
Ada is a structured, statically typed, imperative, and object-oriented high-level programming language, inspired by Pascal and other languages. It has built-in language support for design by contract (DbC), extremely strong typing, explicit concurrency, tasks, synchronous message passing, protected objects, and non-determinism. Ada improves code safety and maintainability by using the compiler to find errors in favor of runtime errors. Ada is an international technical standard, jointly defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). As of May 2023, the standard, called Ada 2022 informally, is ISO/IEC 8652:2023.
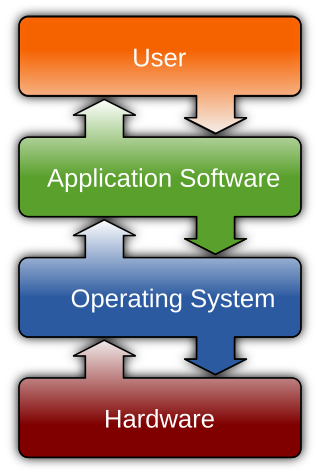
Software is a collection of programs and data that tell a computer how to perform specific tasks. Software often includes associated software documentation. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.

The GNU Manifesto is a call-to-action by Richard Stallman encouraging participation and support of the GNU Project's goal in developing the GNU free computer operating system. The GNU Manifesto was published in March 1985 in Dr. Dobb's Journal of Software Tools. It is held in high regard within the free software movement as a fundamental philosophical source.

A computer programmer, sometimes referred to as a software developer, a software engineer, a programmer or a coder, is a person who creates computer programs.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to software engineering:

Edward Nash Yourdon was an American software engineer, computer consultant, author and lecturer, and software engineering methodology pioneer. He was one of the lead developers of the structured analysis techniques of the 1970s and a co-developer of both the Yourdon/Whitehead method for object-oriented analysis/design in the late 1980s and the Coad/Yourdon methodology for object-oriented analysis/design in the 1990s.

In software engineering, coupling is the degree of interdependence between software modules; a measure of how closely connected two routines or modules are; the strength of the relationships between modules.
Tom DeMarco is an American software engineer, author, and consultant on software engineering topics. He was an early developer of structured analysis in the 1970s.
Software craftsmanship is an approach to software development that emphasizes the coding skills of the software developers. It is a response by software developers to the perceived ills of the mainstream software industry, including the prioritization of financial concerns over developer accountability.
Cutter Business Technology Journal (CBTJ) (formerly American Programmer) is an independent magazine for programmers and software technologists.

Decline and Fall of the American Programmer is a book written by Edward Yourdon in 1992. It was addressed to American programmers and software organizations of the 1990s, warning that they were about to be driven out of business by programmers in other countries who could produce software more cheaply and with higher quality. Yourdon claimed that American software organizations could only retain their edge by using technologies such as ones he described in the book. Yourdon gave examples of how non-American—specifically Indian and Japanese—companies were making use of these technologies to produce high-quality software.

Larry LeRoy Constantine is an American software engineer, professor in the Center for Exact Sciences and Engineering at the University of Madeira Portugal, and considered one of the pioneers of computing. He has contributed numerous concepts and techniques forming the foundations of modern practice in software engineering and applications design and development.

In software engineering, structured analysis (SA) and structured design (SD) are methods for analyzing business requirements and developing specifications for converting practices into computer programs, hardware configurations, and related manual procedures.
Wolfenstein is a series of World War II video games originally developed by Muse Software. The majority of the games follow William "B.J." Blazkowicz, an American Army captain, and his fight against the Axis powers. Earlier titles are centered around Nazis attempting to harness supernatural and occult forces, while later games are set in an alternate history in which Axis powers won World War II.
Dr. David Gelperin chaired the working groups developing the IEEE 829-1989 software testing documentation standard. With Jerry E. Durant he went on to develop the High Impact Inspection Technology that builds upon traditional inspections but utilizes a test driven additive.

Chrono Resurrection, also known as Chrono Trigger: Resurrection, is an unreleased fangame developed by North American team Resurrection Games under Nathan Lazur's direction. It is based on the critically acclaimed Super NES role-playing game Chrono Trigger by the Japanese company Square. The project was initially called CT64 and was meant to be a complete remake of the original game for the Nintendo 64, with both 2D and 3D playing modes.

A structure chart (SC) in software engineering and organizational theory is a chart which shows the breakdown of a system to its lowest manageable levels. They are used in structured programming to arrange program modules into a tree. Each module is represented by a box, which contains the module's name. The tree structure visualizes the relationships between modules.

Timothée Besset is a French software programmer, best known for supporting Linux, as well as some Macintosh, ports of id Software's products. He was involved with the game ports of various id properties through the 2000s, starting with Quake III Arena. Since the development of Doom 3 he was also in charge of the multiplayer network code and various aspects of game coding for id, a role which had him heavily involved in the development of their online game QuakeLive. Since departing id in January 2012 he has worked as a software contractor, including for Valve Software.
Open ModelSphere was a data, process and UML modeling tool written in Java and distributed as free software under the GPL License. It provided support for forward and reverse engineering between UML and relational schemas.

Software is a set of programmed instructions stored in the memory of stored-program digital computers for execution by the processor. Software is a recent development in human history and is fundamental to the Information Age.













