Financial economics is the branch of economics characterized by a "concentration on monetary activities", in which "money of one type or another is likely to appear on both sides of a trade". Its concern is thus the interrelation of financial variables, such as share prices, interest rates and exchange rates, as opposed to those concerning the real economy. It has two main areas of focus: asset pricing and corporate finance; the first being the perspective of providers of capital, i.e. investors, and the second of users of capital. It thus provides the theoretical underpinning for much of finance.
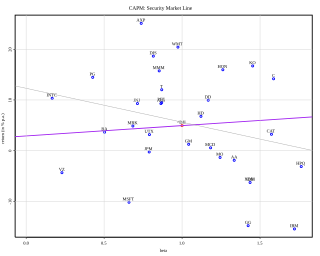
In finance, the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) is a model used to determine a theoretically appropriate required rate of return of an asset, to make decisions about adding assets to a well-diversified portfolio.

In economics and finance, risk aversion is the tendency of people to prefer outcomes with low uncertainty to those outcomes with high uncertainty, even if the average outcome of the latter is equal to or higher in monetary value than the more certain outcome.
In mathematical finance, a risk-neutral measure is a probability measure such that each share price is exactly equal to the discounted expectation of the share price under this measure. This is heavily used in the pricing of financial derivatives due to the fundamental theorem of asset pricing, which implies that in a complete market, a derivative's price is the discounted expected value of the future payoff under the unique risk-neutral measure. Such a measure exists if and only if the market is arbitrage-free.

A risk premium is a measure of excess return that is required by an individual to compensate being subjected to an increased level of risk. It is used widely in finance and economics, the general definition being the expected risky return less the risk-free return, as demonstrated by the formula below.
Modern portfolio theory (MPT), or mean-variance analysis, is a mathematical framework for assembling a portfolio of assets such that the expected return is maximized for a given level of risk. It is a formalization and extension of diversification in investing, the idea that owning different kinds of financial assets is less risky than owning only one type. Its key insight is that an asset's risk and return should not be assessed by itself, but by how it contributes to a portfolio's overall risk and return. The variance of return is used as a measure of risk, because it is tractable when assets are combined into portfolios. Often, the historical variance and covariance of returns is used as a proxy for the forward-looking versions of these quantities, but other, more sophisticated methods are available.
The expected utility hypothesis is a foundational assumption in mathematical economics concerning decision making under uncertainty. It postulates that rational agents maximize utility, meaning the subjective desirability of their actions. Rational choice theory, a cornerstone of microeconomics, builds this postulate to model aggregate social behaviour.
In finance, arbitrage pricing theory (APT) is a multi-factor model for asset pricing which relates various macro-economic (systematic) risk variables to the pricing of financial assets. Proposed by economist Stephen Ross in 1976, it is widely believed to be an improved alternative to its predecessor, the capital asset pricing model (CAPM). APT is founded upon the law of one price, which suggests that within an equilibrium market, rational investors will implement arbitrage such that the equilibrium price is eventually realised. As such, APT argues that when opportunities for arbitrage are exhausted in a given period, then the expected return of an asset is a linear function of various factors or theoretical market indices, where sensitivities of each factor is represented by a factor-specific beta coefficient or factor loading. Consequently, it provides traders with an indication of ‘true’ asset value and enables exploitation of market discrepancies via arbitrage. The linear factor model structure of the APT is used as the basis for evaluating asset allocation, the performance of managed funds as well as the calculation of cost of capital. Furthermore, the newer APT model is more dynamic being utilised in more theoretical application than the preceding CAPM model. A 1986 article written by Gregory Connor and Robert Korajczyk, utilised the APT framework and applied it to portfolio performance measurement suggesting that the Jensen coefficient is an acceptable measurement of portfolio performance.
Investment management is the professional asset management of various securities, including shareholdings, bonds, and other assets, such as real estate, to meet specified investment goals for the benefit of investors. Investors may be institutions, such as insurance companies, pension funds, corporations, charities, educational establishments, or private investors, either directly via investment contracts/mandates or via collective investment schemes like mutual funds, exchange-traded funds, or REITs.
In accounting, finance, and economics, a risk-seeker or risk-lover is a person who has a preference for risk.

