Related Research Articles
An automatic number announcement circuit (ANAC) is a component of a central office of a telephone company that provides a service to installation and service technicians to determine the telephone number of a telephone line. The facility has a telephone number that may be called to listen to an automatic announcement that includes the caller's telephone number. The ANAC facility is useful primarily during the installation of landline telephones to quickly identify one of multiple wire pairs in a bundle or at a termination point.

A telephone switchboard was a device used to connect circuits of telephones to establish telephone calls between users or other switchboards, throughout the 20th century. The switchboard was an essential component of a manual telephone exchange, and was operated by switchboard operators who used electrical cords or switches to establish the connections.
Phreaking is a slang term coined to describe the activity of a culture of people who study, experiment with, or explore telecommunication systems, such as equipment and systems connected to public telephone networks. The term phreak is a sensational spelling of the word freak with the ph- from phone, and may also refer to the use of various audio frequencies to manipulate a phone system. Phreak, phreaker, or phone phreak are names used for and by individuals who participate in phreaking.
A dial tone is a telephony signal sent by a telephone exchange or private branch exchange (PBX) to a terminating device, such as a telephone, when an off-hook condition is detected. It indicates that the exchange is working and is ready to initiate a telephone call. The tone stops when the first dialed digit is recognized. If no digits are forthcoming, the partial dial procedure is invoked, often eliciting a special information tone and an intercept message, followed by the off-hook tone, requiring the caller to hang up and redial.
Caller identification is a telephone service, available in analog and digital telephone systems, including voice over IP (VoIP), that transmits a caller's telephone number to the called party's telephone equipment when the call is being set up. The caller ID service may include the transmission of a name associated with the calling telephone number, in a service called Calling Name Presentation (CNAM). The service was first defined in 1993 in International Telecommunication Union—Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) Recommendation Q.731.3.

A blue box is an electronic device that produces tones used to generate the in-band signaling tones formerly used within the North American long-distance telephone network to send line status and called number information over voice circuits. This allowed the user, referred to as a "phreaker", to surreptitiously place long-distance calls that would be billed to another number or dismissed entirely as an incomplete call. A number of similar "color boxes" were also created to control other aspects of the phone network.
Wardialing is a technique to automatically scan a list of telephone numbers, usually dialing every number in a local area code to search for modems, computers, bulletin board systems and fax machines. Hackers use the resulting lists for various purposes: hobbyists for exploration, and crackers—malicious hackers who specialize in breaching computer security—for guessing user accounts, or locating modems that might provide an entry-point into computer or other electronic systems. It may also be used by security personnel, for example, to detect unauthorized devices, such as modems or faxes, on a company's telephone network.

A ringtone, ring tone or ring is the sound made by a telephone to indicate an incoming call. Originally referring to and made by the electromechanical striking of bells, the term now refers to any sound on any device alerting of a new incoming call—up to and including recordings of original telephone bells.

An answering machine, answerphone or message machine, also known as telephone messaging machine in the UK and some Commonwealth countries, ansaphone or ansafone, or telephone answering device (TAD), was used for answering telephones and recording callers' messages. If a phone rings a number of times predetermined by the phone's owner, and nobody is present to answer the incoming call, the answering machine will activate and play either a generic announcement or the voice of the person being called announcing that nobody is able to come to the phone at the moment. Following the announcement is a beeping tone which prompts the caller to record a message after the tone concludes.

A telephone call is a connection over a telephone network between the called party and the calling party.
Call waiting is a telephone service where a subscriber can accept a second incoming telephone call by placing an in-progress call on hold—and may also switch between calls. With some providers it can be combined with additional features such as conferencing, call forwarding, and caller ID. Call waiting is intended to alleviate the need to have more than one telephone line or number for voice communications.
In telecommunications, a callback or call-back occurs when the originator of a call is immediately called back in a second call as a response.
Phone fraud, or more generally communications fraud, is the use of telecommunications products or services with the intention of illegally acquiring money from, or failing to pay, a telecommunication company or its customers.

The New Zealand telephone numbering plan describes the allocation of telephone numbers in New Zealand and the Pitcairn Islands.
1-5-7-1 is the name of a family of calling features in the United Kingdom, for residential and business telephone lines and for mobile telephones, that are provided by BT Group and several other telephone service providers. The family is named after the telephone number 1571, the special service number that is used to access it. Call Minder is the name of BT's highest level of 1571 service.
Ringing is a telecommunication signal that causes a bell or other device to alert a telephone subscriber to an incoming telephone call. Historically, this entailed sending a high-voltage alternating current over the telephone line to a customer station which contained an electromagnetic bell. It is therefore also commonly referred to as power ringing, to distinguish it from another signal, audible ringing, or ringing tone, which is sent to the originating caller to indicate that the destination telephone is in fact ringing.
Telephone number verification services are online services used to establish whether a given telephone number is in service. They may include a form of Turing test to further determine if a human answers or answering equipment such as a modem, fax, voice mMail or answering machine.
An automatic dialer is an electronic device or software that automatically dials telephone numbers. Once the call has been answered, the autodialer either plays a recorded message or connects the call to a live person.
In landline telephony, a plant test number or exchange is a number or group of numbers reserved for use by telephone installers or other workers to perform routine tests on an individual telephone line. Most are unlisted numbers.
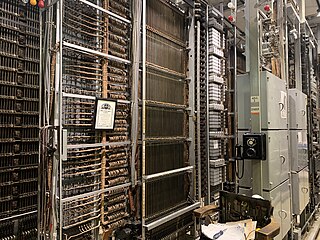
The Panel Machine Switching System is a type of automatic telephone exchange for urban service that was used in the Bell System in the United States for seven decades. The first semi-mechanical types of this design were installed in 1915 in Newark, New Jersey, and the last were retired in the same city in 1983.
References
- ↑ Petersen, Julie (2002). The telecommunications illustrated dictionary. Petersen, Julie K. (2nd ed.). Boca Raton, Fla.: CRC Press. p. 804. ISBN 084931173X. OCLC 51169186.
- 1 2 50 FR 29391 Federal Register,50 (139), (19 July 1985). Seen 03 February 2021.