
Bavarian is a West Germanic language belonging to the Upper German group, spoken in the southeast of the German language area, much of Bavaria, most of Austria and South Tyrol in Italy, as well as Samnaun in Switzerland. Before 1945, Bavarian was also prevalent in parts of the southern Czech Republic and western Hungary. It forms a continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regional variants.
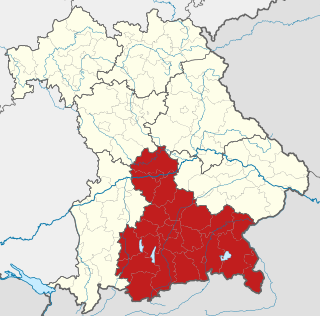
Upper Bavaria is one of the seven administrative districts of Bavaria, Germany.
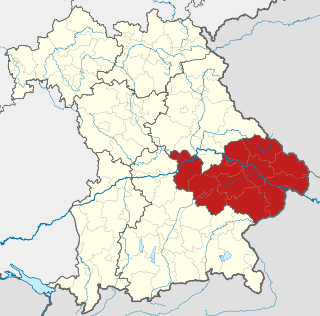
Lower Bavaria is one of the seven administrative regions of Bavaria, Germany, located in the east of the state.

Weilheim-Schongau is a Landkreis (district) in the south of Bavaria, Germany. Neighboring districts are Landsberg, Starnberg, Bad Tölz-Wolfratshausen, Garmisch-Partenkirchen and Ostallgäu.

Bavarian Alps is a summarizing term of several mountain ranges of the Northern Limestone Alps in the German state of Bavaria.

The Duchy of Bavaria was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarian tribes and ruled by dukes (duces) under Frankish overlordship. A new duchy was created from this area during the decline of the Carolingian Empire in the late ninth century. It became one of the stem duchies of the East Frankish realm which evolved as the Kingdom of Germany and the Holy Roman Empire.

The Amper, called the Ammer upstream of the Ammersee, through which it runs, is the largest tributary of the Isar in southern Bavaria, Germany. It flows generally north-eastward, reaching the Isar in Moosburg, about 190 kilometres (120 mi) from its source in the Ammergau Alps, with a flow of 45 m³/s. Including its tributary, Linder, it is 209.5 km (130.2 mi) long. Major tributaries are the Glonn, which springs near Augsburg; the Würm, which is the outflow of Lake Starnberg; and the Maisach.

Herrsching am Ammersee is a municipality in Upper Bavaria, Germany, on the east shore of the Ammersee, southwest of Munich. The population is around 8,000 in winter, increasing to 13,000 in summer.

Dießen am Ammersee is a municipality in the district of Landsberg in Bavaria in Germany. It is located on the shores of Ammersee lake.

Pähl am Ammersee is a municipality in the Weilheim-Schongau district, in Bavaria, Germany. It is on the lake of Ammersee to the southwest of Munich.

Schondorf am Ammersee is a municipality in the district Landsberg am Lech, Bavaria, Germany and is a member of the municipal association Schondorf am Ammersee The municipal association based in Schondorf.
The 1999 Pentecost flood was a 100-year flood around the Pentecost season in 1999 that mostly affected Bavaria, Vorarlberg and Tirol. It was caused by heavy rainfall coinciding with the regular Alpine meltwater.

The Ammersee Railway is a 54 km long single-tracked main line in the provinces of Swabia and Upper Bavaria in southern Germany. It runs from Mering near Augsburg via Geltendorf to Weilheim and is listed by the Deutsche Bahn as Kursbuchstrecke 985.
The Ammersee kilch is a species of freshwater whitefish endemic to Lake Ammersee in the German state of Upper Bavaria. A small, silver-colored fish, it typically lives between 60–85 m (197–279 ft) deep, though shallower in the summer months. In the early 20th century the Ammersee kilch was an important commercial species, but its population declined drastically in the 1930s onward due to overfishing and eutrophication of the only lake in which it is found. Today it is listed as Critically Endangered by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and may be on the verge of extinction.
The Bavarian Administration of State-Owned Palaces, Gardens and Lakes, also known as the Bavarian Palace Department, is a department of the finance ministry of the German state of Bavaria. Tracing its roots back into the 18th century, the administration is now best known for being in charge of Neuschwanstein Castle and the other 19th-century palaces built by Ludwig II of Bavaria.

The Bayerische Seenschifffahrt GmbH, or Bavarian Lakes Shipping Company, is a company that operates shipping services on several lakes in the German state of Bavaria. Services operate on the Königssee, the Starnberger See, the Ammersee and the Tegernsee.

Windach is a river of Bavaria, Germany. It flows into the Amper near Eching am Ammersee.

















