
A water supply network or water supply system is a system of engineered hydrologic and hydraulic components that provide water supply. A water supply system typically includes the following:
- A drainage basin
- A raw water collection point where the water accumulates, such as a lake, a river, or groundwater from an underground aquifer. Raw water may be transferred using uncovered ground-level aqueducts, covered tunnels, or underground water pipes to water purification facilities.
- Water purification facilities. Treated water is transferred using water pipes.
- Water storage facilities such as reservoirs, water tanks, or water towers. Smaller water systems may store the water in cisterns or pressure vessels. Tall buildings may also need to store water locally in pressure vessels in order for the water to reach the upper floors.
- Additional water pressurizing components such as pumping stations may need to be situated at the outlet of underground or aboveground reservoirs or cisterns.
- A pipe network for distribution of water to consumers and other usage points
- Connections to the sewers are generally found downstream of the water consumers, but the sewer system is considered to be a separate system, rather than part of the water supply system.

The Scottish Environment Protection Agency is Scotland's environmental regulator and national flood forecasting, flood warning and strategic flood risk management authority. Its main role is to protect and improve Scotland's environment. SEPA does this by helping business and industry to understand their environmental responsibilities, enabling customers to comply with legislation and good practice and to realise the economic benefits of good environmental practice. One of the ways SEPA does this is through the NetRegs environmental guidance service. It protects communities by regulating activities that can cause harmful pollution and by monitoring the quality of Scotland's air, land and water. The regulations it implements also cover the storage, transport and disposal of radioactive materials.

Environmental policy is the commitment of an organization or government to the laws, regulations, and other policy mechanisms concerning environmental issues. These issues generally include air and water pollution, waste management, ecosystem management, maintenance of biodiversity, the management of natural resources, wildlife and endangered species. For example, concerning environmental policy, the implementation of an eco-energy-oriented policy at a global level to address the issues of global warming and climate changes could be addressed. Policies concerning energy or regulation of toxic substances including pesticides and many types of industrial waste are part of the topic of environmental policy. This policy can be deliberately taken to influence human activities and thereby prevent undesirable effects on the biophysical environment and natural resources, as well as to make sure that changes in the environment do not have unacceptable effects on humans.

Landfills in the United Kingdom were historically the most commonly used option for waste disposal. Up until the 1980s, policies of successive governments had endorsed the "dilute and disperse" approach. Britain has since adopted the appropriate European legislation and landfill sites are generally operated as full containment facilities. However, many dilute and disperse sites remain throughout Britain.
Water supply and sanitation (WSS) in the European Union (EU) is the responsibility of each member state, but in the 21st century union-wide policies have come into effect. Water resources are limited and supply and sanitation systems are under pressure from urbanisation and climate change. Indeed, the stakes are high as the European Environmental Agency found that one European out of ten already suffers a situation of water scarcity and the IEA measured the energy consumption of the water sector to be equivalent to 3,5% of the electricity consumption of the EU.

The Water Framework Directive2000/60/EC is an EU directive which commits European Union member states to achieve good qualitative and quantitative status of all water bodies by 2015. It is a framework in the sense that it prescribes steps to reach the common goal rather than adopting the more traditional limit value approach. The Directive's aim for 'good status' for all water bodies will not be achieved, with 47% of EU water bodies covered by the Directive failing to achieve the aim.
The Murray–Darling Basin Authority (MDBA) is the principal government agency in charge of managing the Murray–Darling basin in an integrated and sustainable manner. The MDBA is an independent statutory agency that manages, in conjunction with the Basin states, the Murray–Darling basin's water resources in the national interest. The MDBA reports to the Australian Government Minister for the Environment and Water, held since June 2022 by the Hon Tanya Plibersek.
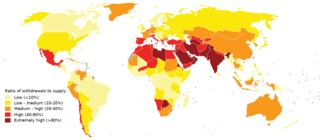
Water scarcity is the lack of fresh water resources to meet the standard water demand. There are two types of water scarcity namely physical water scarcity and economic water scarcity. Physical water scarcity is where there is not enough water to meet all demands, including that needed for ecosystems to function. Arid areas for example Central and West Asia, and North Africa often experience physical water scarcity. Economic water scarcity on the other hand, is the result of lack of investment in infrastructure or technology to draw water from rivers, aquifers, or other water sources, or weak human capacity to meet water demand. Much of Sub-Saharan Africa experience economic water scarcity.
Water resources management is a significant challenge for Mexico. The country has in place a system of water resources management that includes both central (federal) and decentralized institutions. Furthermore, water management is imposing a heavy cost to the economy.
Water resources management is a key element of Brazil's strategy to promote sustainable growth and a more equitable and inclusive society. Brazil's achievements over the past 70 years have been closely linked to the development of hydraulic infrastructure for hydroelectric power generation and just recently to the development of irrigation infrastructure, especially in the Northeast region.

