
Robert Druitt (December 1814 – 15 May 1883), was an English medical writer.

Robert Druitt (December 1814 – 15 May 1883), was an English medical writer.
Druitt, the son of a medical practitioner at Wimborne, Dorset, was born in December 1814. After four years' pupillage with Mr. Charles Mayo, surgeon to the Winchester Hospital, he entered in 1834 as a medical student at King's College and the Middlesex Hospital in London. He became L.S.A. in 1836, and M.R.C.S. in 1837, and settled in general practice in Bruton Street, Berkeley Square.
In 1839 he published the Surgeon's Vade-Mecum, for which he is best known. Written in a very clear and simple style, it became a great favourite with students, and the production of successive editions occupied much of the author's time. The eleventh edition appeared in 1878, and in all more than forty thousand copies were sold. It was reprinted in America, and translated into several European languages.
In 1845 Druitt became F.R.C.S. by examination, and in 1874 F.R.C.P., later receiving the Lambeth degree of M.D. He practised successfully for many years, and also engaged in much literary work, having for ten years (1862–72) edited the Medical Times and Gazette. He was an earnest advocate of improved sanitation, and from 1856 to 1867 was one of the medical officers of health for St. George's, Hanover Square. From 1864 to 1872 he was president of the Metropolitan Association of Medical Officers of Health, before which he delivered numerous valuable addresses.
In 1872 his health broke down, and he for some time lived in Madras, whence he wrote some interesting "Letters from Madras" to the Medical Times and Gazette. On his retirement 370 medical men and other friends presented him with a cheque for 1,215l. in a silver cup, "in evidence of their sympathy with him in a prolonged illness, induced by years of generous and unwearied labours in the cause of humanity, and as a proof of their appreciation of the services rendered by him as an author and sanitary reformer to both the public and the profession." After an exhausting illness he died at Kensington on 15 May 1883. In 1845 he had married a Miss Hopkinson, who with three sons and four daughters survived him.
Druitt was a man of wide culture, being well versed in languages, as well as in science and theology. Church music was one of his special studies, and as early as 1845 he wrote a Popular Tract on Church Music. Besides his principal work, Druitt wrote a small work on Cheap Wines, their use in Diet and Medicine, which appeared first in the Medical Times and Gazette in 1863 and 1864, and was twice reprinted in an enlarged form in 1865 and 1873. In 1872 he contributed an important article on "Inflammation" to Cooper's Dictionary of Practical Surgery. Among his minor writings may also be mentioned his paper on the "Construction and Management of Human Habitations, considered in relation to the Public Health" (Transactions of the Royal Institute of British Architects, 1859–60).
Edward Backhouse Eastwick CB was an English orientalist, diplomat and Conservative Member of Parliament. He wrote and edited a number of books on South Asian countries. These included a Sindhi vocabulary and a grammar of the Hindustani language.

Thomas Caverhill Jerdon was a British physician, zoologist and botanist. He was a pioneering ornithologist who described numerous species of birds in India. Several species of plants and birds including Jerdon's baza, Jerdon's leafbird, Jerdon's bushlark, Jerdon's nightjar, Jerdon's courser, Jerdon's babbler and Jerdon's bush chat are named after him.

Sir Joseph Fayrer, 1st Baronet FRS FRSE FRCS FRCP KCSI LLD was an English physician who served as Surgeon General in India. He is noted for his writings on medicine, work on public health and his studies particularly on the treatment of snakebite, in India. He was also involved in official investigation on cholera, in which he did not accept the idea, proposed by Robert Koch, of germs as the cause of cholera.

William Bland was a transported convict, medical practitioner and surgeon, politician, farmer and inventor in the Colony of New South Wales, Australia.

William Alexander Hammond was an American military physician and neurologist. During the American Civil War he was the eleventh Surgeon General of the United States Army (1862–1864) and the founder of the Army Medical Museum.

Julius Dreschfeld FRCP was a leading British physician and pathologist.
John Roberton was a Scottish physician and social reformer. He was a pioneer of modern obstetrics and of evidence-based medicine, and influential in the intellectual life of Victorian Manchester.

