
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis. This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substances are considered carcinogens, but their carcinogenic activity is attributed to the radiation, for example gamma rays and alpha particles, which they emit. Common examples of non-radioactive carcinogens are inhaled asbestos, certain dioxins, and tobacco smoke. Although the public generally associates carcinogenicity with synthetic chemicals, it is equally likely to arise from both natural and synthetic substances. Carcinogens are not necessarily immediately toxic; thus, their effect can be insidious.

Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents. Species of rats are found throughout the order Rodentia, but stereotypical rats are found in the genus Rattus. Other rat genera include Neotoma, Bandicota and Dipodomys.
Heliox is a breathing gas mixture of helium (He) and oxygen (O2). It is used as a medical treatment for patients with difficulty breathing because mixture generates less resistance than atmospheric air when passing through the airways of the lungs, and thus requires less effort by a patient to breathe in and out of the lungs. It is also used as a breathing gas diluent for deep ambient pressure diving as it is not narcotic at high pressure, and for its low work of breathing.

The guinea pig or domestic guinea pig, also known as the cavy or domestic cavy, is a species of rodent belonging to the genus Cavia in the family Caviidae. Breeders tend to use the word cavy to describe the animal, while in scientific and laboratory contexts, it is far more commonly referred to by the common name guinea pig. Despite their common name, guinea pigs are not native to Guinea, nor are they closely related biologically to pigs, and the origin of the name is still unclear. They originated in the Andes of South America. Studies based on biochemistry and hybridization suggest they are domesticated animals that do not exist naturally in the wild, descendants of a closely related cavy species such as C. tschudii. They were originally domesticated as livestock for a source of meat, and are still consumed in some parts of the world.
A biocide is defined in the European legislation as a chemical substance or microorganism intended to destroy, deter, render harmless, or exert a controlling effect on any harmful organism. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) uses a slightly different definition for biocides as "a diverse group of poisonous substances including preservatives, insecticides, disinfectants, and pesticides used for the control of organisms that are harmful to human or animal health or that cause damage to natural or manufactured products". When compared, the two definitions roughly imply the same, although the US EPA definition includes plant protection products and some veterinary medicines.

Textured or texturized vegetable protein (TVP), also known as textured soy protein (TSP), soy meat, or soya chunks is a defatted soy flour product, a by-product of extracting soybean oil. It is often used as a meat analogue or meat extender. It is quick to cook, with a protein content comparable to certain meats.

CVCC, or Compound Vortex Controlled Combustion, is an internal combustion engine technology developed and trademarked by the Honda Motor Company.

Rodenticides are chemicals made and sold for the purpose of killing rodents. While commonly referred to as "rat poison", rodenticides are also used to kill mice, squirrels, woodchucks, chipmunks, porcupines, nutria, beavers, and voles. Despite the crucial roles that rodents play in nature, there are times when they need to be controlled.

Hopcalite is the trade name for a number of mixtures that mainly consist of oxides of copper and manganese, which are used as catalysts for the conversion of carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide when exposed to the oxygen in the air at room temperature.

Gasoline direct injection (GDI), also known as petrol direct injection (PDI), is a mixture formation system for internal combustion engines that run on gasoline (petrol), where fuel is injected into the combustion chamber. This is distinct from manifold injection systems, which inject fuel into the intake manifold.
Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) is a form of internal combustion in which well-mixed fuel and oxidizer are compressed to the point of auto-ignition. As in other forms of combustion, this exothermic reaction releases energy that can be transformed in an engine into work and heat.

Calcium phosphide (CP) is the inorganic compound with the formula Ca3P2. It is one of several phosphides of calcium, being described as the salt-like material composed of Ca2+ and P3−. Other, more exotic calcium phosphides have the formula CaP, CaP3, Ca2P2, and Ca5P8.
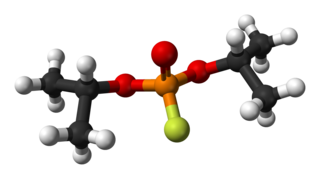
Diisopropyl fluorophosphate (DFP) or Isoflurophate is an oily, colorless liquid with the chemical formula C6H14FO3P. It is used in medicine and as an organophosphorus insecticide. It is stable, but undergoes hydrolysis when subjected to moisture.

Zinc phosphide (Zn3P2) is an inorganic chemical compound. It is a grey solid, although commercial samples are often dark or even black. It is used as a rodenticide. Zn3P2 is a II-V semiconductor with a direct band gap of 1.5 eV and may have applications in photovoltaic cells. A second compound exists in the zinc-phosphorus system, zinc diphosphide (ZnP2).

A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., without breaking chemical bonds. Chemical substances can be simple substances, chemical compounds, or alloys.

Bolam's mouse is a species of nocturnal, burrowing rodent in the family Muridae that inhabits the semi arid and southern arid regions of Australia. It has a number of physiological and behavioural adaptations developed to cope with an extremely varied climate. Including the ability survive by extracting water from seeds alone, the production of highly concentrated urine, low water content faeces and nocturnal activity.

Rodents are commonly used in animal testing, particularly mice and rats, but also guinea pigs, hamsters, gerbils and others. Mice are the most commonly used vertebrate species, due to their availability, size, low cost, ease of handling, and fast reproduction rate.

Hempcrete or hemplime is biocomposite material, a mixture of hemp hurds (shives) and lime, sand, or pozzolans, which is used as a material for construction and insulation. It is marketed under names like Hempcrete, Canobiote, Canosmose, Isochanvre and IsoHemp. Hempcrete is easier to work with than traditional lime mixes and acts as an insulator and moisture regulator. It lacks the brittleness of concrete and consequently does not need expansion joints. Typically, hempcrete has good thermal and acoustic insulation capabilities, but low mechanical performance, specifically compressive strength. In addition, hempcrete’s mechanical properties, when used in prefabricated blocks specifically, act as a carbon sink throughout its lifetime. The result is a lightweight insulating material, finishing plaster, or a non-load bearing wall, ideal for most climates as it combines insulation and thermal mass while providing a positive impact on the environment.

Rodents are mammals of the order Rodentia, which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for New Zealand, Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity.

9-Hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid (or 9-HODE) has been used in the literature to designate either or both of two stereoisomer metabolites of the essential fatty acid, linoleic acid: 9(S)-hydroxy-10(E),12(Z)-octadecadienoic acid (9(S)-HODE) and 9(R)-hydroxy-10(E),12(Z)-octadecadienoic acid (9(R)-HODE); these two metabolites differ in having their hydroxy residues in the S or R configurations, respectively. The accompanying figure gives the structure for 9(S)-HETE. Two other 9-hydroxy linoleic acid derivatives occur in nature, the 10E,12E isomers of 9(S)-HODE and 9(R)-HODE viz., 9(S)-hydroxy-10E,12E-octadecadienoic acid (9(S)-EE-HODE) and 9(R)-hydroxy-10E,12E-octadecadienoic acid (13(R)-EE-HODE); these two derivatives have their double bond at carbon 12 in the E or trans configuration as opposed to the Z or cis configuration. The four 9-HODE isomers, particularly under conditions of oxidative stress, may form together in cells and tissues; they have overlapping but not identical biological activities and significances. Because many studies have not distinguished between the S and R stereoisomers and, particularly in identifying tissue levels, the two EE isomers, 9-HODE is used here when the isomer studied is unclear.

















