Roger Cobban Sanders (born June 17, 1936) is an American doctor specializing in Ultrasound and Radiology. Originally from the United Kingdom, he obtained a degree in physiology at Oxford University, from the Oxford Clinical Medical School. In 1970 Sanders traveled to the United States to begin a one-year teaching position at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Maryland. During this time the University was presented a bistable ultrasound system, at the time the only one in Maryland, which Sanders was asked to oversee and use. Eventually he became professor of Radiology, Urology, Obstetric, and Gynecology, as well as director of Ultrasound at the University. He helped develop the department within the University, and it has grown into one of the foremost radiology institutions in the United States, having been named the "Cream of the Crop" by Medical Imaging Magazine in April 2007. [1]
In 1990, Sanders left to form his own practice in Baltimore, The Ultrasound Institute of Baltimore and to work part time at the university of Maryland. Currently he lives i San Diego and works part-time at New Mexico Sonographics telereporting gynecological ultrasound studies. Sanders has written nine books on Ultrasound & Sonography, including "Clinical Sonography: A Practical Guide", which is now in its fifth edition, and over 150 peer-reviewed articles. He is generally recognized as one of the pioneers of the use of Ultrasound in relation to Obstetrics and Gynecology, [2] and has been recognized for his work with the Biparietal diameter [3] among other work in the field. He is a fellow of several different Societies in the field of Ultrasound, including the Society of Radiology in Ultrasound, the American College of Radiology, and the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine (the AIUM), the latter awarding him the Presidential Award in 1984, and the Joseph H. Holmes Pioneer Award in 2001.
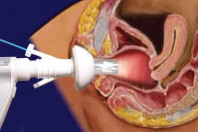
Gynaecology or gynecology is the medical practice dealing with the health of the female reproductive system. Outside medicine, the term means "the science of women". Its counterpart is andrology, which deals with medical issues specific to the male reproductive system.
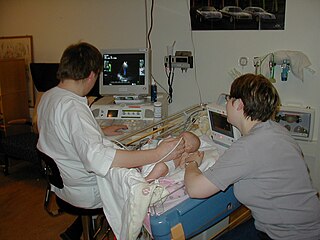
Medical ultrasound is a diagnostic imaging technique, or therapeutic application of ultrasound. It is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs. Its aim is often to find a source of a disease or to exclude pathology. The practice of examining pregnant women using ultrasound is called obstetric ultrasound, and was an early development and application of clinical ultrasonography.

Obstetric ultrasonography, or prenatal ultrasound, is the use of medical ultrasonography in pregnancy, in which sound waves are used to create real-time visual images of the developing embryo or fetus in the uterus (womb). The procedure is a standard part of prenatal care in many countries, as it can provide a variety of information about the health of the mother, the timing and progress of the pregnancy, and the health and development of the embryo or fetus.

Shigeo Satomura was a Japanese physicist credited with introducing the ultrasonic Doppler techniques to practical medical diagnostics in the 1950s. These techniques made possible non-invasive monitoring of blood flow in the human body.

Gynecologic ultrasonography or gynecologic sonography refers to the application of medical ultrasonography to the female pelvic organs as well as the bladder, the adnexa, and the recto-uterine pouch. The procedure may lead to other medically relevant findings in the pelvis.
The University of Maryland School of Medicine, located in Baltimore City, Maryland, U.S., is the medical school of the University of Maryland, Baltimore and is affiliated with the University of Maryland Medical Center and Medical System. Established in 1807 as the College of Medicine of Maryland, it is the first public and the fifth oldest medical school in the United States. It was also the first medical school to institute a residency training program. UMB SOM's campus includes Davidge Hall, which was built in 1812, and is the oldest building in continuous use for medical education in the Northern Hemisphere.
Frank A. Chervenak, MD currently serves as Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Lenox Hill Hospital; Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology and Associate Dean of International Medicine, Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell.

