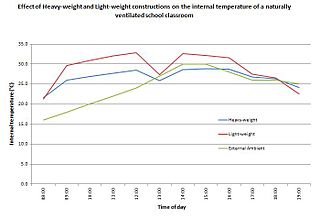
In building design, thermal mass is a property of the mass of a building which enables it to store heat, providing "inertia" against temperature fluctuations. It is sometimes known as the thermal flywheel effect. For example, when outside temperatures are fluctuating throughout the day, a large thermal mass within the insulated portion of a house can serve to "flatten out" the daily temperature fluctuations, since the thermal mass will absorb thermal energy when the surroundings are higher in temperature than the mass, and give thermal energy back when the surroundings are cooler, without reaching thermal equilibrium. This is distinct from a material's insulative value, which reduces a building's thermal conductivity, allowing it to be heated or cooled relatively separately from the outside, or even just retain the occupants' thermal energy longer.

Plattenbau is a building constructed of large, prefabricated concrete slabs. The word is a compound of Platte and Bau (building). Such buildings are often found in housing development areas.

Lustron houses are prefabricated enameled steel houses developed in the post-World War II era United States in response to the shortage of homes for returning G.I.s by Chicago industrialist and inventor Carl Strandlund. Considered low-maintenance and extremely durable, they were expected to attract modern families who might not have the time or interest in repairing and painting conventional wood and plaster houses. Lustron production ceased in 1950 due to the company's inability to pay back the startup loans it had received from the Reconstruction Finance Corporation. Over 2,000 homes were constructed during the Lustron's brief production period, and many remain in use today. Several have been added to the National Register of Historic Places.

Building material is material used for construction. Many naturally occurring substances, such as clay, rocks, sand, wood, and even twigs and leaves, have been used to construct buildings. Apart from naturally occurring materials, many man-made products are in use, some more and some less synthetic. The manufacturing of building materials is an established industry in many countries and the use of these materials is typically segmented into specific specialty trades, such as carpentry, insulation, plumbing, and roofing work. They provide the make-up of habitats and structures including homes.

Tilt-up,tilt-slab or tilt-wall is a type of building and a construction technique using concrete. Though it is a cost-effective technique with a shorter completion time, poor performance in earthquakes has mandated significant seismic retrofit requirements in older buildings.
Prefabrication is the practice of assembling components of a structure in a factory or other manufacturing site, and transporting complete assemblies or sub-assemblies to the construction site where the structure is to be located. The term is used to distinguish this process from the more conventional construction practice of transporting the basic materials to the construction site where all assembly is carried out.

Prefabricated homes, often referred to as prefab homes or simply prefabs, are specialist dwelling types of prefabricated building, which are manufactured off-site in advance, usually in standard sections that can be easily shipped and assembled. Some current prefab home designs include architectural details inspired by postmodernism or futurist architecture.

A concrete slab is a common structural element of modern buildings, consisting of a flat, horizontal surface made of cast concrete. Steel-reinforced slabs, typically between 100 and 500 mm thick, are most often used to construct floors and ceilings, while thinner mud slabs may be used for exterior paving (see below).

Pantelimon is a neighbourhood located in north-eastern Bucharest, Romania, in Sector 2. Outside Bucharest, there is an adjacent town named Pantelimon, administered separately.

Precast concrete is a construction product produced by casting concrete in a reusable mold or "form" which is then cured in a controlled environment, transported to the construction site and maneuvered into place; examples include precast beams, and wall panels for tilt up construction. In contrast, cast-in-place concrete is poured into site-specific forms and cured on site.

Underfloor heating and cooling is a form of central heating and cooling that achieves indoor climate control for thermal comfort using hydronic or electrical heating elements embedded in a floor. Heating is achieved by conduction, radiation and convection. Use of underfloor heating dates back to the Neoglacial and Neolithic periods.

A prefabricated building, informally a prefab, is a building that is manufactured and constructed using prefabrication. It consists of factory-made components or units that are transported and assembled on-site to form the complete building.

Khrushchyovka or Khrushchoba is an unofficial name for a type of low-cost, concrete-paneled or brick three- to five-storied apartment building which was developed in the Soviet Union during the early 1960s, during the time its namesake Nikita Khrushchev directed the Soviet government. They are sometimes compared to the Japanese danchi, similar housing projects from the same period, which by some accounts were directly inspired by them. Preceding this type of housing, the majority of the Soviet housing stock was of low-rise communal apartments.

Building insulation is any object in a building used as insulation for thermal management. While the majority of insulation in buildings is for thermal purposes, the term also applies to acoustic insulation, fire insulation, and impact insulation. Often an insulation material will be chosen for its ability to perform several of these functions at once.
The architecture of Iceland draws from Scandinavian influences and traditionally was influenced by the lack of native trees on the island. As a result, grass- and turf-covered houses were developed. Later on, the Swiss chalet style became a prevailing influence in Icelandic architecture as many timber buildings were constructed in this way. Stone and later concrete were popular building materials, the latter especially with the arrival of functionalism in the country. Contemporary architecture in Iceland is influenced by many sources, with styles varying greatly around the country.

Cross-laminated timber (CLT) is a wood panel product made from gluing together layers of solid-sawn lumber, i.e., lumber cut from a single log. Each layer of boards is usually oriented perpendicular to adjacent layers and glued on the wide faces of each board, usually in a symmetric way so that the outer layers have the same orientation. An odd number of layers is most common, but there are configurations with even numbers as well. Regular timber is an anisotropic material, meaning that the physical properties change depending on the direction at which the force is applied. By gluing layers of wood at right angles, the panel is able to achieve better structural rigidity in both directions. It is similar to plywood but with distinctively thicker laminations.
Studcast concrete, also called "pre-framed concrete", combines relatively thin concrete layers with cold formed steel framing to create hybrid panels; the result is a panelized system usable for cladding, curtain walls, shaft walls, and load-bearing exterior and interior walls. Studcast panels install in the same manner as prefabricated steel stud panels. The technology is applicable for both factory prefabrication and site-cast (tilt-up) wall construction on almost all types of buildings, including multifamily housing, schools, industrial, commercial and institutional structures.

Prefabs were a major part of the delivery plan to address the United Kingdom's post–Second World War housing shortage. They were envisaged by war-time prime minister Winston Churchill in March 1944, and legally outlined in the Housing Act 1944.

Q3A is an abbreviation for a type of three, four and five storey prefabricated buildings constructed in the GDR in the 1950s and 1960s. The letter "Q" in the word stands for "Querwandbau".
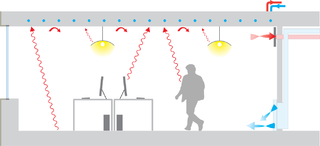
Radiant heating and cooling is a category of HVAC technologies that exchange heat by both convection and radiation with the environments they are designed to heat or cool. There are many subcategories of radiant heating and cooling, including: "radiant ceiling panels", "embedded surface systems", "thermally active building systems", and infrared heaters. According to some definitions, a technology is only included in this category if radiation comprises more than 50% of its heat exchange with the environment; therefore technologies such as radiators and chilled beams are usually not considered radiant heating or cooling. Within this category, it is practical to distinguish between high temperature radiant heating, and radiant heating or cooling with more moderate source temperatures. This article mainly addresses radiant heating and cooling with moderate source temperatures, used to heat or cool indoor environments. Moderate temperature radiant heating and cooling is usually composed of relatively large surfaces that are internally heated or cooled using hydronic or electrical sources. For high temperature indoor or outdoor radiant heating, see: Infrared heater. For snow melt applications see: Snowmelt system.
















