Related Research Articles

Seismology is the scientific study of earthquakes and the generation and propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or other planetary bodies. It also includes studies of earthquake environmental effects such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, glacial, fluvial, oceanic microseism, atmospheric, and artificial processes such as explosions and human activities. A related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes is paleoseismology. A recording of Earth motion as a function of time, created by a seismograph is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist works in basic or applied seismology.

Earthquakes are caused by movements within the Earth's crust and uppermost mantle. They range from weak events detectable only by seismometers, to sudden and violent events lasting many minutes which have caused some of the greatest disasters in human history. Below, earthquakes are listed by period, region or country, year, magnitude, cost, fatalities, and number of scientific studies.

The Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology is a Philippine national institution dedicated to provide information on the activities of volcanoes, earthquakes, and tsunamis, as well as other specialized information and services primarily for the protection of life and property and in support of economic, productivity, and sustainable development. It is one of the service agencies of the Department of Science and Technology.
The 2008 Illinois earthquake was one of the largest earthquakes ever recorded in the Midwest state of Illinois. This moderate strike-slip shock measured 5.2 on the moment magnitude scale and had a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII (Very strong). It occurred at 04:36:59 local time on April 18 near Bellmont and Mount Carmel, Illinois, within the Wabash Valley Seismic Zone. Earthquakes in this part of the country are often felt at great distances.
The 1868 Hawaiʻi earthquake was the largest recorded in the history of Hawaiʻi island, with an estimated magnitude of 7.9 Mfa and a maximum Mercalli intensity of X (Extreme). The earthquake occurred at 4 p.m. local time on April 2, 1868 and caused a landslide and tsunami that led to 77 deaths. The aftershock sequence for this event has continued up to the present day.

The Coordinating Committee for Earthquake Prediction (CCEP) in Japan was founded in April 1969, as part of the Geodesy Council's Second Earthquake Prediction Plan, in order to carry out a comprehensive evaluation of earthquake data in Japan. The committee consists of 30 members and meets four times each year, as well as publishing a report on its activities twice each year. The CCEP brings together representatives from 20 governmental bodies and universities engaged in earthquake prediction and research. It has a secretariat within the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism.
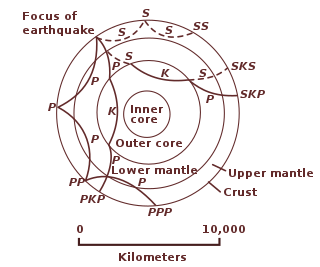
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geophysics:
The 1931 Zangezur earthquake occurred on April 27 at 20:50:45 local time with a moment magnitude of 6.5. The earthquake was located in the Zangezur Mountains near the boundary between southwestern Armenia and Azerbaijan's exclave, the Nakhichivan Autonomous Republic. Both territories were part of the Soviet Union at that time.

Gurban Jalal Yetirmishli — doctor of geological-mineralogical sciences, corr. member of Azerbaijan National Academy of Sciences (ANAS).
General director of Republican Seismic Survey Center of ANAS head of seismology division

Habib Saher, was an Azerbaijani poet, writer, translator and literary researcher. The founder of Turkish free poetry in Iran.
The Advanced National Seismic System (ANSS) is a collaboration of the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) and regional, state, and academic partners that collects and analyzes data on significant earthquakes to provide near real-time information to emergency responders and officials, the news media, and the public. Such information is used to anticipate the likely severity and extent of damage, and to guide decisions on the responses needed.

Aydin Balamirza oghlu Mammadov is an Azerbaijani historian, scientist-demographer, specialist on historical demography, Ph.D. in history, and associate professor of the department of "source study, historiography and methods" of Baku State University. He is one of the 100 Notable alumni of Baku State University.
William L. Ellsworth is an American seismologist who is a research faculty member at Stanford University. His research covers a range of topics of earthquake science focusing on the physics of earthquake nucleation, earthquake hazard assessment, and active fault processes as studied through earthquakes. He is the 2021 recipient of the Harry Fielding Reid medal, the highest honor of the Seismological Society of America.
Hamid Mammadzadeh – Azerbaijani writer, literary critic.
Continuously Operating Caribbean GPS Observational Network (COCONet) was a global positioning system (GPS) observation network that spanned across the Caribbean and the neighboring area It was part of UNAVCO (University Navstar Corporation). UNAVCO and IRIS (Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology) Consortium later merged to create EarthScope Consortium in 2023.
References
- ↑ "Republican Seismic Survey Center of ANAS".
- ↑ "Science.az" (in Azerbaijani).
- ↑ Tahir Mammadli (2010). Azərbaycan ərazisinin zəif seysmikliyi və onun müasir geodinamika ilə əlaqəsi. Baku: Elm nəşriyyatı. p. 7-14.
- ↑ Gurban Yetirmishli (2022-04-10). "Keçmişdən gələcəyə uzanan uğurlu yol" (in Azerbaijani). Republic newspaper. Archived from the original on 2023-05-12. Retrieved 2023-09-01.
- ↑ Tahir Mammadli (2010). Azərbaycan ərazisinin zəif seysmikliyi və onun müasir geodinamika ilə əlaqəsi. Baku: Elm nəşriyyatı. p. 15.
- ↑ "Gurban Yetirmishli".
- ↑ "Republican Seismic Survey Center of ANAS". Archived from the original on 2023-05-12.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ↑ "FDSN: AB: National Seismic Network of Azerbaijan". 2023-02-05. Archived from the original on 2023-02-05. Retrieved 2023-09-01.
- ↑ "Republican Seismic Survey Center".
- ↑ "Members". 2023-08-06. Archived from the original on 2023-08-06. Retrieved 2023-09-01.
- ↑ "ORFEUS Participants". orfeus-eu.org. Archived from the original on 2023-08-02. Retrieved 2023-09-01.
- ↑ "Titular members". 2023-03-28. Archived from the original on 2023-03-28. Retrieved 2023-09-01.
- 1 2 Seismology.Az. "Beynəlxalq əlaqələr". Seismology.Az (in Azerbaijani). Retrieved 2023-09-01.
- ↑ Seismology.Az (2023-07-17). "AFAD Department of Earthquakes and RSSC signed a protocol of agreement". Seismology.Az (in Azerbaijani). Retrieved 2023-09-01.
- ↑ "AFAD Heyeti Azerbaycan'a Çalışma Ziyareti Gerçekleştirdi". 2022-01-25. Archived from the original on 2022-01-25. Retrieved 2023-09-01.