Howard Atwood Kelly, M.D., was an American gynecologist. He obtained his B.A. degree and M.D. degree from the University of Pennsylvania. He, William Osler, William Halsted, and William Welch together are known as the "Big Four", the founding professors at the Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, Maryland. He is credited with establishing gynecology as a specialty by developing new surgical approaches to gynecological diseases and pathological research. He also developed several medical innovations, including the improved cystoscope, Kelly's clamp, Kelly's speculum, and Kelly's forceps. Because Kelly was a famous prohibitionist and Fundamentalist Christian, many of his contemporaries expressed skepticism towards his medical professionalism.
Stuart Campbell DSc FRCPEd FRCOG FACOG, was born in Glasgow, Scotland, and graduated from the medical school of Glasgow University. During his training he worked with Ian Donald, who had published some of the first papers on the use of ultrasound in obstetrics.
The American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS), incorporated in June 1975, is an independent nonprofit organization that administers examinations and awards credentials in the areas of diagnostic medical sonography, diagnostic cardiac sonography, vascular technology, physicians’ vascular interpretation, musculoskeletal sonography and midwifery ultrasound. ARDMS has over 90,000 certified individuals in the U.S., Canada and throughout the world. ARDMS provides certifications, resources, and career information to healthcare practitioners and students practicing medical sonography.

A corpus luteum cyst is a type of ovarian cyst which may rupture about the time of menstruation, and take up to three months to disappear entirely. A corpus luteum cyst rarely occurs in women over the age of 50, because eggs are no longer being released after menopause. Corpus luteum cysts may contain blood and other fluids. The physical shape of a corpus luteum cyst may appear as an enlargement of the ovary itself, rather than a distinct mass -like growth on the surface of the ovary.
Master of Medicine (MMed) is a postgraduate academic degree awarded by medical schools to physicians following a period of instruction and examination. The degree is awarded by both surgical and medical subspecialties and usually includes a dissertation component involving original research. The degree may complement an existing fellowship in the chosen specialty or be the sole qualification necessary for registration as a specialist.
Fernando María Bonilla-Musoles, is a Spanish obstetrician and gynecologist, with a special influence in Europe and Latin America. In 1982, Bonilla's team began to develop in vitro propagation techniques of Britain's Robert Edwards, in Spain.
Hamdard College of Medicine & Dentistry trains students for the degree of Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery and Bachelor of Dental Surgery. These degrees will be awarded to candidates who successfully complete all requirements set out in the rules and regulations specified by the Pakistan Medical and Dental Council (PMDC). The college is located at the main campus of Hamdard University located in the northern part of Karachi, the largest city in Pakistan.
Dr. Jean R. Anderson is an internationally recognized obstetrician and gynaecologist, most well known for being the founder and first director of Johns Hopkins HIV Women's Health Program (1991).

Howard Wilbur Jones, Jr. was an American gynecological surgeon and in vitro fertilization (IVF) specialist. Jones and his wife, Georgeanna Seegar Jones, were two of the earliest reproductive medicine specialists in the United States. They established the reproductive medicine center that was responsible for the birth of the first IVF baby in the U.S. He wrote articles on the beginning of human personhood and testified before legislators on the same subject. He was one of the early physicians to perform sex reassignment surgeries.
Steven R. Goldstein is an inventor, author and a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at NYU School of Medicine. He is the director of NYU’s Gynecological Ultrasound and the co-director of the Bone Densitometry and Body Composition Unit.
Sven Becker is a German gynaecologist, gynaecologic surgeon, and oncologist.
Paul D. Blumenthal is an American physician, researcher, cervical cancer prevention advocate, and abortion provider who is certified in obstetrics and gynecology. He is known for his cervical cancer, abortion, and contraception research. He is also known for his commitment to international women’s health—evidenced by his contribution to public health initiatives in over 30 countries.

Rituko Kimata Pooh is a Japanese obstetrician and gynecologist.