
Open educational resources (OER) are teaching, learning, and research materials intentionally created and licensed to be free for the end user to own, share, and in most cases, modify. The term "OER" describes publicly accessible materials and resources for any user to use, re-mix, improve, and redistribute under some licenses. These are designed to reduce accessibility barriers by implementing best practices in teaching and to be adapted for local unique contexts.
A learning management system (LMS) or virtual learning environment (VLE) is a software application for the administration, documentation, tracking, reporting, automation, and delivery of educational courses, training programs, materials or learning and development programs. The learning management system concept emerged directly from e-Learning. Learning management systems make up the largest segment of the learning system market. The first introduction of the LMS was in the late 1990s. LMSs have been adopted by almost all higher education institutions in the English-speaking world. Learning management systems have faced a massive growth in usage due to the emphasis on remote learning during the COVID-19 pandemic.
OpenStax CNX, formerly called Connexions, is a global repository of educational content provided by volunteers. The open source platform is provided and maintained by OpenStax, which is based at Rice University. The collection is available free of charge, can be remixed and edited, and is available for download in various digital formats.
Inquiry-based learning is a form of active learning that starts by posing questions, problems or scenarios. It contrasts with traditional education, which generally relies on the teacher presenting facts and their knowledge about the subject. Inquiry-based learning is often assisted by a facilitator rather than a lecturer. Inquirers will identify and research issues and questions to develop knowledge or solutions. Inquiry-based learning includes problem-based learning, and is generally used in small-scale investigations and projects, as well as research. The inquiry-based instruction is principally very closely related to the development and practice of thinking and problem-solving skills.

Open education is an educational movement founded on openness, with connections to other educational movements such as critical pedagogy, and with an educational stance which favours widening participation and inclusiveness in society. Open education broadens access to the learning and training traditionally offered through formal education systems and is typically offered through online and distance education. The qualifier "open" refers to the elimination of barriers that can preclude both opportunities and recognition for participation in institution-based learning. One aspect of openness or "opening up" education is the development and adoption of open educational resources in support of open educational practices.
An open textbook is a textbook licensed under an open license, and made available online to be freely used by students, teachers and members of the public. Many open textbooks are distributed in either print, e-book, or audio formats that may be downloaded or purchased at little or no cost.
The Tufts OpenCourseWare (OCW) project, was a web-based publication of educational material from a number of Tufts University courses, providing open sharing of free, searchable, high-quality course content to educators, students, and self-learners throughout the global community. The Tufts OCW initiative encouraged the publication and free exchange of course materials on the World Wide Web. First launched in June 2005, Tufts OCW provided materials with strong representation from Tufts' health sciences schools, some of which were equivalent to textbooks in depth. All materials on the Tufts OCW site were accessible and free of charge. As Tufts OCW is not a distance learning program, no registration, applications, prerequisites, or fees are required and no credit is granted. Tufts ended funding for its Open Courseware initiative in 2014, and content on the Tufts OCW web site was removed on June 30, 2018.
Open.Michigan is a collection of open initiatives and projects at the University of Michigan (U-M). Open.Michigan supports the open access and use of U-M resources for teaching, learning, and research. Open.Michigan promotes open content licensing and supports the reuse, redistribution, and remixing of educational materials for use by others worldwide. Some of the key efforts underway under the Open.Michigan umbrella include U-M's Open Educational Resources publishing activities, development of software tools that support creating open content, and various open content repositories.
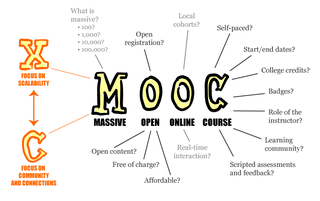
A massive open online course or an open online course is an online course aimed at unlimited participation and open access via the Web. In addition to traditional course materials, such as filmed lectures, readings, and problem sets, many MOOCs provide interactive courses with user forums or social media discussions to support community interactions among students, professors, and teaching assistants (TAs), as well as immediate feedback to quick quizzes and assignments. MOOCs are a widely researched development in distance education, first introduced in 2008, that emerged as a popular mode of learning in 2012, a year called the "Year of the MOOC".
MyMathLab is an online interactive and educational system designed by Pearson Education to accompany its published math textbooks. It covers courses from basic math through calculus and statistics, as well as math for business, engineering and future educators. Pearson designed MyMathLab to respond to the needs of instructors and students who wanted more opportunity for practice, immediate feedback, and automated grading.

The Institute for the Study of Knowledge Management in Education (ISKME), is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization founded in 2002. Located in Half Moon Bay, California, its mission is to make learning and knowledge sharing participatory, equitable, and open.

Open educational practices (OEP) are part of the broader open education landscape, including the openness movement in general. It is a term with multiple layers and dimensions and is often used interchangeably with open pedagogy or open practices. OEP represent teaching and learning techniques that draw upon open and participatory technologies and high-quality open educational resources (OER) in order to facilitate collaborative and flexible learning. Because OEP emerged from the study of OER, there is a strong connection between the two concepts. OEP, for example, often, but not always, involve the application of OER to the teaching and learning process. Open educational practices aim to take the focus beyond building further access to OER and consider how in practice, such resources support education and promote quality and innovation in teaching and learning. The focus in OEP is on reproduction/understanding, connecting information, application, competence, and responsibility rather than the availability of good resources. OEP is a broad concept which can be characterised by a range of collaborative pedagogical practices that include the use, reuse, and creation of OER and that often employ social and participatory technologies for interaction, peer-learning, knowledge creation and sharing, empowerment of learners, and open sharing of teaching practices.

OER Commons is a freely accessible online library that allows teachers and others to search and discover open educational resources (OER) and other freely available instructional materials.
Open educational resources (OER) are learning materials that reside in the public domain or have been released under an intellectual property license that permits their free use and re-purposing by others. OER policies are adopted by governments, institutions or organisations in support of the creation and use of open content, specifically open educational resources (OER), and related open educational practices.

Boundless was an American company, founded in 2011, which created free and low-cost textbooks and distributed them online. In April 2015, it was acquired by Valore. The combined company is based in Boston, Massachusetts.
Open Course Library (OCL) is an effort by the State of Washington to identify and make available digitally, to community and technical college instructors and students across that state, free textbooks, interactive assignments, and videos. Instructional materials can be "a smorgasbord of teaching modules and exercises developed by other open-learning projects.. . Interactive-learning Web sites and even instructional videos on YouTube. . ." However, OCL is not an OER publishing project, although it did contribute to the development of some widely used resources. Goals include: lowering textbook costs for students, providing new resources for faculty to use in their courses; and fully engaging in the global OER or open educational resources discussion.

OER Africa is an initiative of Saide, established in 2008 with support from the William and Flora Hewlett Foundation, to collaborate with higher education institutions in Africa in the development and use of Open Educational Resources (OER), to enhance teaching and learning.
The UNESCO 2012 Paris OER Declaration, otherwise known as the Paris declaration on Open Educational Resources, is a declaration urging governments to promote the use of open educational resources (OERs) and calling for publicly funded educational materials to be released in a freely reusable form.
Open Educational Practices in Australia refers to the development, implementation and use of Open educational resources (OER), open access, open learning design, open policies, and Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) to open up education in Australia.
Open educational resources in Canada are the various initiatives related to open education, open educational resources (OER), open pedagogies (OEP), open educational practices (OEP), and open scholarship that are established nationally and provincially across Canadian K-12 and higher education sectors, and where Canadian based inititatives extend to international collaborations.









