Related Research Articles
Bacterial conjugation is the transfer of genetic material between bacterial cells by direct cell-to-cell contact or by a bridge-like connection between two cells. This takes place through a pilus. It is a parasexual mode of reproduction in bacteria.

In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritance. This is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues, while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own copy of the DNA. The cell possesses the distinctive property of division, which makes replication of DNA essential.

Escherichia coli, also known as E. coli, is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus Escherichia that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes (EPEC, ETEC etc.) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. The harmless strains are part of the normal microbiota of the gut, and can benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2, and preventing colonisation of the intestine with pathogenic bacteria, having a mutualistic relationship. E. coli is expelled into the environment within fecal matter. The bacterium grows massively in fresh fecal matter under aerobic conditions for three days, but its numbers decline slowly afterwards.
A bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) is a DNA construct, based on a functional fertility plasmid, used for transforming and cloning in bacteria, usually E. coli. F-plasmids play a crucial role because they contain partition genes that promote the even distribution of plasmids after bacterial cell division. The bacterial artificial chromosome's usual insert size is 150–350 kbp. A similar cloning vector called a PAC has also been produced from the DNA of P1 bacteriophage.

A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create two identical DNA duplexes from a single original DNA duplex. During this process, DNA polymerase "reads" the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones. These enzymes catalyze the chemical reaction

DNA polymerase III holoenzyme is the primary enzyme complex involved in prokaryotic DNA replication. It was discovered by Thomas Kornberg and Malcolm Gefter in 1970. The complex has high processivity and, specifically referring to the replication of the E.coli genome, works in conjunction with four other DNA polymerases. Being the primary holoenzyme involved in replication activity, the DNA Pol III holoenzyme also has proofreading capabilities that corrects replication mistakes by means of exonuclease activity reading 3'→5' and synthesizing 5'→3'. DNA Pol III is a component of the replisome, which is located at the replication fork.

Okazaki fragments are short sequences of DNA nucleotides which are synthesized discontinuously and later linked together by the enzyme DNA to create the lagging strand during DNA replication. They were discovered in the 1960s by the Japanese molecular biologists Reiji and Tsuneko Okazaki, along with the help of some of their colleagues.

The origin of replication is a particular sequence in a genome at which replication is initiated. Propagation of the genetic material between generations requires timely and accurate duplication of DNA by semiconservative replication prior to cell division to ensure each daughter cell receives the full complement of chromosomes. This can either involve the replication of DNA in living organisms such as prokaryotes and eukaryotes, or that of DNA or RNA in viruses, such as double-stranded RNA viruses. Synthesis of daughter strands starts at discrete sites, termed replication origins, and proceeds in a bidirectional manner until all genomic DNA is replicated. Despite the fundamental nature of these events, organisms have evolved surprisingly divergent strategies that control replication onset. Although the specific replication origin organization structure and recognition varies from species to species, some common characteristics are shared.

The nucleoid is an irregularly shaped region within the prokaryotic cell that contains all or most of the genetic material. The chromosome of a prokaryote is circular, and its length is very large compared to the cell dimensions, so it needs to be compacted in order to fit. In contrast to the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, it is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Instead, the nucleoid forms by condensation and functional arrangement with the help of chromosomal architectural proteins and RNA molecules as well as DNA supercoiling. The length of a genome widely varies and a cell may contain multiple copies of it.

DNA polymerase II is a prokaryotic DNA-Dependent DNA polymerase encoded by the PolB gene.

The start codon is the first codon of a messenger RNA (mRNA) transcript translated by a ribosome. The start codon always codes for methionine in eukaryotes and Archaea and a N-formylmethionine (fMet) in bacteria, mitochondria and plastids. The most common start codon is AUG.

Bacteriophage T7 is a bacteriophage, a virus that infects bacteria. It infects most strains of Escherichia coli and relies on these hosts to propagate. Bacteriophage T7 has a lytic life cycle, meaning that it destroys the cell it infects. It also possesses several properties that make it an ideal phage for experimentation: its purification and concentration have produced consistent values in chemical analyses; it can be rendered noninfectious by exposure to UV light; and it can be used in phage display to clone RNA binding proteins.
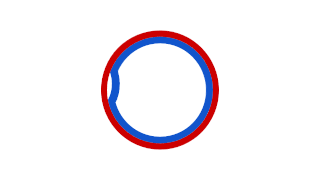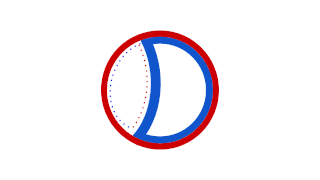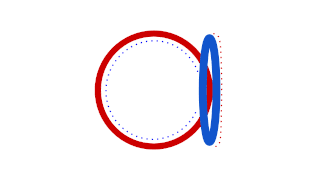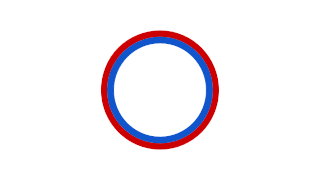
Prokaryotic DNA Replication is the process by which a prokaryote duplicates its DNA into another copy that is passed on to daughter cells. Although it is often studied in the model organism E. coli, other bacteria show many similarities. Replication is bi-directional and originates at a single origin of replication (OriC). It consists of three steps: Initiation, elongation, and termination.
A P1-derived artificial chromosome, or PAC, is a DNA construct derived from the DNA of P1 bacteriophages and Bacterial artificial chromosome. It can carry large amounts of other sequences for a variety of bioengineering purposes in bacteria. It is one type of the efficient cloning vector used to clone DNA fragments in Escherichia coli cells.
The Escherichia coli chromosome shows two main levels of global organization: macrodomains and replichores. Macrodomains were discovered by cytological studies. They contain loci showing the same intracellular positioning and choreography during the cell cycle.
A centisome is a unit of length defined as one percent of the length of a particular chromosome. This course unit of physical DNA length began to be used in the early exploration of genomes through molecular biology before the resolution of the nucleic acid sequences of chromosomes was possible.

Escherichia coli is a Gram-negative gammaproteobacterium commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms (endotherms). The descendants of two isolates, K-12 and B strain, are used routinely in molecular biology as both a tool and a model organism.
Monica Riley was an American scientist who contributed to the discovery of messenger RNA in her Ph.D work with Arthur Pardee, and was later a pioneer in the exploration and computer representation of the Escherichia coli genome.
The bacterial, archaeal and plant plastid code is the DNA code used by bacteria, archaea, prokaryotic viruses and chloroplast proteins. It is essentially the same as the standard code, however there are some variations in alternative start codons.
Julio Collado-Vides is a Guatemalan scientist and Professor of Computational Genomics at the National Autonomous University of Mexico. His research focuses on genomics and bioinformatics.
References
- ↑ Lesterlin C, Mercier R, Boccard F, Barre FX, Cornet F (June 2005). "Roles for replichores and macrodomains in segregation of the Escherichia coli chromosome". EMBO Rep. 6 (6): 557–62. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7400428. PMC 1369093 . PMID 15891766.
- ↑ Blattner FR, Plunkett G, Bloch CA, et al. (September 1997). "The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12". Science. 277 (5331): 1453–62. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5331.1453 . PMID 9278503.
→