
Solaris is a proprietary Unix operating system originally developed by Sun Microsystems. After the Sun acquisition by Oracle in 2010, it was renamed Oracle Solaris.
Turbolinux is a discontinued Japanese Linux distribution targeting Asian users.

Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) is a commercial open-source Linux distribution developed by Red Hat for the commercial market. Red Hat Enterprise Linux is released in server versions for x86-64, Power ISA, ARM64, and IBM Z and a desktop version for x86-64. Fedora Linux and CentOS Stream serve as its upstream sources. All of Red Hat's official support and training, together with the Red Hat Certification Program, focuses on the Red Hat Enterprise Linux platform.

CentOS is a discontinued Linux distribution that provided a free and open-source community-supported computing platform, functionally compatible with its upstream source, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). In January 2014, CentOS announced the official joining with Red Hat while staying independent from RHEL, under a new CentOS governing board.
Technical variations of Linux distributions include support for different hardware devices and systems or software package configurations. Organizational differences may be motivated by historical reasons. Other criteria include security, including how quickly security upgrades are available; ease of package management; and number of packages available.

Red Hat Enterprise Linux derivatives are Linux distributions that are based on the source code of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL).
Vine Linux is a Japanese Linux distribution sponsored by VineCaves. It has been a fork of Red Hat Linux 7.2 since Vine Linux 3.0. Work on Vine Linux was started in 1998.
Cambridge Technology Partners is a Japan-based multinational professional services company that specializes in business and IT consulting.

Linux is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution (distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses and recommends the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the use and importance of GNU software in many distributions, causing some controversy.
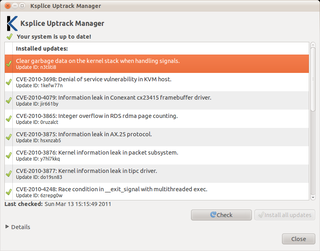
Ksplice is an open-source extension of the Linux kernel that allows security patches to be applied to a running kernel without the need for reboots, avoiding downtimes and improving availability. Ksplice supports only the patches that do not make significant semantic changes to kernel's data structures.

This is a list of development studios owned by Sega, a Japanese video game developer and publisher based in Tokyo, Japan. Accompanied with the list is their history of game development. Also included are the companies that Sega has acquired over the years. For a full list of games developed and published by Sega, see List of Sega video games, List of Sega mobile games and List of Sega arcade games.

D4 Enterprise Co., Ltd. is a Japanese video game publisher currently specializing in content delivery services like Project EGG, EGGY and PicoPico over the Internet. The company has also collaborated with Nintendo to re-release Neo Geo, MSX and arcade titles for the Wii, and MSX titles for the Wii U; as part of the Virtual Console services on both consoles.

Helmz is a sports bicycle from Bridgestone Cycle Co., Ltd. jointly developed with fashion brand narifuri.
Showroom, stylized as SHOWROOM, is a Japanese live streaming service used primarily for Japanese idols and voice actors. A development of DeNA, it has been integrated into the audition process for idol groups such as 22/7, Nogizaka46, and Keyakizaka46.

Abema is a Japanese streaming service that launched on April 11, 2016, under the name AbemaTV. It is majority-owned by CyberAgent, with a 55.2% stake, and TV Asahi, with a 36.8% stake, while the remaining ownership belongs to various other companies, mostly in the media and entertainment industry.

Rocky Linux is a Linux distribution developed by Rocky Enterprise Software Foundation, which is a privately owned benefit corporation that describes itself as a "self-imposed not-for-profit". It is intended to be a downstream, complete binary-compatible release using the Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) operating system source code. The project's aim is to provide a community-supported, production-grade enterprise operating system. Rocky Linux, along with RHEL and SUSE Linux Enterprise (SLE), has become popular for enterprise operating system use.
AlmaLinux is a free and open source Linux distribution, developed by the AlmaLinux OS Foundation, a 501(c) organization, to provide a community-supported, production-grade enterprise operating system that is binary-compatible with Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). The name of the distribution comes from the word "alma", meaning "soul" in Spanish and other Latin languages. It was chosen to be a homage to the Linux community.
Uuum Co., Ltd. is a Japanese multi-channel network and YouTuber-related label company headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
TwitCasting is a livestreaming service operated by Moi Co., Ltd., headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. In early 2013, TwitCasting was developed as a way to use the Twitter feed to stream content from smartphones directly onto a user's channel. As of July 2021, it had over 33 million registered users. As of March 2020, it had the most monthly active users among livestreaming apps in Japan, according to App Ape Lab analytics.












