Related Research Articles

Diatomic molecules are molecules composed of only two atoms, of the same or different chemical elements. If a diatomic molecule consists of two atoms of the same element, such as hydrogen or oxygen, then it is said to be homonuclear. Otherwise, if a diatomic molecule consists of two different atoms, such as carbon monoxide or nitric oxide, the molecule is said to be heteronuclear. The bond in a homonuclear diatomic molecule is non-polar.

A quantum mechanical system or particle that is bound—that is, confined spatially—can only take on certain discrete values of energy, called energy levels. This contrasts with classical particles, which can have any amount of energy. The term is commonly used for the energy levels of the electrons in atoms, ions, or molecules, which are bound by the electric field of the nucleus, but can also refer to energy levels of nuclei or vibrational or rotational energy levels in molecules. The energy spectrum of a system with such discrete energy levels is said to be quantized.

Raman spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified.
Rotational–vibrational spectroscopy is a branch of molecular spectroscopy that is concerned with infrared and Raman spectra of molecules in the gas phase. Transitions involving changes in both vibrational and rotational states can be abbreviated as rovibrational transitions. When such transitions emit or absorb photons, the frequency is proportional to the difference in energy levels and can be detected by certain kinds of spectroscopy. Since changes in rotational energy levels are typically much smaller than changes in vibrational energy levels, changes in rotational state are said to give fine structure to the vibrational spectrum. For a given vibrational transition, the same theoretical treatment as for pure rotational spectroscopy gives the rotational quantum numbers, energy levels, and selection rules. In linear and spherical top molecules, rotational lines are found as simple progressions at both higher and lower frequencies relative to the pure vibration frequency. In symmetric top molecules the transitions are classified as parallel when the dipole moment change is parallel to the principal axis of rotation, and perpendicular when the change is perpendicular to that axis. The ro-vibrational spectrum of the asymmetric rotor water is important because of the presence of water vapor in the atmosphere.

Rotational spectroscopy is concerned with the measurement of the energies of transitions between quantized rotational states of molecules in the gas phase. The rotational spectrum of polar molecules can be measured in absorption or emission by microwave spectroscopy or by far infrared spectroscopy. The rotational spectra of non-polar molecules cannot be observed by those methods, but can be observed and measured by Raman spectroscopy. Rotational spectroscopy is sometimes referred to as pure rotational spectroscopy to distinguish it from rotational-vibrational spectroscopy where changes in rotational energy occur together with changes in vibrational energy, and also from ro-vibronic spectroscopy where rotational, vibrational and electronic energy changes occur simultaneously.
Molecular physics is the study of the physical properties of molecules and molecular dynamics. The field overlaps significantly with physical chemistry, chemical physics, and quantum chemistry. It is often considered as a sub-field of atomic, molecular, and optical physics. Research groups studying molecular physics are typically designated as one of these other fields. Molecular physics addresses phenomena due to both molecular structure and individual atomic processes within molecules. Like atomic physics, it relies on a combination of classical and quantum mechanics to describe interactions between electromagnetic radiation and matter. Experiments in the field often rely heavily on techniques borrowed from atomic physics, such as spectroscopy and scattering.

Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters that determine the position of each atom.
In physics and chemistry, a selection rule, or transition rule, formally constrains the possible transitions of a system from one quantum state to another. Selection rules have been derived for electromagnetic transitions in molecules, in atoms, in atomic nuclei, and so on. The selection rules may differ according to the technique used to observe the transition. The selection rule also plays a role in chemical reactions, where some are formally spin-forbidden reactions, that is, reactions where the spin state changes at least once from reactants to products.
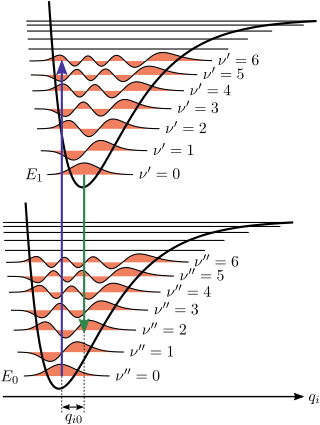
The Franck–Condon principle is a rule in spectroscopy and quantum chemistry that explains the intensity of vibronic transitions. The principle states that during an electronic transition, a change from one vibrational energy level to another will be more likely to happen if the two vibrational wave functions overlap more significantly.
The Jahn–Teller effect is an important mechanism of spontaneous symmetry breaking in molecular and solid-state systems which has far-reaching consequences in different fields, and is responsible for a variety of phenomena in spectroscopy, stereochemistry, crystal chemistry, molecular and solid-state physics, and materials science. The effect is named for Hermann Arthur Jahn and Edward Teller, who first reported studies about it in 1937.
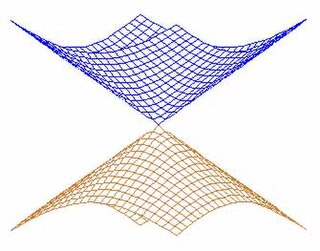
In quantum chemistry, a conical intersection of two or more potential energy surfaces is the set of molecular geometry points where the potential energy surfaces are degenerate (intersect) and the non-adiabatic couplings between these states are non-vanishing. In the vicinity of conical intersections, the Born–Oppenheimer approximation breaks down and the coupling between electronic and nuclear motion becomes important, allowing non-adiabatic processes to take place. The location and characterization of conical intersections are therefore essential to the understanding of a wide range of important phenomena governed by non-adiabatic events, such as photoisomerization, photosynthesis, vision and the photostability of DNA. The conical intersection involving the ground electronic state potential energy surface of the C6H3F3+ molecular ion is discussed in connection with the Jahn–Teller effect in Section 13.4.2 on pages 380-388 of the textbook by Bunker and Jensen.

