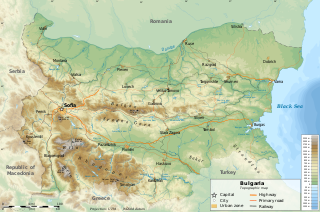
Bulgaria is a country situated in Southeast Europe and occupies the eastern quarter of the Balkan peninsula, being the largest country within its geographic boundaries. It is bordering Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. The northern border with Romania follows the river Danube until the city of Silistra. The land area of Bulgaria is 110,994 square kilometres (42,855 sq mi), slightly larger than that of Iceland or the U.S. state of Tennessee. Considering its relatively small size, Bulgaria has a great variety of topographical features. Even within small parts of the country, the land may be divided into plains, plateaus, hills, mountains, basins, gorges, and deep river valleys. The geographic center of Bulgaria is located in Uzana.

North Macedonia is a country situated in southeastern Europe with geographic coordinates 41°50′N22°00′E, bordering Kosovo and Serbia to the north, Bulgaria to the east, Greece to the south and Albania to the west. The country is part of the wider region of Macedonia and makes up most of Vardar Macedonia. The country is a major transportation corridor from Western and Central Europe to Southern Europe and the Aegean Sea. North Macedonia is a landlocked country but has three major natural lakes: Lake Ohrid, Lake Prespa and Lake Dojran. It has a water area of 857 km2, while its land area is 24,856 km2.

The Vardar or Axios is the longest river in North Macedonia and the second longest river in Greece, in which it reaches the Aegean Sea at Thessaloniki. It is 388 km (241 mi) long, out of which 76 km are in Greece, and drains an area of around 25,000 km2 (9,653 sq mi). The maximum depth of the river is 4 m (13 ft).

The Rhodopes are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, with over 83% of its area in southern Bulgaria and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak at 2,191 meters (7,188 ft). The mountain range gives its name to the terrestrial ecoregion Rodope montane mixed forests that belongs in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome and the Palearctic realm. The region is particularly notable for its karst areas with their deep river gorges, large caves and specific sculptured forms, such as the Trigrad Gorge.

Serbia is a sovereign state situated at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the far southern edges of the Pannonian Plain and the central Balkans. It shares borders with Bosnia-Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Hungary, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Romania and Albania through the disputed territory of Kosovo. Serbia is landlocked, though it is able to access the Adriatic Sea through Montenegro and inland Europe and the Black Sea via the Danube.

Rhodope is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of East Macedonia and Thrace. Its name is derived from the Rhodope Mountains, which cover the northern part of its territory. Together with the regional units Evros and Xanthi, it forms the geographical region of Western Thrace. The capital of the prefecture is the city of Komotini. The second largest town is Sapes. Most of the Muslims of Thrace, the only officially recognized minority in Greece, are settled in this area, where they form around half of the population.

The Alpine orogeny or Alpide orogeny is an orogenic phase in the Late Mesozoic (Eoalpine) and the current Cenozoic that has formed the mountain ranges of the Alpide belt. These mountains include the Atlas, the Rif, the Baetic Cordillera, the Cantabrian Mountains, the Pyrenees, the Alps, the Apennine Mountains, the Dinaric Alps, the Pindus (Hellenides), the Carpathians, the Balkanides, the Pontic Mountains, the Taurus, the Armenian Highlands, the Caucasus, the Alborz, the Zagros, the Hindu Kush, the Pamir, the Karakoram, and the Himalayas. Sometimes other names occur to describe the formation of separate mountain ranges: for example Carpathian orogeny for the Carpathians, Hellenic orogeny for the Pindus, Altai orogeny for Altai Mountains or the Himalayan orogeny for the Himalayas.

Western Thrace or West Thrace is a geographic and historical region of Greece, between the Nestos and Evros rivers in the northeast of the country; East Thrace, which lies east of the river Evros, forms the European part of Turkey, and the area to the north, in Bulgaria, is known as Northern Thrace.

Mountain formation refers to the geological processes that underlie the formation of mountains. These processes are associated with large-scale movements of the Earth's crust. Folding, faulting, volcanic activity, igneous intrusion and metamorphism can all be parts of the orogenic process of mountain building. The formation of mountains is not necessarily related to the geological structures found on it.

