Related Research Articles

Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula HOOC-CH-(NH2)-CH2-SH. Cysteine can be made from the essential amino acid methionine. The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile. The thiol is susceptible to oxidation to give the disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins. When used as a food additive, it has the E number E920. It is encoded by the codons UGU and UGC.
In biochemistry, a disulfide refers to a functional group with the structure R−S−S−R′. The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and is usually derived by the coupling of two thiol groups. In biology, disulfide bridges formed between thiol groups in two cysteine residues are an important component of the secondary and tertiary structure of proteins. Persulfide usually refers to R−S−S−H compounds.

A thiol or thiol derivative is any organosulfur compound of the form R−SH, where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The –SH functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl group, or a sulfanyl group. Thiols are the sulfur analogue of alcohols, and the word is a blend of "thio-" with "alcohol", where the first word deriving from Greek θεῖον (theion) meaning "sulfur".
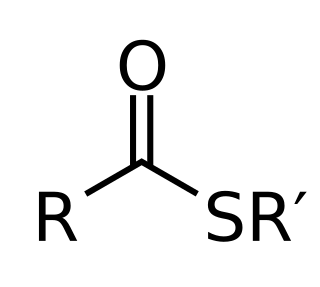
In chemistry thioesters are compounds with the functional group R–S–CO–R'. They are analogous to carboxylate esters with the sulfur in the thioester playing the role of the linking oxygen in the carboxylate ester. They are the product of esterification between a carboxylic acid and a thiol. In biochemistry, the best-known thioesters are derivatives of coenzyme A, e.g., acetyl-CoA.
Thiophene is a heterocyclic compound with the formula C4H4S. Consisting of a planar five-membered ring, it is aromatic as indicated by its extensive substitution reactions. It is a colorless liquid with a benzene-like odor. In most of its reactions, it resembles benzene. Compounds analogous to thiophene include furan (C4H4O) selenophene (C4H4Se) and pyrrole (C4H4NH), which each vary by the heteroatom in the ring.

Sulfur monoxide is an inorganic compound with formula SO. It is only found as a dilute gas phase. When concentrated or condensed, it converts to S2O2 (disulfur dioxide). It has been detected in space but is rarely encountered intact otherwise.
Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is essential for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.
Nitrosation is a process of converting organic compounds into nitroso derivatives, i.e. compounds containing the R-NO functionality.

Dithiothreitol (DTT) is the common name for a small-molecule redox reagent also known as Cleland's reagent. DTT's formula is C4H10O2S2 and the chemical structure of one of its enantiomers in its reduced form is shown on the right; its oxidized form is a disulfide bonded 6-membered ring (shown below). The reagent is commonly used in its racemic form, as both enantiomers are reactive. Its name derives from the four-carbon sugar, threose. DTT has an epimeric ('sister') compound, dithioerythritol (DTE).
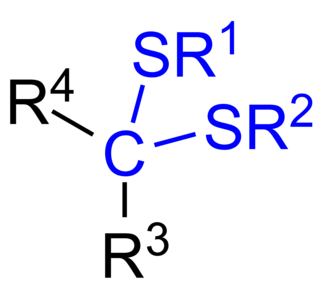
In chemistry, a thioketal is the sulfur analogue of a ketal, with one of the oxygen replaced by sulfur. A dithioketal has both oxygens replaced by sulfur.

