Related Research Articles

An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computation machine (computer) that uses the continuous variation aspect of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities to model the problem being solved. In contrast, digital computers represent varying quantities symbolically and by discrete values of both time and amplitude.

Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other electrically charged particles. Electronics is a subfield of physics and electrical engineering which uses active devices such as transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits to control and amplify the flow of electric current and to convert it from one form to another, such as from alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) or from analog signals to digital signals.

An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal. It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a proportionally greater amplitude signal at its output. The amount of amplification provided by an amplifier is measured by its gain: the ratio of output voltage, current, or power to input. An amplifier is defined as a circuit that has a power gain greater than one.

In electronics, the metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which determines the conductivity of the device. This ability to change conductivity with the amount of applied voltage can be used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. The term metal–insulator–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MISFET) is almost synonymous with MOSFET. Another near-synonym is insulated-gate field-effect transistor (IGFET).
A signal generator is one of a class of electronic devices that generates electrical signals with set properties of amplitude, frequency, and wave shape. These generated signals are used as a stimulus for electronic measurements, typically used in designing, testing, troubleshooting, and repairing electronic or electroacoustic devices, though it often has artistic uses as well.
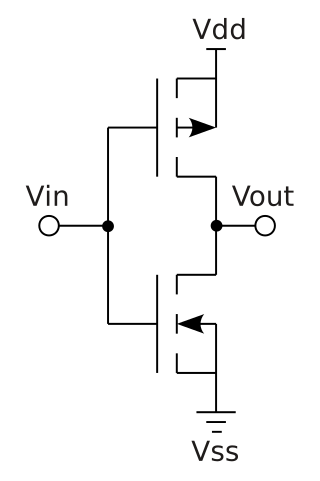
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuit (IC) chips, including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors, data converters, RF circuits, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication.

In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a system that converts a digital signal into an analog signal. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) performs the reverse function.
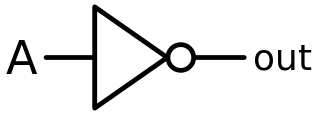
In digital logic, an inverter or NOT gate is a logic gate which implements logical negation. It outputs a bit opposite of the bit that is put into it. The bits are typically implemented as two differing voltage levels.
A phase detector or phase comparator is a frequency mixer, analog multiplier or logic circuit that generates a signal which represents the difference in phase between two signal inputs.

A remote terminal unit (RTU) is a microprocessor-controlled electronic device that interfaces objects in the physical world to a distributed control system or SCADA system by transmitting telemetry data to a master system, and by using messages from the master supervisory system to control connected objects. Other terms that may be used for RTU are remote telemetry unit and remote telecontrol unit.
Bipolar CMOS (BiCMOS) is a semiconductor technology that integrates two semiconductor technologies, those of the bipolar junction transistor and the CMOS logic gate, into a single integrated circuit. In more recent times the bipolar processes have been extended to include high mobility devices using silicon–germanium junctions.
An integrator in measurement and control applications is an element whose output signal is the time integral of its input signal. It accumulates the input quantity over a defined time to produce a representative output.
RS-485, also known as TIA-485(-A) or EIA-485, is a standard, originally introduced in 1983, defining the electrical characteristics of drivers and receivers for use in serial communications systems. Electrical signaling is balanced, and multipoint systems are supported. The standard is jointly published by the Telecommunications Industry Association and Electronic Industries Alliance (TIA/EIA). Digital communications networks implementing the standard can be used effectively over long distances and in electrically noisy environments. Multiple receivers may be connected to such a network in a linear, multidrop bus. These characteristics make RS-485 useful in industrial control systems and similar applications.

The Standard Modular System (SMS) is a system of standard transistorized circuit boards and mounting racks developed by IBM in the late 1950s, originally for the IBM 7030 Stretch. They were used throughout IBM's second-generation computers, peripherals, the 7000 series, the 1400 series, and the 1620. SMS was superseded by Solid Logic Technology (SLT) introduced with System/360 in 1964, however they remained in use with legacy systems through the 1970s.
A resistor ladder is an electrical circuit made from repeating units of resistors, in specific configurations.

PSoC is a family of microcontroller integrated circuits by Cypress Semiconductor. These chips include a CPU core and mixed-signal arrays of configurable integrated analog and digital peripherals.
The Serial Low-power Inter-chip Media Bus (SLIMbus) is a standard interface between baseband or application processors and peripheral components in mobile terminals. It was developed within the MIPI Alliance, founded by ARM, Nokia, STMicroelectronics and Texas Instruments. The interface supports many digital audio components simultaneously, and carries multiple digital audio data streams at differing sample rates and bit widths.
An operating temperature is the allowable temperature range of the local ambient environment at which an electrical or mechanical device operates. The device will operate effectively within a specified temperature range which varies based on the device function and application context, and ranges from the minimum operating temperature to the maximum operating temperature. Outside this range of safe operating temperatures the device may fail.

USB-C, or USB Type-C, is a 24-pin connector that supersedes previous USB connectors and can carry audio, video, and other data, to connect to monitors or external drives. It can also provide and receive power, to power, e.g., a laptop or a mobile phone. It is used not only by USB technology, but also by other protocols, including Thunderbolt, PCIe, HDMI, DisplayPort, and others. It is extensible to support future protocols.
This glossary of electrical and electronics engineering is a list of definitions of terms and concepts related specifically to electrical engineering and electronics engineering. For terms related to engineering in general, see Glossary of engineering.
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).