Appomattox is a town in Appomattox County, Virginia, United States. The population was 1,733 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Appomattox County.

This section of the Timeline of United States history concerns events from 1860 to 1899.

Edward Otho Cresap Ord was an American engineer and United States Army officer who saw action in the Seminole War, the Indian Wars, and the American Civil War. He commanded an army during the final days of the Civil War, and was instrumental in forcing the surrender of Confederate General Robert E. Lee. He also designed Fort Sam Houston. He died in Havana, Cuba of yellow fever.

Wilmer McLean was an American wholesale grocer from Virginia. His house, near Manassas, Virginia, was involved in the First Battle of Bull Run in 1861. After the battle, he moved to Appomattox, Virginia, to escape the war, thinking that it would be safe. Instead, in 1865, General Robert E. Lee surrendered to Ulysses S. Grant in McLean's house in Appomattox. His houses were, therefore, involved in one of the first and one of the last encounters of the American Civil War.

The Appomattox Court House National Historical Park is a preserved 19th-century village in Appomattox County, Virginia. The village is the site of the Battle of Appomattox Court House, and contains the McLean House, where the surrender of the Army of Northern Virginia under Robert E. Lee to Union commander Ulysses S. Grant took place on April 9, 1865, an event widely symbolic of the end of the American Civil War. The village itself began as the community of Clover Hill, which was made the county seat of Appomattox County in the 1840s. The village of Appomattox Court House entered a stage of decline after it was bypassed by a railroad in 1854. In 1930, the United States War Department was authorized to erect a monument at the site, and in 1933 the War Department's holdings there was transferred to the National Park Service. The site was greatly enlarged in 1935, and a restoration of the McLean House was planned but was delayed by World War II. In 1949, the restored McLean House was reopened to the public. Several restored buildings, as well as a number of original 19th-century structures.

The Battle of Fort Blakeley took place from April 2 to April 9, 1865, in Baldwin County, Alabama, about 6 miles (9.7 km) north of Spanish Fort, Alabama, as part of the Mobile Campaign of the American Civil War. At the time, Blakeley, Alabama, had been the county seat of Baldwin County.

The Battle of Appomattox Court House, fought in Appomattox County, Virginia, on the morning of April 9, 1865, was one of the last battles of the American Civil War (1861–1865). It was the final engagement of Confederate General in Chief, Robert E. Lee, and his Army of Northern Virginia before they surrendered to the Union Army of the Potomac under the Commanding General of the United States Army, Ulysses S. Grant.

Bennett Place is a former farm and homestead in Durham, North Carolina, which was the site of the last surrender of a major Confederate army in the American Civil War, when Joseph E. Johnston surrendered to William T. Sherman. The first meeting saw Sherman agreeing to certain political demands by the Confederates, which were promptly rejected by the Union cabinet in Washington. Another meeting had to be held to agree on military terms only, in line with Robert E. Lee’s recent surrender to Ulysses S. Grant. This effectively ended the war.

Between 73 and 79 days after the presidential election, the president-elect of the United States is inaugurated as president by taking the presidential oath of office. The inauguration takes place for each new presidential term, even if the president is continuing in office for a second term.

Lee and Grant at Appomattox is an historical fiction children's novel by MacKinlay Kantor. It was originally published in 1950 by Random House, and later published in paperback by Sterling Point Books.

Sailor's Creek Battlefield Historical State Park is a 321-acre (130 ha) state park near Rice, Virginia, located mostly in Amelia County with a small portion in Prince Edward County. It includes a portion of the landmarked Sayler's Creek Battlefield, an area of 1,022 acres (414 ha) that was the site of the April 6, 1865 Battle of Sayler's Creek, one of the last major engagements in the Eastern Theater of the war involving Confederate General-in-Chief Robert E. Lee (1807-1870). The battle occurred during his week-long retreat to the southwest in the final Appomattox campaign from the fallen Confederate capital at Richmond and nearby Petersburg, three days before his surrender at Appomattox Court House to Union Army General-in-Chief Ulysses S. Grant (1822-1885), which effectively ended the American Civil War (1861-1865).
Kirkwood Otey served as the commanding officer of the 11th Virginia Infantry in the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia during the American Civil War.

Appomattox Station was located in the town of Appomattox, Virginia and was the site of the Battle of Appomattox Station on the day before General Robert E. Lee surrendered the Army of Northern Virginia to Lieutenant General Ulysses S. Grant, effectively ending the Civil War. That station was destroyed by fire in 1898 and its replacement by fire in 1923. The current railway station, built within a block of the original location, is the Appomattox Depot (1923), a contributing property to the Appomattox Historic District. The depot is now home to the Appomattox Visitor Information Center.

The McLean House near Appomattox, Virginia is within the Appomattox Court House National Historical Park. The house was owned by Wilmer McLean and his wife Virginia near the end of the American Civil War. It served as the location of the surrender conference for the Confederate army of General Robert E. Lee on April 9, 1865, after a nearby battle.

The Old Appomattox Court House is a former county court house within the Appomattox Court House National Historical Park. In the 1800s this structure gave the surrounding village the name Appomattox Court House. The 1865 surrender of the Army of Northern Virginia on April 9 at the nearby McLean House by General Robert E. Lee to General Ulysses S. Grant commenced the conclusion of the American Civil War that finalized with the surrender of the Shenandoah on November 6, 1865.

The Bocock–Isbell House is a structure within the Appomattox Court House National Historical Park. It was registered in the National Park Service's database of Official Structures on June 26, 1989.

The Mariah Wright house is a structure within the Appomattox Court House National Historical Park. It was registered in the National Park Service's database of Official Structures on June 26, 1989.
Deatonville is a rural unincorporated community in the western part of Amelia County in the U.S. state of Virginia. It is located along SR 616 at its intersection with the eastern terminus of SR 617. Deatonville straddles the boundary between ZIP codes 23083 (Jetersville) and 23966 (Rice).
Appomattox Court House could refer to:
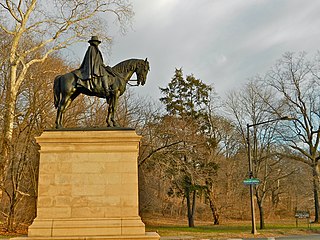
The equestrian statue of Ulysses S. Grant is a public monument in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. Located in Fairmount Park, the monument honors Ulysses S. Grant, who served as a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War and later as President of the United States. The monument was designed by Daniel Chester French and Edward Clark Potter and consists of an equestrian statue atop a pedestal. The statue was dedicated in 1899.