A sulfenic acid is an organosulfur compound and oxoacid with the general formula RSOH. It is the first member of the family of organosulfur oxoacids, which also include sulfinic acids and sulfonic acids, RSO2H and RSO3H, respectively. The base member of the sulfenic acid series with R = H is hydrogen thioperoxide.
In chemistry, persulfide refers to the functional group R-S-S-H. Persulfides are intermediates in the biosynthesis of iron-sulfur proteins and are invoked as precursors to hydrogen sulfide, a signaling molecule.
Glutathione synthetase (GSS) is the second enzyme in the glutathione (GSH) biosynthesis pathway. It catalyses the condensation of gamma-glutamylcysteine and glycine, to form glutathione. Glutathione synthetase is also a potent antioxidant. It is found in many species including bacteria, yeast, mammals, and plants.
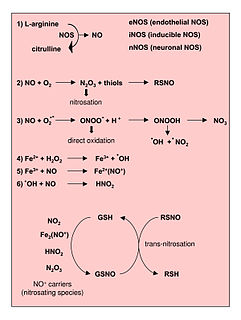
Reactive nitrogen species (RNS) are a family of antimicrobial molecules derived from nitric oxide (•NO) and superoxide (O2•−) produced via the enzymatic activity of inducible nitric oxide synthase 2 (NOS2) and NADPH oxidase respectively. NOS2 is expressed primarily in macrophages after induction by cytokines and microbial products, notably interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS).

S-Nitrosothiols, also known as thionitrites, are organic compounds or functional groups containing a nitroso group attached to the sulfur atom of a thiol. S-Nitrosothiols have the general formula RSNO, where R denotes an organic group. Originally suggested by Ignarro to serve as intermediates in the action of organic nitrates, endogenous S-nitrosothiols were discovered by Stamler and colleagues and shown to represent a main source of NO bioactivity in vivo. More recently, S-nitrosothiols have been implicated as primary mediators of protein S-nitrosylation, the oxidative modification of cysteine thiol that provides ubiquitous regulation of protein function.

The Liebeskind–Srogl coupling reaction is an organic reaction forming a new carbon–carbon bond from a thioester and a boronic acid using a metal catalyst. It is a cross-coupling reaction. This reaction was invented by and named after Jiri Srogl from the Academy of Sciences, Czech Republic, and Lanny S. Liebeskind from Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia, USA. There are three generations of this reaction, with the first generation shown below. The original transformation used catalytic Pd(0), TFP = tris(2-furyl)phosphine as an additional ligand and stoichiometric CuTC = copper(I) thiophene-2-carboxylate as a co-metal catalyst. The overall reaction scheme is shown below.

Ergothioneine is a naturally occurring amino acid and is a thiourea derivative of histidine, containing a sulfur atom on the imidazole ring. This compound occurs in relatively few organisms, notably Actinobacteria, Cyanobacteria, and certain fungi. Ergothioneine was discovered in 1909 and named after the ergot fungus from which it was first purified, with its structure being determined in 1911.
Arsenic biochemistry refers to biochemical processes that can use arsenic or its compounds, such as arsenate. Arsenic is a moderately abundant element in Earth's crust, and although many arsenic compounds are often considered highly toxic to most life, a wide variety of organoarsenic compounds are produced biologically and various organic and inorganic arsenic compounds are metabolized by numerous organisms. This pattern is general for other related elements, including selenium, which can exhibit both beneficial and deleterious effects. Arsenic biochemistry has become topical since many toxic arsenic compounds are found in some aquifers, potentially affecting many millions of people via biochemical processes.

Dimethyl trisulfide (DMTS) is an organic chemical compound and the simplest organic trisulfide, with the chemical formula CH3SSSCH3. It is a flammable liquid with a foul odor, which is detectable at levels as low as 1 part per trillion.

Reactive carbonyl species (RCS) are molecules with highly reactive carbonyl groups, and often known for their damaging effects on proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. They are often generated as metabolic products. Important RCSs include 3-deoxyglucosone, glyoxal, and methylglyoxal. RCSs react with amines and thiol groups leading to advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs). AGE's are indicators of diabetes.
References
- ↑ Giles, GI; Jacob, C (2002). "Reactive sulfur species: an emerging concept in oxidative stress". Biol Chem. 383 (3–4): 375–88. doi:10.1515/BC.2002.042. PMID 12033429. S2CID 24273615.
- ↑ Mishanina, Tatiana V.; Libiad, Marouane; Banerjee, Ruma (2015). "Biogenesis of reactive sulfur species for signaling by hydrogen sulfide oxidation pathways". Nature Chemical Biology. 11 (7): 457–464. doi:10.1038/nchembio.1834. PMC 4818113 . PMID 26083070.