
A royal funeral chariot is a wheeled vehicle traditionally used to transport the bodies of royalty during funeral processions in some cultures of Mainland Southeast Asia. Today, they remain in use in Thailand and Cambodia.

A royal funeral chariot is a wheeled vehicle traditionally used to transport the bodies of royalty during funeral processions in some cultures of Mainland Southeast Asia. Today, they remain in use in Thailand and Cambodia.
The royal funeral chariots of Thailand were used since the Ayutthaya period, but they were destroyed when Ayutthaya was completely sacked in 1767. New funeral chariots were commissioned during the reign of King Rama I, at the beginning of the Rattanakosin period. They include, among other smaller accompanying vehicles, the two main chariots which have been used to transport the bodies of kings of the Chakri dynasty, the Maha Phichai Ratcharot ("Royal Great Victory Carriage" or "Royal Chariot of Great Victory"), built in 1795, and Vejayanta Ratcharot (Named after Indra's chariot Vejayanta), built in 1799. The chariots, built of teak and ornately carved, gilded and decorated, have a tall, tiered design symbolizing Mount Meru surrounded by devata (angels) and nāga . The chariots are topped with a butsabok (open-sided roofed structure) which houses the royal funerary urn containing the royal body. Despite the term used, the "chariots" have four wheels and are pulled by hundreds of men. [1] [2]
The Maha Phichai Ratcharot was used for the funeral procession of King Bhumibol Adulyadej in October 2017. It was drawn by 216 men. The 13.7 tonne chariot is 18 metres long, 11.2 metres high, and 4.8 metres wide. It has been used 25 times, most recently in 2012 for the cremation of Princess Bejaratana Rajasuda, the late king's cousin. [3]
The royal chariots are housed in the Bangkok National Museum and undergo restoration when they are needed for royal funerals. Following custom, The doorsill of the exhibition hall and a section of the museum wall are demolished and a path is laid each time the chariots need to be brought outside. Then the structures are rebuilt and the path removed after the ceremony ends, signifying that their future use is not anticipated. [4]

An additional chariot, the Rajarot Puen Yai (royal gun carriage), is used only for the cremations of the King in his constitutional duty as Head of the Royal Thai Armed Forces (a tradition started by King Vajiravudh on his request to recognize the royal patronage and support for the armed services of the Kingdom, used for the first time in his state cremation in 1926) [5] as the urn carrying his remains is carried in procession around the royal crematorium at the Sanam Luang Royal Plaza thrice before the cremation services begin. The carriage is modeled on those used in the royal and state funerals in the United Kingdom, and was restored yet again in 2017.

Wat Phra Kaew, commonly known in English as the Temple of the Emerald Buddha and officially as Wat Phra Si Rattana Satsadaram, is regarded as the most sacred Buddhist temple in Thailand. The complex consists of a number of buildings within the precincts of the Grand Palace in the historical centre of Bangkok. It houses the statue of the Emerald Buddha, which is venerated as the country's palladium.

The Grand Palace is a complex of buildings at the heart of Bangkok, Thailand. The palace has been the official residence of the Kings of Siam since 1782. The king, his court, and his royal government were based on the grounds of the palace until 1925. King Bhumibol Adulyadej, resided at the Chitralada Royal Villa and his successor King Vajiralongkorn resides at the Amphorn Sathan Residential Hall, both in the Dusit Palace, but the Grand Palace is still used for official events. Several royal ceremonies and state functions are held within the walls of the palace every year. The palace is one of the most popular tourist attractions in Thailand, with over eight million people visiting each year.

Galyani Vadhana, Princess of Naradhiwas was a princess of Thailand and the elder sister of King Ananda Mahidol and King Bhumibol Adulyadej. She was also a direct granddaughter of King Chulalongkorn and Queen Sri Savarindira and the aunt of King Vajiralongkorn.

Thailand's Royal Barge Procession is a ceremony of both religious and royal significance which has taken place for nearly 700 years. The royal barges are a blend of craftsmanship and traditional Thai art. The Royal Barge Procession takes place rarely, marking only the most significant cultural and religious events. During the long reign of King Bhumibol Adulyadej, spanning over 70 years, the procession only occurred 16 times.

Sunanda Kumariratana was a queen consort of Siam. She was one of the four royal wives of King Chulalongkorn.

The Bangkok National Museum is the main branch museum of the National Museums in Thailand and also one of the largest museums in Southeast Asia. It features exhibits of Thai art and history. It occupies the former palace of the vice king, set between Thammasat University and the National Theater, facing Sanam Luang.

Krom Phra Ratchawang Bowon Sathan Mongkhon กรมพระราชวังบวรสถานมงคล, colloquially known as the Front Palace, was the title of the uparaja of Siam, variously translated as "viceroy", "vice king" or "Lord/Prince of the Front Palace", as the titleholder resided in the physical residence of the same name. The office of Front Palace was considered second only to the king and regarded as the heir presumptive. The name, with its dual meaning, originated in the Ayutthaya period, and the holder later gained significant powers during the Rattanakosin period. Front Palace occupants were usually a son or brother of the reigning monarch. The office existed until the death of the last occupant, Prince Wichaichan, in 1885. King Chulalongkorn then abolished the office of an heir presumptive, introducing in its stead the Western concept of a crown prince as heir apparent, and styled the new office "Crown Prince of Siam".

