
The Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and Their Disposal, usually known as the Basel Convention, is an international treaty that was designed to reduce the movements of hazardous waste between nations, and specifically to prevent transfer of hazardous waste from developed to less developed countries. It does not, however, address the movement of radioactive waste. The convention is also intended to minimize the rate and toxicity of wastes generated, to ensure their environmentally sound management as closely as possible to the source of generation, and to assist developing countries in environmentally sound management of the hazardous and other wastes they generate.

Hazardous waste is waste that must be handled properly to avoid damaging human health or the environment. Waste can be hazardous because it is toxic, reacts violently with other chemicals, or is corrosive, among other traits. As of 2022, humanity produces 300-500 metric tons of hazardous waste annually. Some common examples are electronics, batteries, and paints. An important aspect of managing hazardous waste is safe disposal. Hazardous waste can be stored in hazardous waste landfills, burned, or recycled into something new. Managing hazardous waste is important to achieve worldwide sustainability. Hazardous waste is regulated on national scale by national governments as well as on an international scale by the United Nations (UN) and international treaties.

Dessel is a municipality located in the Belgian province of Antwerp. The municipality comprises only the town of Dessel proper. In 2021, Dessel had a total population of 9,659 inhabitants. The total area is 27.03 km2.

Waste management or waste disposal includes the processes and actions required to manage waste from its inception to its final disposal. This includes the collection, transport, treatment, and disposal of waste, together with monitoring and regulation of the waste management process and waste-related laws, technologies, and economic mechanisms.
Thermal depolymerization (TDP) is the process of converting a polymer into a monomer or a mixture of monomers, by predominantly thermal means. It may be catalysed or un-catalysed and is distinct from other forms of depolymerisation which may rely on the use of chemicals or biological action. This process is associated with an increase in entropy.

Incineration is a waste treatment process that involves the combustion of substances contained in waste materials. Industrial plants for waste incineration are commonly referred to as waste-to-energy facilities. Incineration and other high-temperature waste treatment systems are described as "thermal treatment". Incineration of waste materials converts the waste into ash, flue gas and heat. The ash is mostly formed by the inorganic constituents of the waste and may take the form of solid lumps or particulates carried by the flue gas. The flue gases must be cleaned of gaseous and particulate pollutants before they are dispersed into the atmosphere. In some cases, the heat that is generated by incineration can be used to generate electric power.

Waste hierarchy is a tool used in the evaluation of processes that protect the environment alongside resource and energy consumption from most favourable to least favourable actions. The hierarchy establishes preferred program priorities based on sustainability. To be sustainable, waste management cannot be solved only with technical end-of-pipe solutions and an integrated approach is necessary.
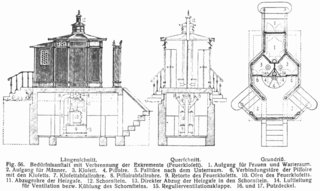
An incinerating toilet is a type of dry toilet that burns human feces instead of flushing them away with water, as does a flush toilet. The thermal energy used to incinerate the waste can be derived from electricity, fuel, oil, or liquified petroleum gas. They are relatively inefficient because of the fuel used.

Waste-to-energy (WtE) or energy-from-waste (EfW) is the process of generating energy in the form of electricity and/or heat from the primary treatment of waste, or the processing of waste into a fuel source. WtE is a form of energy recovery. Most WtE processes generate electricity and/or heat directly through combustion, or produce a combustible fuel commodity, such as methane, methanol, ethanol or synthetic fuels, often derived from the product syngas.

