Related Research Articles

Central Asia is a region in Asia which stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north, including the former Soviet republics of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. It is also colloquially referred to as "the stans" as the countries all have names ending with the Persian suffix "-stan", meaning "land of".

The Southern African Development Community (SADC) is an inter-governmental organization headquartered in Gaborone, Botswana. Its goal is to further regional socio-economic cooperation and integration as well as political and security cooperation among 16 countries in southern Africa.

The Economic Cooperation Organization or ECO is an Asian political and economic intergovernmental organization which was founded in 1985 in Tehran by the leaders of Iran, Pakistan, and Turkey. It provides a platform to discuss ways to improve development and promote trade and investment opportunities. The ECO is an ad hoc organisation under the United Nations Charter. The objective is to establish a single market for goods and services, much like the European Union. The ECO's secretariat and cultural department are located in Iran, its economic bureau is in Turkey and its scientific bureau is situated in Pakistan.

European integration is the process of industrial, economic, political, legal, social and cultural integration of states wholly or partially in Europe or nearby. European integration has primarily come about through the European Union and its policies.

The East African Community (EAC) is an intergovernmental organisation composed of six countries in the African Great Lakes region in eastern Africa: Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda, South Sudan, Tanzania, and Uganda. Uhuru Kenyatta, the president of Kenya, is the EAC's chairman. The organisation was founded in 1967, collapsed in 1977, and was revived on 7 July 2000. In 2008, after negotiations with the Southern African Development Community (SADC) and the Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA), the EAC agreed to an expanded free trade area including the member states of all three organizations. The EAC is an integral part of the African Economic Community. The capital of the EAC is Arusha, while the most populous city is Dar es Salaam, both of which are in Tanzania.
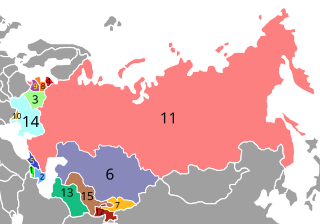
The post-Soviet states, also known as the former Soviet Union (FSU), the former Soviet Republics and in Russia as the near abroad, are the 15 sovereign states that were union republics of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics; that emerged and re-emerged from the Soviet Union following its breakup in 1991.

Regional Integration is a process in which neighboring countries enter into an agreement in order to upgrade cooperation through common institutions and rules. The objectives of the agreement could range from economic to political to environmental, although it has typically taken the form of a political economy initiative where commercial interests are the focus for achieving broader socio-political and security objectives, as defined by national governments. Regional integration has been organized either via supranational institutional structures or through intergovernmental decision-making, or a combination of both.

The Department of Foreign Affairs is the executive department of the Philippine government tasked to contribute to the enhancement of national security and the protection of the territorial integrity and national sovereignty, to participate in the national endeavor of sustaining development and enhancing the Philippines' competitive edge, to protect the rights and promote the welfare of Filipinos overseas and to mobilize them as partners in national development, to project a positive image of the Philippines, and to increase international understanding of Philippine culture for mutually-beneficial relations with other countries.

The Central American Integration System has been the economic and political organization of Central American states since 1 February 1993. On 13 December 1991, the ODECA countries signed the Protocol of Tegucigalpa, extending earlier cooperation for regional peace, political freedom, democracy and economic development. SICA's General Secretariat is in El Salvador.

The Ministry of Foreign Affairs and European Integration of Moldova (MFAEI) is one of the nine ministries of the Government of Moldova.

The Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Belarus is the Belarusian government ministry which oversees the foreign relations of Belarus.

The African Free Trade Zone (AFTZ) is a free trade zone announced at the EAC-SADC-COMESA Summit on 22 October 2008 by the heads of Southern African Development Community (SADC), the Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) and the East African Community (EAC). The African Free Trade Zone is also referred to as the African Free Trade Area in some official documents and press releases.
Integration is a political and economic agreement among countries that gives preference to member countries to the agreement. General integration can be achieved in three different approachable ways: through the World Trade Organization (WTO), bilateral integration, and regional integration. In bilateral integration, only two countries economically cooperate with one another, whereas in regional integration, several countries within the same geographic distance become joint to form organizations such as the European Union (EU) and the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). Indeed, factors of mobility like capital, technology and labour are indicating strategies for cross-national integration along with those mentioned above.

European Union–Kazakhstan relations are the international relations between the Republic of Kazakhstan and the common foreign policy and trade relations of the European Union.

The Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) is an economic union of states located in Eastern Europe, Western Asia, and Central Asia. The Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union was signed on 29 May 2014 by the leaders of Belarus, Kazakhstan and Russia, and came into force on 1 January 2015. Treaties aiming for Armenia's and Kyrgyzstan's accession to the Eurasian Economic Union were signed on 9 October and 23 December 2014, respectively. Armenia's accession treaty came into force on 2 January 2015. Kyrgyzstan's accession treaty came into effect on 6 August 2015. Kyrgyzstan participated in the EAEU from the day of its establishment as an acceding state.

Policies advocating Middle East economic integration aim to bring about peace, stability, and prosperity in the Middle East, which they believe can only be sustained over the long run via regional economic cooperation.
South-South cooperation is cooperation between two or more developing countries. This article monitors recent developments in South-South cooperation in the field of science and technology.
Science and technology in Uzbekistan examines government efforts to develop a national innovation system and the impact of these policies.