Water resources are natural resources of water that are potentially useful for humans, for example as a source of drinking water supply or irrigation water. 97% of the water on Earth is salt water and only three percent is fresh water; slightly over two-thirds of this is frozen in glaciers and polar ice caps. The remaining unfrozen freshwater is found mainly as groundwater, with only a small fraction present above ground or in the air. Natural sources of fresh water include surface water, under river flow, groundwater and frozen water. Artificial sources of fresh water can include treated wastewater and desalinated seawater. Human uses of water resources include agricultural, industrial, household, recreational and environmental activities.
There is a long and established framework for water resources management in Colombia. The Environment Ministry and up to 33 Regional Authorities, are in charge of water resources management and policies at the national and regional and watershed level, respectively. Other sectoral ministries are in charge of water demand for energy, water supply and sanitation and water for irrigation.

The aim of water security is to make the most of water's benefits for humans and ecosystems. The second aim is to limit the risks of destructive impacts of water to an acceptable level. These risks include for example too much water (flood), too little water or poor quality (polluted) water. People who live with a high level of water security always have access to "an acceptable quantity and quality of water for health, livelihoods and production". For example, access to WASH services is one component of water security. Some organizations use the term water security more narrowly for water supply aspects only.

Water resources management (WRM) functions in Argentina are handled by multiple institutions operating at the national, provincial, and river basin level, with a variety of functions and jurisdictions. On the national level, the National Institute for Water and the Environment (INA) and the National Water and Sanitation Utility (AySA) are charged with the duties of researching, water resources preservation, developing services, and implementing water projects.
Integrated urban water management in Aracaju, the capital city of the Brazilian State of Sergipe (SSE) has been and still is a challenging prospect. Home to half a million people, Aracaju is located in a tropical coastal zone within a semi-arid state and receives below average rainfall of 1,200 mm/year where average rainfall in Latin America is higher at 1,556 mm/yr. (Source:FAO 2000) Most of the residents do have access to the potable water supply and non-revenue water losses are nearly 50%.

Climate change in Jordan has serious impacts on the water resources in Jordan. The country needs to prepare for the impacts of climate change. Water resources in Jordan are scarce. Besides the rapid population growth, the impacts of climate change are likely to further exacerbate the problem. Temperatures will increase and the total annual precipitation is likely to decrease, however with a fair share of uncertainty. Hence, existing and new activities with the objective to minimize the gap between water supply and demand contribute to adapt Jordan to tomorrow's climate. This might be accompanied by activities improving Jordan's capacity to monitor and project meteorological and hydrological data and assess its own vulnerability to climate change.

Water resource policy, sometimes called water resource management or water management, encompasses the policy-making processes and legislation that affect the collection, preparation, use, disposal, and protection of water resources. Water is a necessity for all forms of life as well as industries on which humans are reliant, like technology development and agriculture. This global need for clean water access necessitates water resource policy to determine the means of supplying and protecting water resources. Water resource policy varies by region and is dependent on water availability or scarcity, the condition of aquatic systems, and regional needs for water. Since water basins do not align with national borders, water resource policy is also determined by international agreements, also known as hydropolitics. Water quality protection also falls under the umbrella of water resource policy; laws protecting the chemistry, biology, and ecology of aquatic systems by reducing and eliminating pollution, regulating its usage, and improving the quality are considered water resource policy. When developing water resource policies, many different stakeholders, environmental variables, and considerations have to be taken to ensure the health of people and ecosystems are maintained or improved. Finally, ocean zoning, coastal, and environmental resource management are also encompassed by water resource management, like in the instance of offshore wind land leasing.
Soil governance refers to the policies, strategies, and the processes of decision-making employed by nation states and local governments regarding the use of soil. Globally, governance of the soil has been limited to an agricultural perspective due to increased food insecurity from the most populated regions on earth. The Global Soil Partnership, GSP, was initiated by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and its members with the hope to improve governance of the limited soil resources of the planet in order to guarantee healthy and productive soils for a food-secure world, as well as support other essential ecosystem services.
The Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes, also known as the Water Convention, is an international environmental agreement and one of five UNECE's negotiated environmental treaties. The purpose of this Convention is to improve national attempts and measures for protection and management of transboundary surface waters and groundwaters. On the international level, Parties are obliged to cooperate and create joint bodies. The Convention includes provisions on: monitoring, research, development, consultations, warning and alarm systems, mutual assistance and access as well as exchange of information.

Water in Africa is an important issue encompassing the sources, distribution and economic uses of the water resources on the continent. Overall, Africa has about 9% of the world's fresh water resources and 16% of the world's population. Among its rivers are the Congo, Nile, Zambezi, and Niger, and also has Lake Victoria, considered the world’s second largest lake. Yet the continent is the second driest in the world, with millions of Africans still suffering from water shortages throughout the year.











