
In physics, interference is a phenomenon in which two waves combine by adding their displacement together at every single point in space and time, to form a resultant wave of greater, lower, or the same amplitude. Constructive and destructive interference result from the interaction of waves that are correlated or coherent with each other, either because they come from the same source or because they have the same or nearly the same frequency. Interference effects can be observed with all types of waves, for example, light, radio, acoustic, surface water waves, gravity waves, or matter waves.

Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties.

The Michelson–Morley experiment was an attempt to detect the existence of the luminiferous aether, a supposed medium permeating space that was thought to be the carrier of light waves. The experiment was performed between April and July 1887 by American physicists Albert A. Michelson and Edward W. Morley at what is now Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland, Ohio, and published in November of the same year.
Interferometry is a technique which uses the interference of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy, quantum mechanics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, remote sensing, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, velocimetry, optometry, and making holograms.
In physics, two wave sources are coherent if their frequency and waveform are identical. Coherence is an ideal property of waves that enables stationary interference. It contains several distinct concepts, which are limiting cases that never quite occur in reality but allow an understanding of the physics of waves, and has become a very important concept in quantum physics. More generally, coherence describes all properties of the correlation between physical quantities of a single wave, or between several waves or wave packets.

The Mach–Zehnder interferometer is a device used to determine the relative phase shift variations between two collimated beams derived by splitting light from a single source. The interferometer has been used, among other things, to measure phase shifts between the two beams caused by a sample or a change in length of one of the paths. The apparatus is named after the physicists Ludwig Mach and Ludwig Zehnder; Zehnder's proposal in an 1891 article was refined by Mach in an 1892 article. Demonstrations of Mach–Zehnder interferometry with particles other than photons had been demonstrated as well in multiple experiments.

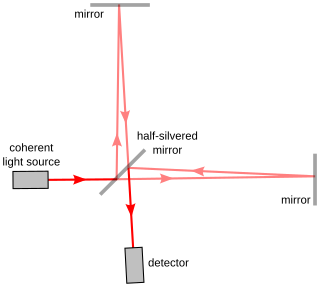
The Michelson interferometer is a common configuration for optical interferometry and was invented by the 19/20th-century American physicist Albert Abraham Michelson. Using a beam splitter, a light source is split into two arms. Each of those light beams is reflected back toward the beamsplitter which then combines their amplitudes using the superposition principle. The resulting interference pattern that is not directed back toward the source is typically directed to some type of photoelectric detector or camera. For different applications of the interferometer, the two light paths can be with different lengths or incorporate optical elements or even materials under test.

Newton's rings is a phenomenon in which an interference pattern is created by the reflection of light between two surfaces, typically a spherical surface and an adjacent touching flat surface. It is named after Isaac Newton, who investigated the effect in 1666. When viewed with monochromatic light, Newton's rings appear as a series of concentric, alternating bright and dark rings centered at the point of contact between the two surfaces. When viewed with white light, it forms a concentric ring pattern of rainbow colors because the different wavelengths of light interfere at different thicknesses of the air layer between the surfaces.

The Sagnac effect, also called Sagnac interference, named after French physicist Georges Sagnac, is a phenomenon encountered in interferometry that is elicited by rotation. The Sagnac effect manifests itself in a setup called a ring interferometer or Sagnac interferometer. A beam of light is split and the two beams are made to follow the same path but in opposite directions. On return to the point of entry the two light beams are allowed to exit the ring and undergo interference. The relative phases of the two exiting beams, and thus the position of the interference fringes, are shifted according to the angular velocity of the apparatus. In other words, when the interferometer is at rest with respect to a nonrotating frame, the light takes the same amount of time to traverse the ring in either direction. However, when the interferometer system is spun, one beam of light has a longer path to travel than the other in order to complete one circuit of the mechanical frame, and so takes longer, resulting in a phase difference between the two beams. Georges Sagnac set up this experiment in an attempt to prove the existence of the aether that Einstein's theory of special relativity had discarded.

A Twyman–Green interferometer is a variant of the Michelson interferometer principally used to test optical components. It was introduced in 1916 by Frank Twyman and Arthur Green.

The shearing interferometer is an extremely simple means to observe interference and to use this phenomenon to test the collimation of light beams, especially from laser sources which have a coherence length which is usually significantly longer than the thickness of the shear plate so that the basic condition for interference is fulfilled.

In interferometry experiments such as the Michelson–Morley experiment, a fringe shift is the behavior of a pattern of “fringes” when the phase relationship between the component sources change.
Lloyd's mirror is an optics experiment that was first described in 1834 by Humphrey Lloyd in the Transactions of the Royal Irish Academy. Its original goal was to provide further evidence for the wave nature of light, beyond those provided by Thomas Young and Augustin-Jean Fresnel. In the experiment, light from a monochromatic slit source reflects from a glass surface at a small angle and appears to come from a virtual source as a result. The reflected light interferes with the direct light from the source, forming interference fringes. It is the optical wave analogue to a sea interferometer.

A Fizeau interferometer is an interferometric arrangement whereby two reflecting surfaces are placed facing each other. As seen in Fig 1, the rear-surface reflected light from the transparent first reflector is combined with front-surface reflected light from the second reflector to form interference fringes.

A Mirau interferometer works on the same basic principle as a Michelson interferometer. The difference between the two is in the physical location of the reference arm. The reference arm of a Mirau interferometer is located within a microscope objective assembly.

A white light scanner (WLS) is a device for performing surface height measurements of an object using coherence scanning interferometry (CSI) with spectrally-broadband, "white light" illumination. Different configurations of scanning interferometer may be used to measure macroscopic objects with surface profiles measuring in the centimeter range, to microscopic objects with surface profiles measuring in the micrometer range. For large-scale non-interferometric measurement systems, see structured-light 3D scanner.
Self-mixing or back-injection laser interferometry is an interferometric technique in which a part of the light reflected by a vibrating target is reflected into the laser cavity, causing a modulation both in amplitude and in frequency of the emitted optical beam. In this way, the laser becomes sensitive to the distance traveled by the reflected beam thus becoming a distance, speed or vibration sensor. The advantage compared to a traditional measurement system is a lower cost thanks to the absence of collimation optics and external photodiodes.
A common-path interferometer is a class of interferometers in which the reference beam and sample beams travel along the same path. Examples include the Sagnac interferometer, Zernike phase-contrast interferometer, and the point diffraction interferometer. A common-path interferometer is generally more robust to environmental vibrations than a "double-path interferometer" such as the Michelson interferometer or the Mach–Zehnder interferometer. Although travelling along the same path, the reference and sample beams may travel along opposite directions, or they may travel along the same direction but with the same or different polarization.

As described here, white light interferometry is a non-contact optical method for surface height measurement on 3-D structures with surface profiles varying between tens of nanometers and a few centimeters. It is often used as an alternative name for coherence scanning interferometry in the context of areal surface topography instrumentation that relies on spectrally-broadband, visible-wavelength light.
















