Related Research Articles

Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body.
Radiology is the medical specialty that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography, but today it includes all imaging modalities, including those that use no ionizing electromagnetic radiation, as well as others that do, such as computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET). Interventional radiology is the performance of usually minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above.

Nuclear medicine or nucleology is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging, in a sense, is "radiology done inside out" because it records radiation emitted from within the body rather than radiation that is transmitted through the body from external sources like X-ray generators. In addition, nuclear medicine scans differ from radiology, as the emphasis is not on imaging anatomy, but on the function. For such reason, it is called a physiological imaging modality. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans are the two most common imaging modalities in nuclear medicine.

A bone scan or bone scintigraphy is a nuclear medicine imaging technique of the bone. It can help diagnose a number of bone conditions, including cancer of the bone or metastasis, location of bone inflammation and fractures, and bone infection (osteomyelitis).
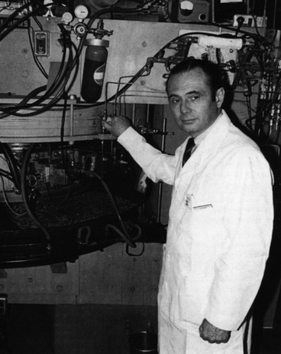
Michel Matthew Ter-Pogossian was an American medical physicist. He was professor of radiology at the Washington University School of Medicine for over 30 years. A pioneer in nuclear medicine, he is best known for his research on the positron emission tomography (PET). He is considered one of its creators and often referred to as the "father of PET."
Abass Alavi is an Iranian-American physician-scientist specializing in the field of molecular imaging, most notably in the imaging modality of positron emission tomography (PET). In August 1976, he was part of the team that performed the first human PET studies of the brain and whole body using the radiotracer [18F]Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG). Alavi holds the position of Professor of Radiology and Neurology, as well as Director of Research Education in the Department of Radiology at the University of Pennsylvania. Over a career spanning five decades, he has amassed over 2,300 publications and 60,000 citations, earning an h-index of 125 and placing his publication record in the top percentile of scientists.
Nuclear medicine physicians, also called nuclear radiologists or simply nucleologists, are medical specialists that use tracers, usually radiopharmaceuticals, for diagnosis and therapy. Nuclear medicine procedures are the major clinical applications of molecular imaging and molecular therapy. In the United States, nuclear medicine physicians are certified by the American Board of Nuclear Medicine and the American Osteopathic Board of Nuclear Medicine.

David Edmund Kuhl was an American scientist specializing in nuclear medicine. He was well known for his pioneering work in positron emission tomography. Dr. Kuhl served as the Chief of the Division of Nuclear Medicine at the University of Michigan for 20 years and retired in June 2011.

Albert Gjedde: is a Danish-Canadian neuroscientist. He is Professor of Neurobiology and Pharmacology at the Faculty of Health Sciences and Center of Neuroscience at the University of Copenhagen. He is currently also Adjunct Professor of Neurology and Neurosurgery in the Department of Neurology, Montreal Neurological Institute, McGill University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, Adjunct Professor of Radiology and Radiological Science in the Division of Nuclear Medicine, Department of Radiology and Radiological Science, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, US, Adjunct Professor of Translational Neuropsychiatry Research, University of Southern Denmark, Odense, Denmark, and adjunct professor of psychiatry at Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, East Azerbadjan, Iran.

Zang-Hee Cho is a Korean neuroscientist who developed the first Ring-PET scanner and the scintillation detector BGO. More recently, Cho developed the first PET-MRI fusion molecular imaging device for neuro-molecular imaging.
The Alvin J. Siteman Cancer Center at Barnes-Jewish Hospital and Washington University School of Medicine is a cancer treatment, research and education institution with six locations in the St. Louis area. Siteman is the only cancer center in Missouri and within 240 miles of St. Louis to be designated a Comprehensive Cancer Center by the National Cancer Institute (NCI). Siteman is also the only area member of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, a nonprofit alliance of 32 cancer centers dedicated to improving the quality and effectiveness of cancer care.

Ronald J. Ross is a Cleveland, Ohio radiologist known for research on brain injury in professional and amateur boxers and for the first clinical use of nuclear magnetic resonance imaging on human patients. Ross is also credited with the first use of head and whole body computed tomography imaging (CT) in a private clinical setting in the United States.
Henry N. Wagner (1927–2012), a former professor at Johns Hopkins University, is one of the pioneering researchers in nuclear medicine.

Frank Michael Bengel is a German professor and nuclear medicine physician. He is the current director of the Department of Nuclear Medicine at the Hannover Medical School.
Samuel Achilefu is a Nigerian-born scientist and medical researcher who has pioneered both fundamental and applied research in science, engineering, and medicine. Dr. Samuel Achilefu is Professor and Chair of the Department of Biomedical Engineering at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, where he holds the Lyda Hill Distinguished University Chair in Biomedical Engineering. He is also Professor of Radiology and a member of the Simmons Comprehensive Cancer Center. Before joining UT Southwestern, he was the Michel M. Ter-Pogossian Professor of Radiology and Vice Chair for Innovation and Entrepreneurship at the Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington University School of Medicine. He held joint appointments as a professor of medicine, biochemistry and molecular biophysics, and biomedical engineering. He also served as the Director of the Washington University Molecular Imaging Center and the privately funded Theranostic Innovation Program and was co-director of the Center for Multiple Myeloma Nanotherapy and co-Leader of the Oncologic Imaging Program of the Alvin J. Siteman Cancer Center at Washington University.
The Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology (MIR), established 1931, is an academic radiology center associated with the Washington University School of Medicine, located within the Washington University Medical Center in St. Louis, Missouri. In addition to providing diagnostic and therapeutic patient-care services, the institute is a top research and education center. It employs over 140 academic staff and is among the top recipients of National Institutes of Health funding of radiology departments. The center provides radiology services to Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children's hospitals, as well as multiple other hospitals and outpatient centers in the St. Louis area. The center performs 700,000 examinations and procedures annually.
Elliot K. Fishman is an American diagnostic radiologist, currently the director of diagnostic imaging and body CT and professor of radiology and radiological science at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
Jason S. Lewis is a British radiochemist whose work relates to oncologic therapy and diagnosis. His research focus is a molecular imaging-based program focused on radiopharmaceutical development as well as the study of multimodality small- and biomolecule-based agents and their clinical translation. He has worked on the development of small molecules as well as radiolabeled peptides and antibodies probing the overexpression of receptors and antigens on tumors.
Christine O. "Cooky" Menias is an American radiologist, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine and Science professor, and editor designate of RadioGraphics, one of the leading educational journals in radiology.
Pamela K. Woodard is an American radiologist specializing in cardiovascular imaging. She is the Elizabeth E. Mallinckrodt Professor of Radiology and the Director the Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology at Washington University in Saint Louis. She also holds appointments as a professor of Internal Medicine, Pediatrics, and Biomedical Engineering at the Washington University in St. Louis. She was elected a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in 2022.
References
- ↑ Applied Radiology. Anderson Pub. 2007.
- ↑ University of Michigan. Office of the Vice President for Research (1994). Research Report to the Board of Regents. The Office.
- ↑ The Michigan Alumnus. UM Libraries. 1994. pp. 5–. UOM:39015071120342.
- ↑ Henry N. Wagner (December 23, 2007). A Personal History of Nuclear Medicine. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 139–. ISBN 978-1-84628-072-6.
- ↑ Hopkins Radiologist Richard Wahl Appointed to New Professorship in Nuclear Medicine.