The environment of Belgium is generally affected by the high population density in most of the country. However, due to consistent efforts by the various levels of government in Belgium, the state of the environment in Belgium is gradually improving. These efforts have led to Belgium being ranked as one of the top 10 countries in terms of environmental protection trends. However, water quality still suffers from a relatively low, yet increasing percentage of sewage waste-water treatment, and from historical pollution accumulated in sediments. Air quality is generally good to average, but is affected by emissions from traffic and house heating, and industrial air pollution blowing over from the neighboring heavily industrialized Ruhr-area in Germany. Biodiversity is lower in Flanders than in Wallonia because of population density and fragmentation of habitats, but efforts are being made to boost bio-diversity through connecting fragmented forests and national parks through wildlife crossing "ecoducts" such as in Kikbeek.
The Waste Incineration Directive, more formally Directive 2000/76/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 4 December 2000 on the incineration of waste, was a Directive issued by the European Union and relates to standards and methodologies required by Europe for the practice and technology of incineration. The aim of this Directive is to minimise the impact of negative environmental effects on the environment and human health resulting from emissions to air, soil, surface and ground water from the incineration and co-incineration of waste. The requirements of the Directive were developed to reflect the ability of modern incineration plants to achieve high standards of emission control more effectively. The Directive has been replaced by the Industrial Emissions Directive since 7 January 2014.

Textile recycling is the process of recovering fiber, yarn, or fabric and reprocessing the material into new, useful products. Textile waste is split into pre-consumer and post-consumer waste and is sorted into five different categories derived from a pyramid model. Textiles can be either reused or mechanically/chemically recycled.

Biomedical waste or hospital waste is any kind of waste containing infectious materials generated during the treatment of humans or animals as well as during research involving biologics. It may also include waste associated with the generation of biomedical waste that visually appears to be of medical or laboratory origin, as well research laboratory waste containing biomolecules or organisms that are mainly restricted from environmental release. As detailed below, discarded sharps are considered biomedical waste whether they are contaminated or not, due to the possibility of being contaminated with blood and their propensity to cause injury when not properly contained and disposed. Biomedical waste is a type of biowaste.
Agricultural waste are plant residues from agriculture. These waste streams originate from arable land and horticulture. Agricultural waste are all parts of crops that are not used for human or animal food. Crop residues consist mainly of stems, branchs, and leaves. It is estimated that, on average, 80% of the plant of such crops consists of agricultural waste.
Waste management in Japan today emphasizes not just the efficient and sanitary collection of waste, but also reduction in waste produced and recycling of waste when possible. This has been influenced by its history, particularly periods of significant economic expansion, as well as its geography as a mountainous country with limited space for landfills. Important forms of waste disposal include incineration, recycling and, to a smaller extent, landfills and land reclamation. Although Japan has made progress since the 1990s in reducing waste produced and encouraging recycling, there is still further progress to be made in reducing reliance on incinerators and the garbage sent to landfills. Challenges also exist in the processing of electronic waste and debris left after natural disasters.

Waste are unwanted or unusable materials. Waste is any substance discarded after primary use, or is worthless, defective and of no use. A by-product, by contrast is a joint product of relatively minor economic value. A waste product may become a by-product, joint product or resource through an invention that raises a waste product's value above zero.

The management of waste in New Zealand has become more regulated to reduce associated environmental issues. According to OECD data, New Zealand is the third most wasteful country in the OECD.
Sustainable Materials Management is a systemic approach to using and reusing materials more productively over their entire lifecycles. It represents a change in how a society thinks about the use of natural resources and environmental protection. By looking at a product's entire lifecycle new opportunities can be found to reduce environmental impacts, conserve resources, and reduce costs.
Istanbul Waste Power Plant is a waste-to-energy facility in the Eyüp district of Istanbul near the Odayeri landfill, Turkey, using waste incineration. Opened in 2021 it is owned by the Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality (İBB) and operated by İstanbul Environmental Management Co. (İSTAÇ). It is Turkey's first power plant of this type. Project development started in 2011 with a grant from the United States Trade Development Agency (USTDA) which involved first a Definitional Mission and subsequently a detailed Feasibility Assessment.

International waste is any organic waste product that is deemed unsafe to be released into the environment or standard municipal solid waste stream that has originated from an external country, and sometimes territory. Such waste must be treated before it can be disposed of in the municipal solid waste stream to prevent sickness and environmental damage. If not managed properly, regulated garbage can have detrimental impacts on agriculture, livestock, and crops.