In economics and finance, exponential utility is a specific form of the utility function, used in some contexts because of its convenience when risk is present, in which case expected utility is maximized. Formally, exponential utility is given by:
Goals-Based Investing or Goal-Driven Investing is the use of financial markets to fund goals within a specified period of time. Traditional portfolio construction balances expected portfolio variance with return and uses a risk aversion metric to select the optimal mix of investments. By contrast, GBI optimizes an investment mix to minimize the probability of failing to achieve a minimum wealth level within a set period of time.
Portfolio optimization is the process of selecting an optimal portfolio, out of a set of considered portfolios, according to some objective. The objective typically maximizes factors such as expected return, and minimizes costs like financial risk, resulting in a multi-objective optimization problem. Factors being considered may range from tangible to intangible.
In decision theory, economics, and finance, a two-moment decision model is a model that describes or prescribes the process of making decisions in a context in which the decision-maker is faced with random variables whose realizations cannot be known in advance, and in which choices are made based on knowledge of two moments of those random variables. The two moments are almost always the mean—that is, the expected value, which is the first moment about zero—and the variance, which is the second moment about the mean.
In finance, economics, and decision theory, hyperbolic absolute risk aversion (HARA) refers to a type of risk aversion that is particularly convenient to model mathematically and to obtain empirical predictions from. It refers specifically to a property of von Neumann–Morgenstern utility functions, which are typically functions of final wealth, and which describe a decision-maker's degree of satisfaction with the outcome for wealth. The final outcome for wealth is affected both by random variables and by decisions. Decision-makers are assumed to make their decisions so as to maximize the expected value of the utility function.
In finance, marginal conditional stochastic dominance is a condition under which a portfolio can be improved in the eyes of all risk-averse investors by incrementally moving funds out of one asset and into another. Each risk-averse investor is assumed to maximize the expected value of an increasing, concave von Neumann-Morgenstern utility function. All such investors prefer portfolio B over portfolio A if the portfolio return of B is second-order stochastically dominant over that of A; roughly speaking this means that the density function of A's return can be formed from that of B's return by pushing some of the probability mass of B's return to the left and then spreading out some of the density mass.
Intertemporal portfolio choice is the process of allocating one's investable wealth to various assets, especially financial assets, repeatedly over time, in such a way as to optimize some criterion. The set of asset proportions at any time defines a portfolio. Since the returns on almost all assets are not fully predictable, the criterion has to take financial risk into account. Typically the criterion is the expected value of some concave function of the value of the portfolio after a certain number of time periods—that is, the expected utility of final wealth. Alternatively, it may be a function of the various levels of goods and services consumption that are attained by withdrawing some funds from the portfolio after each time period.
Risk aversion is a preference for a sure outcome over a gamble with higher or equal expected value. Conversely, rejection of a sure thing in favor of a gamble of lower or equal expected value is known as risk-seeking behavior.
Philippe J.S. De Brouwer is a European investment and banking professional as well as academician in finance and investing. As a scientist he is mostly known for his solution to the Fallacy of Large Numbers and his formulation of the Maslowian Portfolio Theory in the field of investment advice.
In finance, the Markowitz model ─ put forward by Harry Markowitz in 1952 ─ is a portfolio optimization model; it assists in the selection of the most efficient portfolio by analyzing various possible portfolios of the given securities. Here, by choosing securities that do not 'move' exactly together, the HM model shows investors how to reduce their risk. The HM model is also called mean-variance model due to the fact that it is based on expected returns (mean) and the standard deviation (variance) of the various portfolios. It is foundational to Modern portfolio theory.



