
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets electromagnetic spectra. In narrower contexts, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.

Raman spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified.
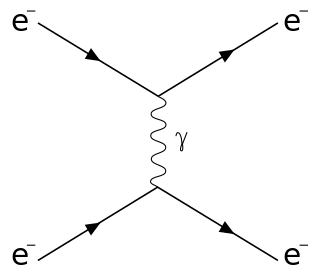
In chemistry and physics, Raman scattering or the Raman effect is the inelastic scattering of photons by matter, meaning that there is both an exchange of energy and a change in the light's direction. Typically this effect involves vibrational energy being gained by a molecule as incident photons from a visible laser are shifted to lower energy. This is called normal Stokes-Raman scattering.

Rudolf Zahradník was a Czech chemist in the field of quantum chemistry and molecular spectroscopy. He held research positions at the Institute of Occupational Medicine and went on to serve as the first director of the J Heyrovsky Institute of Physical Chemistry, president of the Czech Academy of Sciences and chairman of the Learned Society of the Czech Republic, after the Velvet Revolution. During the 1980s, he taught future German leader Angela Merkel, who was then on an internship in Czechoslovakia. He held a doctorate from the University of Chemistry and Technology, Prague.
An infrared spectroscopy correlation table is a list of absorption peaks and frequencies, typically reported in wavenumber, for common types of molecular bonds and functional groups. In physical and analytical chemistry, infrared spectroscopy is a technique used to identify chemical compounds based on the way infrared radiation is absorbed by the compound.
The Chemistry Quality Eurolabels or European Quality Labels in Chemistry is a marketing scheme for chemistry degrees at institutions located within the 45 countries involved in the Bologna process. Labels are awarded to qualifying institutions under the names are Eurobachelor and Euromaster, as well as the proposed Eurodoctorate. Label Committee not only prepares for the ECTN Administrative Council proposals to award the Eurolabels but also judge the quality of chemical education programmes at HEIs. ECTN and its Label Committee closely collaborates with EuCheMS and American Chemical Society.

Laurence David Barron has been Gardiner Professor of Chemistry at the University of Glasgow since 1998. He is a chemist who has conducted pioneering research into the properties of chiral molecules — defined by Lord Kelvin as those that cannot be superimposed onto their mirror image. By extending this definition of chirality to include moving particles and processes that vary with time, he has made a fundamental theoretical contribution to the field. Chiral molecules such as amino acids, sugars, proteins, and nucleic acids play a central role in the chemistry of life, and many drug molecules are chiral. Laurence's work on Raman optical activity — a spectroscopic technique capable of determining the three-dimensional structures of chiral molecules, which he predicted, observed, and applied to problems at the forefront of chemistry and structural biology — has led to its development as a powerful analytical tool used in academic and industrial laboratories worldwide. His much-cited book, Molecular Light Scattering and Optical Activity, has contributed to the growing impact of chirality on many areas of modern science.
Spectroscopy is a trade magazine published since 1985. Spectroscopy has an editorial goal to promote and support the use of spectroscopic instrumentation in applied research, environmental testing, quality control, and the life sciences.
Applied Spectroscopy is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published monthly by the Society for Applied Spectroscopy, and it is also the official journal for this society. The editor-in-chief is Sergei G. Kazarian. The journal covers applications of spectroscopy in analytical chemistry, materials science, biotechnology, and chemical characterization.

Renato Zenobi is a Swiss chemist. He is Professor of Chemistry at ETH Zurich. Throughout his career, Zenobi has contributed to the field of analytical chemistry.
Yukihiro Ozaki is a Japanese scientist. Kwansei Gakuin University, Department of Chemistry, School of Science and Technology, professor emeritus, Fellow.

Halina Abramczyk is a Polish physicist and chemist, a specialist in molecular spectroscopy and laser spectroscopy professor employed at the Lodz University of Technology.

Foil Allan Miller was an American chemist and philatelist best known for his work in infrared and Raman spectroscopy. He was head of the spectroscopy division of the Mellon Institute and later professor and head of the spectroscopy laboratory at the University of Pittsburgh. Among other publications, he co-authored the books Course Notes on the Interpretation of Infrared and Raman Spectra (2004) and A Philatelic Ramble Through Chemistry (1998).
Siva Umapathy is a retired Professor of the Department of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry and also at the department of Instrumentation and Applied Physics at the Indian Institute of Science. He was the Director of the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Bhopal (IISER). He is known for his studies of molecular dynamics using Raman spectroscopy. He is a fellow of the Royal Society of Chemistry and an elected fellow of the Indian Academy of Sciences and also The National Academy of Science of India. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards, in 2004, for his contributions to chemical sciences.
Jeanette Grasselli Brown is an American analytical chemist and spectroscopist who is known for her work with Standard Oil of Ohio as an industrial researcher in the field of spectroscopy.

Robin Jon Hawes Clark was a New Zealand-born chemist initially noted for research of transition metal and mixed-valence complexes, and later for the use of Raman spectroscopy in determining the chemical composition of pigments used in artworks.

The Wilhelm Ostwald Institute for Physical and Theoretical Chemistry at the University of Leipzig, located at Linnéstraße 2 in Leipzig, is the oldest physical chemistry institute in Germany. It is one of seven institutes of the Faculty of Chemistry and Mineralogy of the University of Leipzig. The institute was ceremoniously inaugurated in 1898 by its first director, Nobel Prize winner Wilhelm Ostwald, and has borne the official name "Wilhelm Ostwald Institute for Physical and Theoretical Chemistry" since 1998.
Janina Kneipp is a German scientist who is Professor of Physical Chemistry Humboldt University of Berlin. Her research considers surface enhanced Raman scattering and plasmonic enhancement in multi-modal micro spectroscopy.
Ewa Joanna Bulska is a Polish chemist, and Professor of Chemical Sciences at the University of Warsaw, who specializes in analytical chemistry, atomic and mass spectrometry with over 237 scholarly publications.
Ellis Ridgeway Lippincott Jr. was an American chemist, educator, inventor, science leader, and pioneer in spectroscopy. He was a professor of chemistry at the University of Maryland from 1955-1974 and served as director of the Center for Materials Research. According to Spectroscopy, Lippincott was an "icon of spectroscopy" and "one of the most influential spectroscopists of the past 100 years."










