalist economy. It is similar to the concept of rate of return on investment.
Return on capital (ROC), or return on invested capital (ROIC), is a ratio used in finance, valuation and accounting, as a measure of the profitability and value-creating potential of companies relative to the amount of capital invested by shareholders and other debtholders. It indicates how effective a company is at turning capital into profits.

Consumption of fixed capital (CFC) is a term used in business accounts, tax assessments and national accounts for depreciation of fixed assets. CFC is used in preference to "depreciation" to emphasize that fixed capital is used up in the process of generating new output, and because unlike depreciation it is not valued at historic cost but at current market value ; CFC may also include other expenses incurred in using or installing fixed assets beyond actual depreciation charges. Normally the term applies only to producing enterprises, but sometimes it applies also to real estate assets.
Capitalization rate is a real estate valuation measure used to compare different real estate investments. Although there are many variations, the cap rate is generally calculated as the ratio between the annual rental income produced by a real estate asset to its current market value. Most variations depend on the definition of the annual rental income and whether it is gross or net of annual costs, and whether the annual rental income is the actual amount received, or the potential rental income that could be received if the asset was optimally rented.
Return of capital (ROC) refers to principal payments back to "capital owners" that exceed the growth of a business or investment. It should not be confused with Rate of Return (ROR), which measures a gain or loss on an investment. It is essentially a return of some or all of the initial investment, which reduces the basis on that investment.
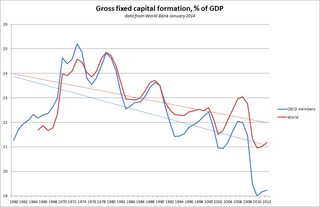
Capital formation is a concept used in macroeconomics, national accounts and financial economics. Occasionally it is also used in corporate accounts. It can be defined in three ways:
Rate-of-return regulation is a system for setting the prices charged by government-regulated monopolies, such as public utilities. It attempts to set prices at efficient levels equal to the efficient costs of production, plus a government-permitted rate of return on capital.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to finance:

Engineering economics, previously known as engineering economy, is a subset of economics concerned with the use and "...application of economic principles" in the analysis of engineering decisions. As a discipline, it is focused on the branch of economics known as microeconomics in that it studies the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of limited resources. Thus, it focuses on the decision making process, its context and environment. It is pragmatic by nature, integrating economic theory with engineering practice. But, it is also a simplified application of microeconomic theory in that it assumes elements such as price determination, competition and demand/supply to be fixed inputs from other sources. As a discipline though, it is closely related to others such as statistics, mathematics and cost accounting. It draws upon the logical framework of economics but adds to that the analytical power of mathematics and statistics.
Accelerated depreciation refers to any one of several methods by which a company, for 'financial accounting' or tax purposes, depreciates a fixed asset in such a way that the amount of depreciation taken each year is higher during the earlier years of an asset's life. For financial accounting purposes, accelerated depreciation is expected to be much more productive during its early years, so that depreciation expense will more accurately represent how much of an asset's usefulness is being used up each year. For tax purposes, accelerated depreciation provides a way of deferring corporate income taxes by reducing taxable income in current years, in exchange for increased taxable income in future years. This is a valuable tax incentive that encourages businesses to purchase new assets.
The building block model is a form of public utility regulation that is common in Australia. Variants of the building block model are currently used in Australia in the regulation of electricity transmission and distribution, gas transmission and distribution, railways, postal services, urban water and sewerage services, irrigation infrastructure, and port access. The Australian Competition & Consumer Commission (ACCC) has stated that it intends to use a version of the building block model to determine indicative access prices for fixed-line telecommunications services. The building block model is so-called because the allowed revenue of the regulated firm is equal to the sum of underlying components or building blocks consisting of the return on capital, the return of capital, the operating expenditure, and various other components such as taxes and incentive mechanisms.
Utility ratemaking is the formal regulatory process in the United States by which public utilities set the prices they will charge consumers. Ratemaking, typically carried out through "rate cases" before a public utilities commission, serves as one of the primary instruments of government regulation of public utilities.
References
- ↑ "Rate base definition". Energy Dictionary. Retrieved 2010-06-07.
- ↑ "As software technology advances, utilities may have to figure out how to do the same". Energy News Network. Retrieved 2019-07-16.
- ↑ "Rate of return definition". Energy Dictionary. Retrieved 2011-01-31.