The Royal Standard of Thailand is the official flag of the King of Thailand. The present form was adopted in 1910 under Vajiravudh, superseding the first Royal Standard created by Mongkut in 1855. In 1979, the designs were codified by law; specifically in Article 2 of the Flag Act of 1979, which also regulated Thailand's other flags. The standard is currently used by Maha Vajiralongkorn, also known as Rama X, since 2016.

King Thong Lan was a king of Ayutthaya, an ancient kingdom in Thailand.
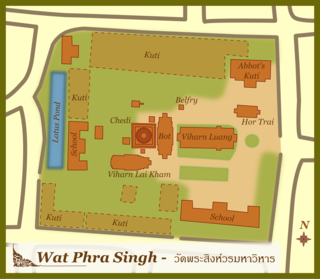
Wat Phra Singh is a Buddhist temple in Chiang Mai, northern Thailand. King Ananda Mahidol, bestowed upon it the status of Royal temple of the first grade in 1935.
Ramrachathirat was a king of Ayutthaya, an ancient kingdom in Thailand.

King Taksin the Great or the King of Thonburi was the only king of the Thonburi Kingdom that ruled Thailand from 1767 to 1782. He had been an aristocrat in the Ayutthaya Kingdom and then was a major leader during the liberation of Siam from Burmese occupation after the Second Fall of Ayutthaya in 1767, and the subsequent unification of Siam after it fell under various warlords. He established the city of Thonburi as the new capital, as the city of Ayutthaya had been almost completely destroyed by the invaders. His reign was characterized by numerous wars; he fought to repel new Burmese invasions and to subjugate the northern Thai kingdom of Lanna, the Laotian principalities, and threatening Cambodia.

King Bhumibol Adulyadej of Thailand died at the age of 88 on 13 October 2016, after a long illness. A year-long period of mourning was subsequently announced. A royal cremation ceremony took place over five days at the end of October 2017. The actual cremation, which was not broadcast on television, was held in the late evening of 26 October 2017. Following cremation his remains and ashes were taken to the Grand Palace and were enshrined at the Chakri Maha Phasat Throne Hall, the Royal Cemetery at Wat Ratchabophit and the Wat Bowonniwet Vihara Royal Temple. Following burial, the mourning period officially ended on midnight of 30 October 2017 and Thais resumed wearing colors other than black in public.
The coronation of the monarch of Thailand is a ceremony in which they are formally consecrated by anointment and crowning. The ceremony is divided into two main events: the coronation rites and the celebration of the Assumption of the Residence. The coronation rites are a blend of Hindu and Buddhist traditions dating back several centuries. The rites included the purification bath of the king, the anointing of the king, the crowning of the king, and the investiture of the royal regalia, the royal utensils, and the royal weapons of sovereignty. The Assumption of the Residence is a private housewarming celebration by members of the royal family at the Grand Palace.

Thai funerals usually follow Buddhist funerary rites, with variations in practice depending on the culture of the region. People of certain religious and ethnic groups also have their own specific practices. Thai Buddhist funerals generally consist of a bathing ceremony shortly after death, daily chanting by Buddhist monks, and a cremation ceremony. Cremation is practised by most peoples throughout the country, with the major exceptions being ethnic Chinese, Muslims and Christians.

Thai royal funerals are elaborate events, organised as royal ceremonies akin to state funerals. They are held for deceased members of the royal family, and consist of numerous rituals which typically span several months to over a year. Featuring a mixture of Buddhist and animist beliefs, as well as Hindu symbolism, these rituals include the initial rites that take place after death, a lengthy period of lying-in-state, during which Buddhist ceremonies take place, and a final cremation ceremony. For the highest-ranking royalty, the cremation ceremonies are grand public spectacles, featuring the pageantry of large funeral processions and ornate purpose-built funeral pyres or temporary crematoria known as merumat or men. The practices date to at least the 17th century, during the time of the Ayutthaya Kingdom. Today, the cremation ceremonies are held in the royal field of Sanam Luang in the historic centre of Bangkok.
The royal cremation ceremony is the final and most major event during Thai royal funerals.

Wat Arun is one of two khwaeng (subdistrict) of Bangkok Yai District, Bangkok, apart from Wat Tha Phra. It can be considered an important area in terms of history and tourism.

A busabok is a small open structure used in Thai culture as a throne for the monarch or for the enshrinement of Buddha images or other sacred objects. It is square-based and open-sided, usually with twelve indented corners, with four posts supporting a roughly pyramidal multi-tiered roof culminating in a pointed spire, and usually richly decorated. The structure of the multi-tiered roof is very similar, but much smaller in size, to the mondop architectural form. The term is derived from the Sanskrit word puṣpaka, a reference to the Pushpaka Vimana, a flying chariot from the Hindu epic Ramayana.