
A Linux distribution is an operating system made from a software collection that is based upon the Linux kernel and, often, a package management system. Linux users usually obtain their operating system by downloading one of the Linux distributions, which are available for a wide variety of systems ranging from embedded devices and personal computers to powerful supercomputers.
Red Hat Linux; created by the company Red Hat, was a widely used Linux distribution until its discontinuation in 2004.

Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) is a Linux distribution developed by Red Hat for the commercial market. Red Hat Enterprise Linux is released in server versions for x86-64, Power ISA, ARM64, and IBM Z and a desktop version for x86-64. All of Red Hat's official support and training, together with the Red Hat Certification Program, focuses on the Red Hat Enterprise Linux platform.

CentOS is a Linux distribution that provides a free and open-source community-supported computing platform, functionally compatible with its upstream source, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). In January 2014, CentOS announced the official joining with Red Hat while staying independent from RHEL, under a new CentOS governing board.
Technical variations of Linux distributions include support for different hardware devices and systems or software package configurations. Organisational differences may be motivated by historical reasons. Other criteria include security, including how quickly security upgrades are available; ease of package management; and number of packages available.

Scientific Linux (SL) is a Linux distribution produced by Fermilab, CERN, DESY and by ETH Zurich. It is a free and open-source operating system based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux.

Red Hat Enterprise Linux derivatives are Linux distributions that are based on the source code of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL).
The 389 Directory Server is a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) server developed by Red Hat as part of the community-supported Fedora Project. The name "389" derives from the port number used by LDAP.
BioLinux is a term used in a variety of projects involved in making access to bioinformatics software on a Linux platform easier using one or more of the following methods:

Oracle Linux is a Linux distribution packaged and freely distributed by Oracle, available partially under the GNU General Public License since late 2006. It is compiled from Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) source code, replacing Red Hat branding with Oracle's. It is also used by Oracle Cloud and Oracle Engineered Systems such as Oracle Exadata and others.

Fedora Linux is a Linux distribution developed by Fedora Project which is sponsored primarily by Red Hat, with additional sponsors from other companies and organizations. Fedora contains software distributed under various open source licenses and aims to be on the leading edge of open source technologies. Fedora is the upstream source for many distributions, like Rocky Linux and Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
IcedTea is a build and integration project for OpenJDK launched by Red Hat in June 2007. IcedTea also includes some addon libraries: IcedTea-Web is a free software implementation of Java Web Start and the Java web browser applet plugin. IcedTea-Sound is a collection of plugins for the Java sound subsystem, including the PulseAudio provider which used to be included with IcedTea. The Free Software Foundation recommends that all Java programmers use IcedTea as their development environment.
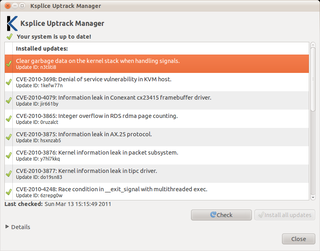
Ksplice is an open-source extension of the Linux kernel that allows security patches to be applied to a running kernel without the need for reboots, avoiding downtimes and improving availability. Ksplice supports only the patches that do not make significant semantic changes to kernel's data structures.

RPM Package Manager (RPM) is a free and open-source package management system. The name RPM refers to .rpm file format and the package manager program itself. RPM was intended primarily for Linux distributions; the file format is the baseline package format of the Linux Standard Base.

Linaro is an engineering organization that works on free and open-source software such as the Linux kernel, the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), power management, graphics and multimedia interfaces for the ARM family of instruction sets and implementations thereof as well as for the Heterogeneous System Architecture (HSA). The company provides a collaborative engineering forum for companies to share engineering resource and funding to solve common problems on ARM software.
In computing, Red Hat Satellite is a systems-management product by the company Red Hat which allows system administrators to deploy and manage Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) hosts.

Linux on IBM Z is the collective term for the Linux operating system compiled to run on IBM mainframes, especially IBM Z and IBM LinuxONE servers. Similar terms which imply the same meaning are Linux on zEnterprise, Linux on zSeries, Linux/390, Linux/390x, etc. The three Linux distributions certified for usage on the IBM Z hardware platform are Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise, and Ubuntu.

Rocky Linux is a Linux distribution developed by Rocky Enterprise Software Foundation. It is intended to be a downstream, complete binary-compatible release using the Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) operating system source code. The project's aim is to provide a community-supported, production-grade enterprise operating system. The first release candidate version of Rocky Linux was released on April 30, 2021, and its first general availability version was released on June 21, 2021. Rocky Linux 8 will be supported through May 2029.

AlmaLinux is a free and open source Linux distribution, created originally by CloudLinux to provide a community-supported, production-grade enterprise operating system that is binary-compatible with Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). The first stable release of AlmaLinux was published on March 30, 2021.














