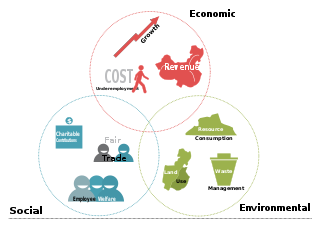
The triple bottom line is an accounting framework with three parts: social, environmental and economic. Some organizations have adopted the TBL framework to evaluate their performance in a broader perspective to create greater business value. Business writer John Elkington claims to have coined the phrase in 1994.

Greenwashing, also called "green sheen", is a form of advertising or marketing spin in which green PR and green marketing are deceptively used to persuade the public that an organization's products, aims and policies are environmentally friendly. Companies that intentionally take up greenwashing communication strategies often do so in order to distance themselves from the environmental lapses of themselves or their suppliers.

Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a form of international private business self-regulation which aims to contribute to societal goals of a philanthropic, activist, or charitable nature by engaging in or supporting volunteering or ethically oriented practices. While once it was possible to describe CSR as an internal organizational policy or a corporate ethic strategy, that time has passed as various national and international laws have been developed. Various organizations have used their authority to push it beyond individual or even industry-wide initiatives. In contrast, it has been considered a form of corporate self-regulation for some time, over the last decade or so it has moved considerably from voluntary decisions at the level of individual organizations to mandatory schemes at regional, national, and international levels. Moreover, scholars and firms are using the term creating shared value- an extension of corporate social responsibility to explain ways of doing business in a socially responsible way while making profits.

Claremont McKenna College (CMC) is a private liberal arts college in Claremont, California. It has a curricular emphasis on government, economics, public affairs, finance, and international relations. CMC is a member of the Claremont Colleges consortium.
A green economy is an economy that aims at reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities, and that aims for sustainable development without degrading the environment. It is closely related with ecological economics, but has a more politically applied focus. The 2011 UNEP Green Economy Report argues "that to be green, an economy must not only be efficient, but also fair. Fairness implies recognizing global and country level equity dimensions, particularly in assuring a Just Transition to an economy that is low-carbon, resource efficient, and socially inclusive."

CEMEX S.A.B. de C.V., known as Cemex, is a Mexican multinational building materials company headquartered in San Pedro, near Monterrey, Mexico. It manufactures and distributes cement, ready-mix concrete and aggregates in more than 50 countries. In 2020 it was ranked as the 5th largest cement company in the world, at 87.09 million tonnes.

The Global Reporting Initiative is an international independent standards organization that helps businesses, governments and other organizations understand and communicate their impacts on issues such as climate change, human rights and corruption. GRI provides the world's most widely used sustainability reporting standards
The mining industry in India is a major economic activity which contributes significantly to the economy of India. The GDP contribution of the mining industry varies from 2.2% to 2.5% only but going by the GDP of the total industrial sector it contributes around 10% to 11%. Even mining done on small scale contributes 6% to the entire cost of mineral production. Indian mining industry provides job opportunities to around 700,000 individuals.

Socially responsible investing (SRI), social investment, sustainable socially conscious, "green" or ethical investing, is any investment strategy which seeks to consider both financial return and social/environmental good to bring about social change regarded as positive by proponents. Socially responsible investments often constitute a small percentage of total funds invested by corporations and are riddled with obstacles.

Sustainability accounting was originated about 20 years ago and is considered a subcategory of financial accounting that focuses on the disclosure of non-financial information about a firm's performance to external stakeholders, such as capital holders, creditors, and other authorities. Sustainability accounting represents the activities that have a direct impact on society, environment, and economic performance of an organisation. Sustainability accounting in managerial accounting contrasts with financial accounting in that managerial accounting is used for internal decision making and the creation of new policies that will have an effect on the organisation's performance at economic, ecological, and social level. Sustainability accounting is often used to generate value creation within an organisation.
The Dow Jones Sustainability Indices (DJSI) launched in 1999, are a family of indices evaluating the sustainability performance of thousands of companies trading publicly, operated under a strategic partnership between S&P Dow Jones Indices and RobecoSAM of the S&P Dow Jones Indices. They are the longest-running global sustainability benchmarks worldwide and have become the key reference point in sustainability investing for investors and companies alike. In 2012, S&P Dow Jones Indices was formed via the merger of S&P Indices and Dow Jones Indexes.

The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) was established in July 1970 when the White House and the United States Congress came together due to the public's demand for cleaner natural resources. The purpose of the EPA is to repair the damage done to the environment and to set up new criteria to allow Americans to make a clean environment a reality. The ultimate goal of the EPA is to protect human health and the environment.
Peak minerals marks the point in time when the largest production of a mineral will occur in an area, with production declining in subsequent years. While most mineral resources will not be exhausted in the near future, global extraction and production has become more challenging. Miners have found ways over time to extract deeper and lower grade ores with lower production costs. More than anything else, declining average ore grades are indicative of ongoing technological shifts that have enabled inclusion of more 'complex' processing – in social and environmental terms as well as economic – and structural changes in the minerals exploration industry and these have been accompanied by significant increases in identified Mineral Reserves.
ESG is an umbrella term that refers to frameworks designed to be integrated into an organization's strategy to create enterprise value by expanding the organizations objectives to include the identification, assessment and management of sustainability-related risks and opportunities in respect to all organizational stakeholders and the environment.
- Environmental aspect: focuses on preserving the natural world. Examples of topics addressed include climate change, greenhouse gas emissions, biodiversity loss, deforestation, pollution, energy efficiency and water management.
- Social aspect: focuses on people and relationships include working to support diversity, equity, and inclusion movements in addition to enhancing customer satisfaction and employee engagement.
- Governance aspect: focuses on moving beyond how organizations have been typically governed in the past and enhance corporate governance. Examples of specific topics include board composition, cybersecurity practices, management structure, executive compensation, preventing bribery and corruption.

Robeco Schweiz is an international investment company with a specific focus on sustainability investments. It was founded in 1995 by Reto Ringger. The company is based in Zurich, Switzerland, and considers economic, environmental and social criteria in its investment strategies. In addition to asset management, the company has an indexes and private equity portion of the business. In 2006 RobecoSAM introduced a division called sustainability services that provides sustainability benchmarking reports to companies. In 2001, the then-RobecoSAM became the first carbon neutral company in Switzerland.
A sustainability organization is (1) an organized group of people that aims to advance sustainability and/or (2) those actions of organizing something sustainably. Unlike many business organizations, sustainability organizations are not limited to implementing sustainability strategies which provide them with economic and cultural benefits attained through environmental responsibility. For sustainability organizations, sustainability can also be an end in itself without further justifications.
Sustainability standards and certifications are voluntary guidelines used by producers, manufacturers, traders, retailers, and service providers to demonstrate their commitment to good environmental, social, ethical, and food safety practices. There are over 400 such standards across the world.

India's National Voluntary Guidelines on Social, Environmental and Economic Responsibilities of Business (NVGs) were released by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) in July 2011 by Mr. Murli Deora, the former Honourable Minister for Corporate Affairs. The national framework on Business Responsibility is essentially a set of nine principles that offer businesses an Indian understanding and approach to inculcating responsible business conduct.
Social accounting is the process of communicating the social and environmental effects of organizations' economic actions to particular interest groups within society and to society at large. Social Accounting is different from public interest accounting as well as from critical accounting.

RepRisk AG is an environmental, social, and corporate governance (ESG) data science company based in Zurich, Switzerland, specializing in ESG and business-conduct risk research, and quantitative solutions.










