
The Maryland Area Rail Commuter (MARC) is a commuter rail system in the Washington–Baltimore area. MARC is administered by the Maryland Transit Administration (MTA) and operated under contract by Alstom and Amtrak on track owned by CSX Transportation (CSXT) and Amtrak. In 2023, the system had a ridership of 3,860,600, or about 13,900 per weekday as of the third quarter of 2024, less than pre-COVID-19 pandemic weekday ridership of 40,000.

The Florida Central Railroad Company is one of several short line railroads run by Regional Rail, LLC. It runs from downtown Orlando northwest to Apopka and Tavares with a branch from Toronto to Ocoee and Winter Garden and branches from Tavares to Umatilla and Sorrento. The Florida Central connects with the Central Florida Rail Corridor in downtown Orlando, Florida and has trackage rights on the CFRC from there south to Taft Yard where they interchange with CSX Transportation. The railroad is based out of the Plymouth freight station.
The Florida Midland Railroad Company, Inc. is one of several short line railroads operated by Regional Rail, LLC in Florida. The Florida Midland Railroad operates two former CSX Transportation railroad lines including their former Lake Wales Subdivision, and their former Bartow Subdivision. It once had a third line from Wildwood to Leesburg that is now mostly abandoned. Florida Midland Railroad began operating the lines in 1987 and uses locomotives branded for the Florida Central Railroad, its sister railroad.
The Florida Northern Railroad Company, Inc. is one of several short line railroads run by Regional Rail, LLC. It has connections to CSX at Ocala, Florida, running north to Lowell, Florida, and south to Candler, Florida. It was formerly run by CSX as their Ocala Subdivision.

Pinsly Railroad Company, based in Westfield, Massachusetts, was a short line railroad holding company. It was one of the oldest such companies in the United States, and has owned railroads continuously since its founding in 1938. As of 2022 Pinsly's sole railroad subsidiary is the Pioneer Valley Railroad in Massachusetts. In August 2023, Macquarie Infrastructure Partners reached an agreement with Pinsly to acquire the railroad through its subsidiary Gulf & Atlantic Railways.
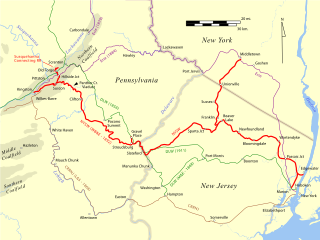
The New Jersey Midland Railway was a 19th-century predecessor to the New York, Susquehanna and Western Railway (NYS&W) that operated in Northern New Jersey and Orange County, New York.

The Middletown and New Jersey Railroad is one of two railroads in the city of Middletown, New York; the other being its interchange partner, Norfolk Southern Railway. The MNJ consists of 43 miles (69 km) of track in southeastern New York serving Orange County and the Hudson Valley. The railroad also operates and has trackage rights on three additional branch lines totalling 40 miles (64 km) leased from Norfolk Southern in Orange County. It was known as the Middletown and New Jersey Railway until 2009, when East Penn Railroad parent Regional Rail, LLC bought the line through a new subsidiary. In 2015, Regional Rail was in turn acquired by Levine Leichtman Capital Partners ("LLCP").

The Keystone Corridor is a 349-mile (562 km) railroad corridor between Philadelphia and Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, that consists of two rail lines: Amtrak and SEPTA's Philadelphia-to-Harrisburg main line, which hosts SEPTA's Paoli/Thorndale Line commuter rail service, and Amtrak's Keystone Service and Pennsylvanian inter-city trains; and the Norfolk Southern Pittsburgh Line. The corridor was originally the Main Line of the Pennsylvania Railroad.

The New York, Ontario and Western Railway, commonly known as the O&W or NYO&W, was a regional railroad founded in 1868. The last train ran from Norwich, New York, to Middletown, New York, in 1957, after which it was ordered liquidated by a U.S. bankruptcy judge. It was the first Class I U.S. railroad to be abandoned in its entirety.

East Penn Railroad is a short-line railroad that operates a number of mostly-unconnected lines in Pennsylvania and Delaware. Except for two industrial park switching operations, all are former Pennsylvania Railroad or Reading Company lines, abandoned or sold by Conrail or its predecessors.
The Chester Creek Branch was a 7.25-mile (11.67 km) railroad line that operated in southern Delaware County, Pennsylvania, from 1869 to 1972.

The Philadelphia, Baltimore and Washington Railroad (PB&W) was a railroad that operated in Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, and the District of Columbia in the 20th century, and was a key component of the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) system. Its 131-mile (211 km) main line ran between Philadelphia and Washington. The PB&W main line is now part of the Northeast Corridor, owned by Amtrak.

The Great Sandhills Railway is a Canadian short line railway company that operates 198 kilometres (123 mi) of track west of Swift Current, Saskatchewan in the provinces of Saskatchewan and Alberta.
The Tyburn Railroad is a short-line railroad in Morrisville, Bucks County, Pennsylvania owned by Regional Rail, LLC. The railroad operates 1.5 miles (2.4 km) of track, serving a rail to truck transload facility. It interchanges with CSX Transportation and Norfolk Southern Railway in Fairless. The Tyburn Railroad was acquired by Regional Rail, LLC in September 2011.
The Delmarva Central Railroad is an American short-line railroad owned by Carload Express that operates 188 miles (303 km) of track on the Delmarva Peninsula in the states of Delaware, Maryland, and Virginia. The railroad operates lines from Porter, Delaware to Hallwood, Virginia and from Harrington, Delaware to Frankford, Delaware along with several smaller branches. The DCR interchanges with the Norfolk Southern Railway and the Maryland and Delaware Railroad. The railroad was created in 2016 to take over the Norfolk Southern Railway lines on the Delmarva Peninsula. The DCR expanded by taking over part of the Bay Coast Railroad in 2018 and the Delaware Coast Line Railroad in 2019.

The Delaware Railroad was the major railroad in the US state of Delaware, traversing almost the entire state north to south from the mid-1850's until 1976. It began in Porter and was extended south through Dover andSeaford before reaching Delmar on the border of Maryland in 1859. Although operated independently, in 1857 it was leased by and under the financial control of the Philadelphia, Wilmington, and Baltimore Railroad, which was purchased by the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) in 1881. In 1891, it was extended north approximately 14 miles (23 km) with the purchase of existing track to New Castle and Wilmington. It remained a part of the PRR system and then Penn Central until 1976 when Penn Central went bankrupt at which point it was absorbed into Conrail.
The Wilmington and Northern Branch is a partially-abandoned railway line in the states of Delaware and Pennsylvania. It was constructed between 1869 and 1870 by the Wilmington and Reading Railroad, a predecessor of the Wilmington and Northern Railroad. At its fullest extent it connected Reading, Pennsylvania, with Wilmington, Delaware. The Philadelphia and Reading Railway leased the line in 1900. With the Reading Company's bankruptcy and the creation of Conrail in 1976 the line's ownership fragmented, and the section between Coatesville, Pennsylvania, and Birdsboro, Pennsylvania, has been abandoned.











