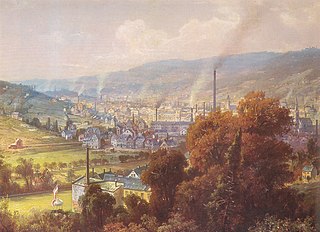Wuppertal is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, with a population of 355,000. Wuppertal is the seventh-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia and 17th-largest in Germany. It was founded in 1929 by the merger of Elberfeld, Barmen, Ronsdorf, Cronenberg and Vohwinkel, and was initially called "Barmen-Elberfeld" before adopting its present name in 1930. It is the capital and largest city of the Bergisches Land.

Rudolf Carnap was a German-language philosopher who was active in Europe before 1935 and in the United States thereafter. He was a major member of the Vienna Circle and an advocate of logical positivism.

Elberfeld is a municipal subdivision of the German city of Wuppertal; it was an independent town until 1929.
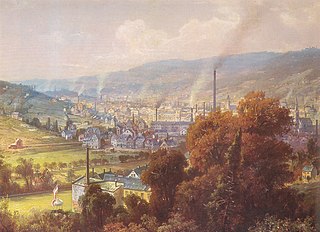
Barmen is a former industrial metropolis of the region of Bergisches Land, Germany, which merged with four other towns in 1929 to form the city of Wuppertal.

Radevormwald is a municipality in the Oberbergischer Kreis, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is one of the oldest towns in the Bergischen Land, formerly the County and Duchy of Berg.
Cronenberg was formerly an independent German town in the Rhine Province.

Knipex is a globally-distributed German manufacturer of hand tools, best known for its pliers. Knipex tools are principally used by professionals in various trades but find increasing popularity in DIY and EDC markets.
Lüttringhausen is a district of the German town of Remscheid with a population of 17,857 in 2005; 11,829 in 1905; 13,560, mostly Protestant, in 1910.
During the Second World War, the city of Wuppertal suffered numerous Allied air raids, primarily nighttime attacks from the Royal Air Force's Bomber Command during its Battle of the Ruhr bomber offensive. The largest raids were on the night of 29-30 May 1943, heavy enough to cause a firestorm, and on 24-25 June. The wartime-era German Feuerwehr fire brigades were ill-equipped to fight the fires. The RAF's airstrikes destroyed areas of Wuppertal's north-eastern Barmen, central Elberfeld and south-eastern Ronsdorf communities, mainly through incendiary area bombing, resulting in destructive firestorms. Other Allied aircraft also carried out numerous smaller air raids on Wuppertal. Overall, more than 6,500 people lost their lives during World War II in Wuppertal from such raids; 38 percent of the built-up urban area was destroyed.

Wuppertal Hauptbahnhof is a railway station in the city of Wuppertal, just south of the Ruhr Area, in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It is on the line between Düsseldorf/Cologne and Dortmund. The 1848 reception building is one of the oldest of its kind. The station was originally Elberfeld station and has been renamed several times since. Since 1992, it has been called Wuppertal Hauptbahnhof. Wuppertal Hauptbahnhof is also the site of lost luggage operations for Deutsche Bahn.

Opernhaus Wuppertal is a German theatre in Wuppertal, North Rhine-Westphalia. It houses mostly performances of operas, but also plays, run by the municipal Wuppertaler Bühnen. The house is also the venue for dance performances by the Tanztheater Wuppertal company created by Pina Bausch.

Schauspielhaus Wuppertal was a Schauspielhaus, a theatre for plays, in Wuppertal, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. The 745-seat municipal theatre is on Bundesallee next to the river Wupper in Elberfeld. Designed by Gerhard Graubner, it was opened in 1966, run from 2001 by 'Wuppertaler Bühnen'. Starting in 2009, the house operated only 135 seats, and it was closed on 30 June 2013.

Wuppertal-Ronsdorf station is a station on the Wuppertal-Oberbarmen–Solingen railway in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 5 station. It is unusual in that it was once connected to lines with three different gauges.

Remscheid-Lüttringhausen station is a station on the Wuppertal-Oberbarmen–Solingen railway in Lüttringhausen in the German state of North Rhine Westphalia. It is served by line S 7 of the Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn.

Oskar Erbslöh was a German aviation pioneer.

Utopiastadt is a sociocultural center in Wuppertal, Germany, located in the city district of Elberfeld in the buildings of the now defunct railway station Wuppertal-Mirke, located at the "Nordbahntrasse", the railway now converted to a bike freeway. Most activities are performed by volunteers.
Eugen Felix Busmann was a German sculptor and academic teacher.
Guido Jendritzko was a German sculptor, painter, graphic artist and photographer. He was an important and versatile representative of Abstract art after the Second World War.

The Tietz department store in Wuppertal-Elberfeld is a historically significant department store building that was seized from its Jewish owners under the Nazis.

Friedrich Wilhelm Dörpfeld was a German pedagogue. A practising teacher, Dörpfeld never held a position at a university but was still considered a pedagogical authority. Dörpfeld applied the Herbartian philosophy to the level of elementary school. His Herbartianism was influenced by German Romanticism and therefore had strong religious undertones. Nevertheless, Dörpfeld defended the self-governance of schools against both secular and religious authorities. After retiring, Dörpfeld devoted himself to writing, most importantly The Connection Between Thought and Memory. He was father to Wilhelm Dörpfeld, the archaeologist, and Anna Carnap-Dörpfeld, the mother of Rudolf Carnap. Dörpfeld's work is said to have influenced Carnap's philosophy.