
Sanibel is an island and city in Lee County, Florida, United States. The population was 6,382 at the 2020 census, down from 6,469 at the 2010 census. It is part of the Cape Coral-Fort Myers, Florida Metropolitan Statistical Area. The island, also known as Sanibel Island, constitutes the entire city. It is a barrier island—a collection of sand on the leeward side of the more solid coral-rock of Pine Island.

Within the atmospheric sciences, atmospheric physics is the application of physics to the study of the atmosphere. Atmospheric physicists attempt to model Earth's atmosphere and the atmospheres of the other planets using fluid flow equations, radiation budget, and energy transfer processes in the atmosphere. In order to model weather systems, atmospheric physicists employ elements of scattering theory, wave propagation models, cloud physics, statistical mechanics and spatial statistics which are highly mathematical and related to physics. It has close links to meteorology and climatology and also covers the design and construction of instruments for studying the atmosphere and the interpretation of the data they provide, including remote sensing instruments. At the dawn of the space age and the introduction of sounding rockets, aeronomy became a subdiscipline concerning the upper layers of the atmosphere, where dissociation and ionization are important.

A data logger is an electronic device that records data over time or about location either with a built-in instrument or sensor or via external instruments and sensors. Increasingly, but not entirely, they are based on a digital processor, and called digital data loggers (DDL). They generally are small, battery-powered, portable, and equipped with a microprocessor, internal memory for data storage, and sensors. Some data loggers interface with a personal computer and use software to activate the data logger and view and analyze the collected data, while others have a local interface device and can be used as a stand-alone device.

Argo is an international programme for researching the ocean. It uses profiling floats to observe temperature, salinity and currents. Recently it has observed bio-optical properties in the Earth's oceans. It has been operating since the early 2000s. The real-time data it provides support climate and oceanographic research. A special research interest is to quantify the ocean heat content (OHC). The Argo fleet consists of almost 4000 drifting "Argo floats" deployed worldwide. Each float weighs 20–30 kg. In most cases probes drift at a depth of 1000 metres. Experts call this the parking depth. Every 10 days, by changing their buoyancy, they dive to a depth of 2000 metres and then move to the sea-surface. As they move they measure conductivity and temperature profiles as well as pressure. Scientists calculate salinity and density from these measurements. Seawater density is important in determining large-scale motions in the ocean.

An underwater glider is a type of autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) that employs variable-buoyancy propulsion instead of traditional propellers or thrusters. It employs variable buoyancy in a similar way to a profiling float, but unlike a float, which can move only up and down, an underwater glider is fitted with hydrofoils that allow it to glide forward while descending through the water. At a certain depth, the glider switches to positive buoyancy to climb back up and forward, and the cycle is then repeated.

A refractometer is a laboratory or field device for the measurement of an index of refraction (refractometry). The index of refraction is calculated from the observed refraction angle using Snell's law. For mixtures, the index of refraction then allows the concentration to be determined using mixing rules such as the Gladstone–Dale relation and Lorentz–Lorenz equation.

A fluorometer, fluorimeter or fluormeter is a device used to measure parameters of visible spectrum fluorescence: its intensity and wavelength distribution of emission spectrum after excitation by a certain spectrum of light. These parameters are used to identify the presence and the amount of specific molecules in a medium. Modern fluorometers are capable of detecting fluorescent molecule concentrations as low as 1 part per trillion.

The Ocean Observatories Initiative (OOI) is a National Science Foundation (NSF) Major Research Facility composed of a network of science-driven ocean observing platforms and sensors in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. This networked infrastructure measures physical, chemical, geological, and biological variables from the seafloor to the sea surface and overlying atmosphere, providing an integrated data collection system on coastal, regional and global scales. OOI's goal is to deliver data and data products for a 25-year-plus time period, enabling a better understanding of ocean environments and critical ocean issues.
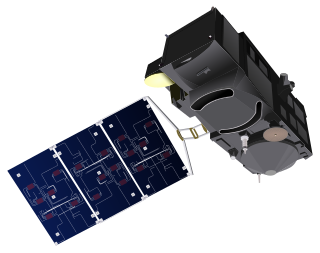
Sentinel-3 is an Earth observation heavy satellite series developed by the European Space Agency as part of the Copernicus Programme. As of 2024, it consists of 2 satellites: Sentinel-3A and Sentinel-3B. After initial commissioning, each satellite was handed over to EUMETSAT for the routine operations phase of the mission. Two recurrent satellites, Sentinel-3C and Sentinel-3D, will follow in approximately 2025 and 2028 respectively to ensure continuity of the Sentinel-3 mission.
The following are considered ocean essential climate variables (ECVs) by the Ocean Observations Panel for Climate (OOPC) that are currently feasible with current observational systems.

