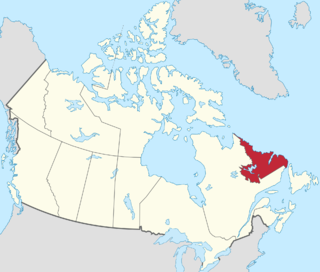
Labrador is a geographic and cultural region within the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is the primarily continental portion of the province and constitutes 71% of the province's area but is home to only 6% of its population. It is separated from the island of Newfoundland by the Strait of Belle Isle. It is the largest and northernmost geographical region in the four Atlantic provinces.

Avondale is a town located on Newfoundland's Avalon Peninsula in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada.
Whitbourne is a town on the Avalon Peninsula in Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada in Division 1.
Clarenville is a town on the east coast of Newfoundland in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. Clarenville was incorporated in 1951. It is located in the Shoal Harbour valley, fronting an arm of the Atlantic Ocean called Random Sound.

Marine Atlantic Inc. is an independent Canadian federal Crown corporation which is mandated to operate ferry services between the provinces of Newfoundland and Labrador and Nova Scotia.

Division 1, Newfoundland and Labrador is a census division covering the entire Avalon Peninsula including the Isthmus of Avalon of the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. Like all census divisions in Newfoundland and Labrador, but unlike the census divisions of some other provinces, the division exists only as a statistical division for census data, and is not a political entity.

The Newfoundland Railway operated on the island of Newfoundland from 1898 to 1988. With a total track length of 906 miles (1,458 km), it was the longest 3 ft 6 in narrow-gauge railway system in North America.
Chapel Arm is a settlement in Newfoundland, Canada, located at the southeast corner of Trinity Bay, approximately 100 km (62 mi) west of St. John's and two km from the Trans-Canada Highway.

Sir Robert Gillespie Reid was a Scottish railway contractor most famous for building large railway bridges in Canada and the United States. Founder of Reid Newfoundland Company, from 1889 until his death, he built, owned, and operated the Newfoundland Railway.

Ernest Harmon Air Force Base is a former United States Air Force base located in Stephenville, Newfoundland and Labrador. The base was built by the United States Army Air Forces in 1941 under the Destroyers for Bases Agreement with the United Kingdom.

The Southwold Railway was a narrow gauge railway line between Halesworth and Southwold in the English county of Suffolk. 8 miles 63+1⁄2 chains (14.15 km) long, it was 3 ft narrow gauge. It opened in 1879 and closed in 1929.

Harbour Grace is a town in Conception Bay on the Avalon Peninsula in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. With roots dating back to the 16th century, it is one of the oldest towns in North America.

SS Sagona was a passenger and freight ferry used in ferry service on the northern coastal routes between the island of Newfoundland and the coast of Labrador in Canada. In winter, Sagona was primarily a sealing vessel, bringing in a total of 165,599 seals from 1912 until 1938 under captains Job Knee, Jack Randell, Lewis Little and Jacob Kean.

Argentia is a Canadian commercial seaport and industrial park located in the Town of Placentia, Newfoundland and Labrador. It is situated on the southwest coast of the Avalon Peninsula and defined by a triangular shaped headland which reaches northward out into Placentia Bay creating a natural harbour 3 km (1.9 mi) in length.
The Alphabet Fleet was a fleet of vessels owned and operated by the Reid Newfoundland Company as part of the provisioning of the 1898 Railway contract between the Dominion of Newfoundland and the Reid Newfoundland Company. The vessels were named after places in Scotland, the native homeland of Sir Robert Gillespie Reid, founder of the Reid Newfoundland Company.
George H. Middleton was a Canadian engineer, who had worked on as a sub-contractor of the Canadian Pacific Railway and partner to Robert G. Reid in the building of the Newfoundland Railway.

The St. John's Street Railway Company was formed by Robert G. Reid in 1896 to build an electrical railway in St. John's to provide urban transportation using street cars.

SS Kyle is a 220 feet (67 m) steam ship that is aground in the harbour of the Town of Harbour Grace, Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. She ran ashore in February 1967. Intended to transport supplies and provide transportation from Carbonear to Labrador, she was also used to transport infantry to Canada during World War II. After her grounding on the shores of Riverhead, Harbour Grace, she has had several owners, from the Earle Brothers Freighting Company, Dominion Metals, and the Government of Newfoundland. Plans to have the vessel moved to the town of Salmon Cove, Newfoundland, and turned into a museum were later aborted due to financial implications.

The Churchill Falls Generating Station is a hydroelectric underground power station in Labrador. At 5,428 MW, it is the sixteenth largest in the world, and the second-largest in Canada, after the Robert-Bourassa generating station in northwestern Quebec.
The Quebec North Shore and Labrador Railway is a private Canadian regional railway that stretches 414 kilometres (257 mi) through the wilderness of northeastern Quebec and western Labrador. It connects Labrador City, Labrador, with the port of Sept-Îles, Quebec, on the north shore of the St. Lawrence River. QNS&L is owned by Iron Ore Company of Canada (IOC), and is a common carrier.














