
Qt is a cross-platform application development framework for creating graphical user interfaces as well as cross-platform applications that run on various software and hardware platforms such as Linux, Windows, macOS, Android or embedded systems with little or no change in the underlying codebase while still being a native application with native capabilities and speed.
Trac is an open-source, web-based project management and bug tracking system. It has been adopted by a variety of organizations for use as a bug tracking system for both free and open-source software and proprietary projects and products. Trac integrates with major version control systems including Subversion and Git. Trac is used, among others, by the Internet Research Task Force, Django, FFmpeg, jQuery UI, WebKit, 0 A.D., and WordPress.

Free and open-source software (FOSS) is software that is available under a license that grants the right to use, modify, and distribute the software, modified or not, to everyone free of charge. The public availability of the source code is, therefore, a necessary but not sufficient condition. FOSS is an inclusive umbrella term for free software and open-source software. FOSS is in contrast to proprietary software, where the software is under restrictive copyright or licensing and the source code is hidden from the users.
Multi-licensing is the practice of distributing software under two or more different sets of terms and conditions. This may mean multiple different software licenses or sets of licenses. Prefixes may be used to indicate the number of licenses used, e.g. dual-licensed for software licensed under two different licenses.

A LAMP is one of the most common software stacks for the web's most popular applications. Its generic software stack model has largely interchangeable components.
A permissive software license, sometimes also called BSD-like or BSD-style license, is a free-software license which instead of copyleft protections, carries only minimal restrictions on how the software can be used, modified, and redistributed, usually including a warranty disclaimer. Examples include the GNU All-permissive License, MIT License, BSD licenses, Apple Public Source License and Apache license. As of 2016, the most popular free-software license is the permissive MIT license.

The WTFPL is a permissive free software license. As a public domain like license, the WTFPL is essentially the same as dedication to the public domain. It allows redistribution and modification of the work under any terms. The name is an abbreviation of Do What The Fuck You Want To Public License.

SchoolTool is a GPL licensed, free student information system for schools around the world. The goals of the project are to create a student information system, including demographics, gradebook, attendance, calendaring and reporting for primary and secondary schools, as well as a framework for building customized applications and configurations for individual schools or states.
License proliferation is the phenomenon of an abundance of already existing and the continued creation of new software licenses for software and software packages in the FOSS ecosystem. License proliferation affects the whole FOSS ecosystem negatively by the burden of increasingly complex license selection, license interaction, and license compatibility considerations.
License compatibility is a legal framework that allows for pieces of software with different software licenses to be distributed together. The need for such a framework arises because the different licenses can contain contradictory requirements, rendering it impossible to legally combine source code from separately-licensed software in order to create and publish a new program. Proprietary licenses are generally program-specific and incompatible; authors must negotiate to combine code. Copyleft licenses are commonly deliberately incompatible with proprietary licenses, in order to prevent copyleft software from being re-licensed under a proprietary license, turning it into proprietary software. Many copyleft licenses explicitly allow relicensing under some other copyleft licenses. Permissive licenses are compatible with everything, including proprietary licenses; there is thus no guarantee that all derived works will remain under a permissive license.
A Contributor License Agreement (CLA) defines the terms under which intellectual property has been contributed to a company/project, typically software under an open source license.

A free-software license is a notice that grants the recipient of a piece of software extensive rights to modify and redistribute that software. These actions are usually prohibited by copyright law, but the rights-holder of a piece of software can remove these restrictions by accompanying the software with a software license which grants the recipient these rights. Software using such a license is free software as conferred by the copyright holder. Free-software licenses are applied to software in source code and also binary object-code form, as the copyright law recognizes both forms.

The GNU General Public Licenses are a series of widely used free software licenses, or copyleft licenses, that guarantee end users the freedoms to run, study, share, and modify the software. The GPL was the first copyleft license for general use and was originally written by Richard Stallman, the founder of the Free Software Foundation (FSF), for the GNU Project. The license grants the recipients of a computer program the rights of the Free Software Definition. The licenses in the GPL series are all copyleft licenses, which means that any derivative work must be distributed under the same or equivalent license terms. It is more restrictive than the Lesser General Public License and even further distinct from the more widely-used permissive software licenses such as BSD, MIT, and Apache.
The Free Software Foundation (FSF) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization founded by Richard Stallman on October 4, 1985, to support the free software movement, with the organization's preference for software being distributed under copyleft terms, such as with its own GNU General Public License. The FSF was incorporated in Boston, Massachusetts, United States, where it is also based.

The Stop Online Piracy Act (SOPA) was a proposed United States congressional bill to expand the ability of U.S. law enforcement to combat online copyright infringement and online trafficking in counterfeit goods. Introduced on October 26, 2011, by Representative Lamar Smith (R-TX), provisions included the requesting of court orders to bar advertising networks and payment facilities from conducting business with infringing websites, and search engines from linking to the websites, and court orders requiring Internet service providers to block access to the websites. The proposed law would have expanded existing criminal laws to include unauthorized streaming of copyrighted content, imposing a maximum penalty of five years in prison.
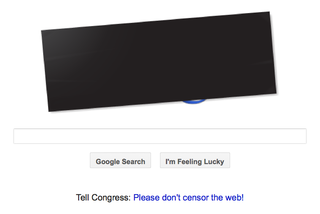
On January 18, 2012, a series of coordinated protests occurred against two proposed laws in the United States Congress—the Stop Online Piracy Act (SOPA) and the PROTECT IP Act (PIPA). These followed smaller protests in late 2011. Protests were based on concerns that the bills, intended to provide more robust responses to copyright infringement arising outside the United States, contained measures that could possibly infringe online freedom of speech, websites, and Internet communities. Protesters also argued that there were insufficient safeguards in place to protect sites based upon user-generated content.
eXeLearning is a free / libre software tool under GPL-2 that can be used to create educational interactive web content.

Django Girls is an international non-profit organization started by two Polish women, Ola Sitarska and Ola Sendecka, to inspire women from all backgrounds to get interested in technology and to become programmers, offering a safe and friendly environment. It is known for the free workshops it hosts to help women to learn to program and for its Django tutorial. It is often supported by the Python Software Foundation, and they often hold sessions at the Python Conference.











