The optical power budget in a fiber-optic communication link is the allocation of available optical power among various loss-producing mechanisms such as launch coupling loss, fiber attenuation, splice losses, and connector losses, in order to ensure that adequate signal strength is available at the receiver. In optical power budget attenuation is specified in decibel (dB) and optical power in dBm.
A transmission medium is a system or substance that can mediate the propagation of signals for the purposes of telecommunication. Signals are typically imposed on a wave of some kind suitable for the chosen medium. For example, data can modulate sound, and a transmission medium for sounds may be air, but solids and liquids may also act as the transmission medium. Vacuum or air constitutes a good transmission medium for electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves. While a material substance is not required for electromagnetic waves to propagate, such waves are usually affected by the transmission media they pass through, for instance, by absorption or reflection or refraction at the interfaces between media. Technical devices can therefore be employed to transmit or guide waves. Thus, an optical fiber or a copper cable is used as transmission media.

In materials science, a thermosetting polymer, often called a thermoset, is a polymer that is obtained by irreversibly hardening ("curing") a soft solid or viscous liquid prepolymer (resin). Curing is induced by heat or suitable radiation and may be promoted by high pressure or mixing with a catalyst. Heat is not necessarily applied externally, and is often generated by the reaction of the resin with a curing agent. Curing results in chemical reactions that create extensive cross-linking between polymer chains to produce an infusible and insoluble polymer network.

Lamination is the technique/process of manufacturing a material in multiple layers, so that the composite material achieves improved strength, stability, sound insulation, appearance, or other properties from the use of the differing materials, such as plastic. A laminate is a layered object or material assembled using heat, pressure, welding, or adhesives. Various coating machines, machine presses and calendering equipment are used.
A mechanical splice is a junction of two or more optical fibers that are aligned and held in place by a self-contained assembly. The fibers are not permanently joined, just precisely held together so that light can pass from one to another. This impermanence is an important advantage over fusion splicing, as splice loss, the amount of power that the splice fails to transmit, can be better measured and prevented.

A cleave in an optical fiber is a deliberate, controlled break, intended to create a perfectly flat end face perpendicular to the fiber's longitudinal axis. The process of cleaving an optical fiber forms one of the steps in the preparation for a fiber splice operation, regardless of the subsequent splice being a fusion splice or a mechanical splice; the other steps in the preparation being those of stripping and fiber alignment. A good cleave is required for a successful low loss splice of an optical fiber, often it is the case that fibers spliced by identical methods tend to have different losses, this difference can often be attributed to the quality of their initial cleaves.

A patch cable, patch cord or patch lead is an electrical or fiber-optic cable used to connect one electronic or optical device to another for signal routing. Devices of different types are connected with patch cords.

An optical fiber, or optical fibre, is a flexible glass or plastic fiber that can transmit light from one end to the other. Such fibers find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths than electrical cables. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with less loss and are immune to electromagnetic interference. Fibers are also used for illumination and imaging, and are often wrapped in bundles so they may be used to carry light into, or images out of confined spaces, as in the case of a fiberscope. Specially designed fibers are also used for a variety of other applications, such as fiber optic sensors and fiber lasers.

Fiber-optic communication is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of infrared or visible light through an optical fiber. The light is a form of carrier wave that is modulated to carry information. Fiber is preferred over electrical cabling when high bandwidth, long distance, or immunity to electromagnetic interference is required. This type of communication can transmit voice, video, and telemetry through local area networks or across long distances.
An optical ground wire is a type of cable that is used in overhead power lines. Such cable combines the functions of grounding and communications. An OPGW cable contains a tubular structure with one or more optical fibers in it, surrounded by layers of steel and aluminum wire. The OPGW cable is run between the tops of high-voltage electricity pylons. The conductive part of the cable serves to bond adjacent towers to earth ground, and shields the high-voltage conductors from lightning strikes. The optical fibers within the cable can be used for high-speed transmission of data, either for the electrical utility's own purposes of protection and control of the transmission line, for the utility's own voice and data communication, or may be leased or sold to third parties to serve as a high-speed fiber interconnection between cities.

Fusion splicing is the act of joining two optical fibers end-to-end. The goal is to fuse the two fibers together in such a way that light passing through the fibers is not scattered or reflected back by the splice, and so that the splice and the region surrounding it are almost as strong as the intact fiber. The source of heat used to melt and fuse the two glass fibers being spliced is usually an electric arc, but can also be a laser, a gas flame, or a tungsten filament through which current is passed.
Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. is a manufacturer of electric wire and optical fiber cables. Its headquarters are in Chūō-ku, Osaka, Japan. The company's shares are listed in the first section of the Tokyo, Nagoya Stock Exchanges, and the Fukuoka Stock Exchange. In the period ending March 2021, the company reported consolidated sales of US$26,5 billion.

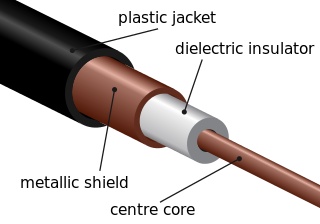
A fiber-optic cable, also known as an optical-fiber cable, is an assembly similar to an electrical cable but containing one or more optical fibers that are used to carry light. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube suitable for the environment where the cable is used. Different types of cable are used for fiber-optic communication in different applications, for example long-distance telecommunication or providing a high-speed data connection between different parts of a building.
Fiber Optic cable termination is the addition of connectors to each optical fiber in a cable. The fibers need to have connectors fitted before they can attach to other equipment. Two common solutions for fiber cable termination are pigtails and fanout kits or breakout kits.
A fiber management system (FMS) manages optical fiber connections from outside of fiber rack to the fiber routers. Fiber-optic cable duct containing many fibers comes from far end sites and terminates on the FMS using splicing technology. FMS has fiber in and fiber out ports. From fiber out port the fiber patch will go to fiber optics based router.
Nyfors Teknologi AB is a high-end supplier of advanced optical fiber handling equipment, based in Stockholm, Sweden. The company develops and manufactures equipment used in optical fiber fusion splicing, including products for stripping and preparation, testing and analysing and fiber end-face inspection, but is most well known for its automated optical fiber recoating and fiber cleaving systems. Nyfors products are sold internationally to customers within a wide range of industrial sectors and to public and private research institutions.

Stripping is the act of removing the protective polymer coating around optical fiber in preparation for fusion splicing. The splicing process begins by preparing both fiber ends for fusion, which requires that all protective coating is removed or stripped from the ends of each fiber. Fiber optical stripping can be done using a special stripping and preparation unit that uses hot sulfuric acid or a controlled flow of hot air to remove the coating. There are also mechanical tools used for stripping fiber which are similar to copper wire strippers. Fiber optical stripping and preparation equipment used in fusion splicing is commercially available through a small number of specialized companies, which usually also design machines used for fiber optical recoating.

Paper chemicals designate a group of chemicals that are used for paper manufacturing, or modify the properties of paper. These chemicals can be used to alter the paper in many ways, including changing its color and brightness, or by increasing its strength and resistance to water. The chemicals can be defined on basis of their usage in the process.

An electrical conduit is a tube used to protect and route electrical wiring in a building or structure. Electrical conduit may be made of metal, plastic, fiber, or fired clay. Most conduit is rigid, but flexible conduit is used for some purposes.
In telecommunications, a line splice is a method of connecting electrical cables or optical fibers.