Edward Green Balfour was a Scottish surgeon, orientalist and pioneering environmentalist in India. He founded museums at Madras and Bangalore, a zoological garden in Madras and was instrumental in raising awareness on forest conservation and public health in India. He published a Cyclopaedia of India, several editions of which were published after 1857, translated works on health into Indian languages and wrote on a variety of subjects.

James Johnson was an influential British writer on diseases of tropical climates in the first half of the nineteenth century. Born in Ireland, at the early age of 15 he became an apprentice to a surgeon-apothecary in Antrim for two years. After spending two further two years in Belfast, he moved to London for the surgeon's examination, which he passed in 1798. Immediately afterwards, he was appointed surgeon's mate on a naval vessel, on which he sailed to Newfoundland and Nova Scotia. In 1800 he took part in an expedition to Egypt and, in 1803, sailed for India.

William Robert Cornish was a British physician who served in India for more than thirty years, and became the Surgeon-General—head of medical services—in the Madras Presidency. During the Great Famine of 1876–78, Cornish, then Sanitary Commissioner of Madras, argued for generous famine relief, which put him at odds with Sir Richard Temple, Famine Envoy for the Government of India, who was promoting reduced rations. Some of Cornish's innovations made their way into the Indian Famine Codes of the late 19th century.

Lieutenant-General Sir Richard Hieram Sankey was an officer in the Royal (Madras) Engineers in the East India Company's army in British India, later transferring to the British Army after the Indian Rebellion of 1857 and the assumption of Crown rule in India. Sankey Tank which he constructed to meet the water demands of Bangalore is named after him. The high court building in Bangalore, Attara Kacheri, was designed by him and built by Arcot Narrainswamy Mudaliar.

Joseph Decatur Bryant was a surgeon, New York City Health Commissioner, Surgeon-General of the National Guard Surgeons and physician to Grover Cleveland and John D. Rockefeller. He also held a series of academic positions at Bellevue Hospital Medical College, culminating with the title of professor of the principles and practice of surgery, and professor of operative and clinical surgery, at New York University and Bellevue Hospital Medical College.

John Bishop Estlin was an English ophthalmic surgeon.

Charles Franklin Watkins was an American physician, surgeon and physiotherapist. He played college baseball for the University of Michigan and later served as the coach of the Michigan Wolverines baseball team for three years. He moved to Billings, Montana in 1905 where he maintained a medical practice for approximately 30 years.

Samuel Fisk Green (1822–1884) was an American medical missionary. He graduated from the College of Physicians and Surgeons in New York city. He served with the American Ceylon Mission (ACM) in Jaffna, Sri Lanka during the period (1847–1873) when it was the British colony of Ceylon. During his tenure he founded the Sri Lanka's first medical hospital and school in what later became the Green Memorial Hospital in Manipay in the Jaffna peninsula. He translated and published over 4000 pages of medical literature from English to Tamil as part of his efforts to train doctors in their native language. He was personally responsible for training over 60 native doctors of whom majority had their instructions in Tamil.
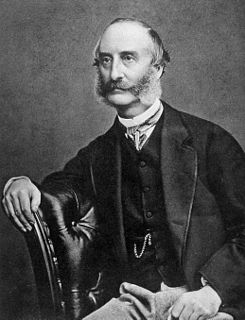
Edmund Alexander Parkes was an English physician, known as a hygienist, particularly in the military context.

Forbes Benignus Winslow DCL, FRCP Edin., MRCP, MRCS, MD, was a British psychiatrist, author and an authority on lunacy during the Victorian era.
Frederick Knight Hunt (1814–1854) was an English journalist and author, known for The Fourth Estate, a history of journalism.

Herbert Mayo, M.D., was a British physiologist, anatomist and medical writer.
Alexander Crombie was a Scottish surgeon who joined the Indian Medical Service and became resident surgeon at Calcutta Medical College, India, where he became professor of materia medica.
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : "Druitt, Robert". Dictionary of National Biography . London: Smith, Elder & Co. 1885–1900.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : "Druitt, Robert". Dictionary of National Biography . London: Smith, Elder & Co. 1885–1900.