In molecular spectroscopy, a Jablonski diagram is a diagram that illustrates the electronic states and often the vibrational levels of a molecule, and also the transitions between them. The states are arranged vertically by energy and grouped horizontally by spin multiplicity. Nonradiative transitions are indicated by squiggly arrows and radiative transitions by straight arrows. The vibrational ground states of each electronic state are indicated with thick lines, the higher vibrational states with thinner lines. The diagram is named after the Polish physicist Aleksander Jabłoński who first proposed it in 1933.
In atomic, molecular, and optical physics and quantum chemistry, the molecular Hamiltonian is the Hamiltonian operator representing the energy of the electrons and nuclei in a molecule. This operator and the associated Schrödinger equation play a central role in computational chemistry and physics for computing properties of molecules and aggregates of molecules, such as thermal conductivity, specific heat, electrical conductivity, optical, and magnetic properties, and reactivity.
The Renner-Teller effect is a phenomenon in molecular spectroscopy where the electronic states of a molecule are coupled to vibrational motion.
A molecular vibration is a periodic motion of the atoms of a molecule relative to each other, such that the center of mass of the molecule remains unchanged. The typical vibrational frequencies range from less than 1013 Hz to approximately 1014 Hz, corresponding to wavenumbers of approximately 300 to 3000 cm−1 and wavelengths of approximately 30 to 3 µm.

In chemistry, molecular symmetry describes the symmetry present in molecules and the classification of these molecules according to their symmetry. Molecular symmetry is a fundamental concept in chemistry, as it can be used to predict or explain many of a molecule's chemical properties, such as whether or not it has a dipole moment, as well as its allowed spectroscopic transitions. To do this it is necessary to use group theory. This involves classifying the states of the molecule using the irreducible representations from the character table of the symmetry group of the molecule. Symmetry is useful in the study of molecular orbitals, with applications to the Hückel method, to ligand field theory, and to the Woodward-Hoffmann rules. Many university level textbooks on physical chemistry, quantum chemistry, spectroscopy and inorganic chemistry discuss symmetry. Another framework on a larger scale is the use of crystal systems to describe crystallographic symmetry in bulk materials.
Molecular Spectra and Molecular Structure IV. Constants of Diatomic Molecules, by K. P. Huber and Gerhard Herzberg, is a classic comprehensive multidisciplinary reference text contains a critical compilation of available data for all diatomic molecules and ions known at the time of publication - over 900 diatomic species in all - including electronic energies, vibrational and rotational constants, and observed transitions. Extensive footnotes discuss the reliability of these data and additional detailed informationon potential energy curves, spin-coupling constants, /\-type doubling, perturbations between electronic states, hyperfine structure, rotational g factors, dipole moments, radiative lifetimes, oscillator strengths, dissociation energies and ionization potentials when available, and other aspects. Herzberg received the 1971 Nobel Prize in Chemistry; both authors are world-renowned highly respected scientists.
Vibronic spectroscopy is a branch of molecular spectroscopy concerned with vibronic transitions: the simultaneous changes in electronic and vibrational energy levels of a molecule due to the absorption or emission of a photon of the appropriate energy. In the gas phase, vibronic transitions are accompanied by changes in rotational energy also.
Molecular symmetry in physics and chemistry describes the symmetry present in molecules and the classification of molecules according to their symmetry. Molecular symmetry is a fundamental concept in the application of Quantum Mechanics in physics and chemistry, for example it can be used to predict or explain many of a molecule's properties, such as its dipole moment and its allowed spectroscopic transitions, without doing the exact rigorous calculations. To do this it is necessary to classify the states of the molecule using the irreducible representations from the character table of the symmetry group of the molecule. Among all the molecular symmetries, diatomic molecules show some distinct features and they are relatively easier to analyze.

Jim Watson, FRS, who published under the name J.K.G. Watson, was a molecular spectroscopist most well known for the development of the widely used molecular Hamiltonians named after him. These Hamiltonians are used to describe the quantum dynamics of molecules.
References
- ↑ Jungen, Ch (2019-01-22). Molecular Applications of Quantum Defect Theory. Routledge. p. 8. ISBN 978-1-351-43034-0.