Europe is traditionally defined as one of seven continents. Physiographically, it is the northwestern peninsula of the larger landmass known as Eurasia ; Asia occupies the eastern bulk of this continuous landmass and all share a common continental shelf. Europe's eastern frontier is delineated by the Ural Mountains in Russia. The southeast boundary with Asia is not universally defined, but the modern definition is generally the Ural River or, less commonly, the Emba River. The boundary continues to the Caspian Sea, the crest of the Caucasus Mountains, and on to the Black Sea. The Bosporus, the Sea of Marmara, and the Dardanelles conclude the Asian boundary. The Mediterranean Sea to the south separates Europe from Africa. The western boundary is the Atlantic Ocean. Iceland, though on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and nearer to Greenland than Mainland Europe, is generally included in Europe for cultural reasons and because it is over twice as close to mainland Europe as mainland North America. There is ongoing debate on where the geographical centre of Europe falls.

The Nišava or Nishava is a river in Bulgaria and Serbia, a right tributary, and with a length of 218 km also the longest one, of the South Morava.

The South Morava is a river in eastern Kosovo and in southern Serbia, which represents the shorter headwater of Great Morava. Today, it is 295 km long, including its source river Binačka Morava. It flows generally in the south to north direction, from the Macedonian border to Kosovo and onwards to Central Serbia, where it meets West Morava at Stalać, to create Great Morava.

The Pčinja is a 135 km long river in Serbia and North Macedonia, a left tributary of the Vardar river.

The Morava Valley, is a general term which in its widest sense marks valleys of any of three Morava rivers in Serbia: the West Morava, the South Morava and the Great Morava. In the narrow sense, the term is applied only to the Great Morava Valley. The Serbian term follows the general manner of coining river valley names in Serbian using the prefix po- and suffix -je, meaning literally "(land) along the Morava". Morava valley lies in the central Balkans, at the crossroads which lead eastwards, towards the Black sea and Asia Minor, and further south, down the Vardar river into the Aegean sea.
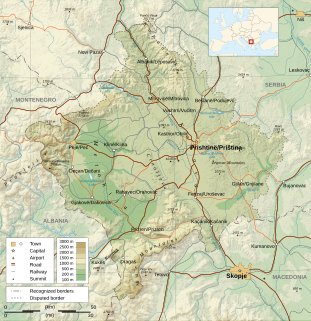
Kosovo is a small and landlocked disputed territory in Southeastern Europe. The country is strategically positioned in the center of the Balkan Peninsula enclosed by Montenegro to the west, Serbia to the north and east, North Macedonia to the southeast, and Albania to the southwest. It has no direct access to the Mediterranean Sea but its rivers flow into three seas, the Adriatic, Aegean and Black Sea.

The Upper Blateštičko Lake is a small lake in the south of Kosovo. The lake is found on an altitude of 2,220 m (7,283 ft) above sea level in the high Šar Mountains. The lake is found near the peak of Crni Kamen rising up to 2,536 m (8,320 ft). It is located 200m from the Lower Blateštičko Lake.

Greece is a country of the Balkans, in Southeastern Europe, bordered to the north by Albania, North Macedonia and Bulgaria; to the east by Turkey, and is surrounded to the east by the Aegean Sea, to the south by the Cretan and the Libyan Seas, and to the west by the Ionian Sea which separates Greece from Italy.

Jastrebac is a mountain in central Serbia, between cities of Niš, Kruševac and Prokuplje. It consists of two massifs, Great (Veliki) and Small (Mali) Jastrebac. Its highest peak Velika Đulica has an elevation of 1,491 meters above sea level. It is well-forested and presents a popular hiking and mountaineering destination.

The regional geology of Serbia describes the geologic structure and history inside the borders of Serbia.
The geology of Bulgaria consists of two major structural features. The Rhodope Massif in southern Bulgaria is made up of Archean, Proterozoic and Cambrian rocks and is a sub-province of the Thracian-Anatolian polymetallic province. It has dropped down, faulted basins filled with Cenozoic sediments and volcanic rocks. The Moesian Platform to the north extends into Romania and has Paleozoic rocks covered by rocks from the Mesozoic, typically buried by thick Danube River valley Quaternary sediments. In places, the Moesian Platform has small oil and gas fields. Bulgaria is a country in southeastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east.



















