| Rosen Росен | |
|---|---|
| Village | |
| Coordinates: 42°23′N27°34′E / 42.383°N 27.567°E | |
| Country | |
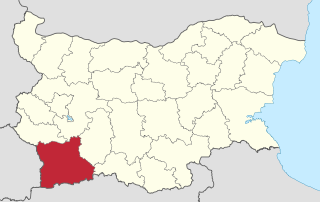
| Province | Burgas Province |
| Municipality | Sozopol |
| Area | |
| • Total | 38.386 km2 (14.821 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 87 m (285 ft) |
| Population (2013) [1] | |
| • Total | 1,470 |
| Time zone | EET (UTC+2) |
| • Summer (DST) | EEST (UTC+3) |
Rosen (Bulgarian : Росен) is a village in Sozopol Municipality, in Burgas Province, in south-eastern Bulgaria. As of 2013 it has 1470 inhabitants. [1]

Bulgarian, is an Indo-European language and a member of the Southern branch of the Slavic language family.

Sozopol Municipality is located in the southern Bulgarian Black Sea Coast and borders Burgas Municipality and Primorsko Municipality. The coast stretches 51 km of which 17.1 km are excellent beaches. There are many small bays and peninsulas as well as several isles. The climate is favourable for growing different crops such as grapes, apples, peaches, cherries, strawberries and others. Sozopol is the biggest fishing port of the country with two major plants processing fish. Tourism is now the most important industry with more than 50,000 beds in the territory of the municipality. As of 2006 the population is 13,401.

Burgas Province is a province in southeastern Bulgaria, including southern Bulgarian Black Sea Coast. It is bounded on the south by Turkey. The province is named after its administrative and industrial centre - the city of Burgas - the fourth biggest town in the country. It is the largest province by area, embracing a territory of 7,748.1 km² that is divided into 13 municipalities with a total population, as of December 2009, of 422,319 inhabitants.
The village is situated at the river Rosenska, a tributary to the Ropotamo, at the western foothills of Medni Rid Ridge, which is the north-eastern extreme of the Bosna Ridge in the Strandzha Mountains. [2] It is located at about 22 km south of Burgas and 19 km of the municipal centre Sozopol on the Bulgarian Black Sea coast. [1] [3]

The Ropotamo is a river in south-eastern Bulgaria. It takes its source from the Bosna Ridge in the Strandzha Mountains, running for 48.5 km to empty into the Black Sea near Cape Saint Demetrius between Dyuni and Primorsko.

Medni Rid, also known as Bakarlak (Бакърлък) until 1942, is a ridge in south-eastern Bulgaria. It forms the north-eastern extreme of the Bosna Ridge in the Strandzha Mountains. Administratively, it lies in the municipalities of Sozopol and Primorsko, Burgas Province.
Bosna is a ridge in the northern reaches of the Strandzha mountain range situated in the south-eastern part of the Balkan peninsula close to the Black Sea coast. While Strandzha is shared between Bulgaria and Turkey, the Bosna ridge is located entirely within the Bulgarian section of the mountain range. Its highest peak is Papiya. The ridge is approximately 65 km in length and 25 km in width. Most of Bosna falls within the borders of Strandzha Nature Park, the largest protected area in Bulgaria.
The vestiges of the medieval fortress of Krimna are situated at Bakarlaka peak in Medni Rid. In 1328 the Bulgarian emperor Michael Shishman and the Byzantine emperor Andronikos III Palaiologos signed an alliance treaty there. [4] The first school in what is now Sozopol Municipality was established in Rosen in 1830. The Church of Saint George was constructed in 1882. [4]

Michael Asen III, ruled as emperor (tsar) of Bulgaria from 1323 to 1330. The exact year of his birth is unknown but it was between 1280 and 1292. He was the founder of the last ruling dynasty of the Second Bulgarian Empire, the Shishman dynasty. After he was crowned, however, Michael used the name Asen to emphasize his connection with the Asen dynasty, the first one to rule over the Second Empire.

Andronikos III Palaiologos, commonly Latinized as Andronicus III Palaeologus, was Byzantine emperor from 1328 to 1341. Born Andronikos Doukas Angelos Komnenos Palaiologos, he was the son of Michael IX Palaiologos and Rita of Armenia. He was proclaimed co-emperor in his youth, before 1313, and in April 1321 he rebelled in opposition to his grandfather, Andronikos II Palaiologos. He was formally crowned co-emperor in February 1325, before ousting his grandfather outright and becoming sole emperor on 24 May 1328.