CTD stands for conductivity, temperature, and depth. A CTD instrument is an oceanography sonde used to measure the electrical conductivity, temperature, and pressure of seawater. The pressure is closely related to depth. Conductivity is used to determine salinity.
A video plankton recorder (VPR) is towed underwater video microscope system, which photographs small to fine-scale structure of plankton, from 50 micrometers and up to a few centimeters in size. A VPR consists of five general components: cameras, strobe, additive sensor and flight control, underwater platform and interface software for plankton identification.

NOAAS Reuben Lasker is a National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) fishery research vessel. The ship's namesake, Reuben Lasker, was a fisheries biologist who served with the Southwest Fisheries Center, National Marine Fisheries Service, and taught at the Scripps Institution of Oceanography.
A temperature data logger, also called temperature monitor, is a portable measurement instrument that is capable of autonomously recording temperature over a defined period of time. The digital data can be retrieved, viewed and evaluated after it has been recorded. A data logger is commonly used to monitor shipments in a cold chain and to gather temperature data from diverse field conditions.
The Tropical Atmosphere Ocean (TAO) project is a major international effort that instrumented the entire tropical Pacific Ocean, with approximately 70 deep ocean moorings. The development of the TAO array in 1985 was motivated by the 1982-1983 El Niño event and ultimately designed for the study of year-to-year climate variations related to El Niño and the Southern Oscillation (ENSO). Led by the TAO Project Office of the Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory (PMEL), the full array of 70 moorings was completed in 1994.

RV Falkor is an oceanographic research vessel operated by the Schmidt Ocean Institute. Ship time aboard the vessel is made freely available to researchers once they have undergone an application, peer review process, and their proposal has been accepted. One condition for using the Falkor is that research findings and data from all expeditions are made publicly available. Researchers aboard Falkor receive expert shipboard support, use of scientific equipment, as well as robotic and computational resources. RV Falkor is adaptable and can facilitate new technologies and external resources as required for each science expedition. Falkor’s current status and a virtual ship tour are publicly available on the Schmidt Ocean Institute website. The Schmidt Ocean Institute announced the change of ownership of the vessel on 14. March 2022. It was renamed to Gaia Blu and is used by the italian National Research Council. It concluded its first science expedition at the 20. October 2022.

NOAAS Pisces is an American fisheries and oceanographic research vessel in commission in the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) fleet since 2009.

A fixed-point ocean observatory is an ocean observing autonomous system of automatic sensors and samplers that continuously gathers data from deep sea, water column and lower atmosphere, and transmits the data to shore in real or near real-time.

Ocean optics is the study of how light interacts with water and the materials in water. Although research often focuses on the sea, the field broadly includes rivers, lakes, inland waters, coastal waters, and large ocean basins. How light acts in water is critical to how ecosystems function underwater. Knowledge of ocean optics is needed in aquatic remote sensing research in order to understand what information can be extracted from the color of the water as it appears from satellite sensors in space. The color of the water as seen by satellites is known as ocean color. While ocean color is a key theme of ocean optics, optics is a broader term that also includes the development of underwater sensors using optical methods to study much more than just color, including ocean chemistry, particle size, imaging of microscopic plants and animals, and more.

The Sanibel-Captiva Conservation Foundation (SCCF) is an American ecosystem protection group. It was founded in 1967 on Sanibel Island, Florida to preserve the island's interior freshwater system. The non-profit's mission has since evolved to also protect and care for Southwest Florida's coastal ecosystems.

















