
Rudbar Mahal was one of seventeen districts in the Shirvan Khanate at the time it was annexed by Russia in 1820. [1]

Rudbar Mahal was one of seventeen districts in the Shirvan Khanate at the time it was annexed by Russia in 1820. [1]
The Rudbar Mahal was present in Sabirabad, Saatly, Neftchala and Hajigabul Districts.[ clarification needed ]
The governor (naib) of mahal was Dargha Mammadkhan (the second half of the 18th century).
In 1821 there were eighteen settlements (Javad, Dabbaglar, Balvan, Qarali, Yenikend, Gazili, Ahmedbeyli, Guruzmanli, Abdulyan, Yenica, Mustafali, Ahtaci, Meyniman, Kovratlı, Surra Atamoghlan, Surra Aghabedal, Surra Mammad, Surra Abdulla bey, Alimadatli) where 422 families lived. [2]
Residents of the Rudbar district were engaged in agriculture and sericulture.

Shirvan is a historical region in the eastern Caucasus, as known in both pre-Islamic Sasanian and Islamic times. Today, the region is an industrially and agriculturally developed part of the Republic of Azerbaijan that stretches between the western shores of the Caspian Sea and the Kura River, centered on the Shirvan Plain.

The Karabakh Khanate was a khanate under Iranian and later Russian suzerainty, which controlled the historical region of Karabakh, now divided between modern-day Armenia and Azerbaijan. In terms of structure, the Karabakh Khanate was a miniature version of Iranian kingship. The administrative and literary language in Karabakh until the end of the 19th century was Persian, with Arabic being used only for religious studies, despite the fact that most of the Muslims in the region spoke a Turkic dialect.
The Russo-Persian Wars or Russo-Iranian Wars were a series of conflicts between 1651 and 1828, concerning Persia and the Russian Empire. Russia and Persia fought these wars over disputed governance of territories and countries in the Caucasus. The main territories disputed were Aran, Georgia and Armenia, as well as much of Dagestan – generally referred to as Transcaucasia – and considered part of the Safavid Iran prior to the Russo-Persian Wars. Over the course of the five Russo-Persian Wars, the governance of these regions transferred between the two empires. Between the Second and Third Russo-Persian Wars, there was an interbellum period in which a number of treaties were drawn up between the Russian and the Persian Empires, as well as between both parties and the Ottoman Empire. Ottoman interest in these territories further complicated the wars, with both sides forming alliances with the Ottoman Empire at different points throughout the wars. Following the Treaty of Turkmenchay, which concluded the Fifth Russo-Persian War, Persia ceded much of its Transcaucasian territory to the Russian Empire.

The Baku Khanate, was a khanate under Iranian suzerainty, which controlled the city of Baku and its surroundings from 1747 to 1806.

The Quba Khanate was one of the most significant semi-independent khanates that existed from 1747 to 1806, under Iranian suzerainty. It bordered Caspian sea to the east, Derbent Khanate to the north, Shaki Khanate to the west, and Baku and Shirvan Khanates to the south. In 1755 it captured Salyan from the Karabakh Khanate.
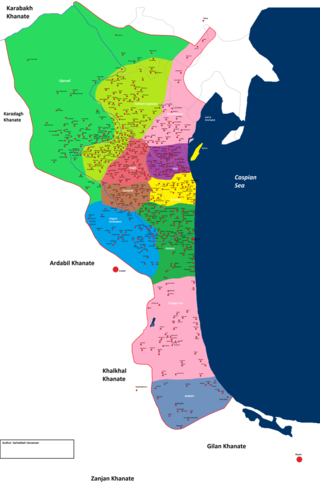
Talysh Khanate or Talish Khanate was an Iranian khanate of Iranian origin that was established in Afsharid Persia and existed from the middle of the 18th century till the beginning of the 19th century, located in the south-west coast of the Caspian Sea.

The Ganja Khanate was a khanate under Iranian suzerainty, which controlled the town of Ganja and its surroundings, now located in present-day Azerbaijan.

The Shaki Khanate was a khanate under Iranian and later Russian suzerainty, which controlled the town of Shaki and its surroundings, now located in present-day Azerbaijan.

Shirvan Khanate was a Caucasian khanate under Iranian suzerainty, which controlled the Shirvan region from 1761 to 1820.

The Erivan Khanate, also known as Chokhur-e Sa'd, was a khanate that was established in Afsharid Iran in the 18th century. It covered an area of roughly 19,500 km2, and corresponded to most of present-day central Armenia, the Iğdır Province and the Kars Province's Kağızman district in present-day Turkey and the Sharur and Sadarak districts of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic of present-day Azerbaijan.
Zayn al-Abidin Shirvani, also known by his pen-name of Tamkin, was a Persian scholar, mystic, and traveler from Shirvan.

The khanates of the Caucasus, also known as the Azerbaijani khanates, Persian khanates, or Iranian khanates, were various administrative units in the South Caucasus governed by a hereditary or appointed ruler under the official rule of Iran. The title of the ruler was khan, which was identical to the Ottoman rank of pasha. Following the assassination of Nader Shah in 1747, internal chaos erupted in Iran, particularly in the South Caucasus, where semi-autonomous khanates emerged as a result of the lack of a centralized government. The khans neither had territorial or religious unity, nor an ethnic/national identity. They were mostly interested in preserving their positions and income.

Mughan plain is a plain stretching from northwestern Iran to the southern part of the Republic of Azerbaijan. The highest density of irrigation canals is in the section of the Mughan plain which lies in the Republic of Azerbaijan. It is located on the bank of the Aras river extending to Iran.

The Russian conquest of the Caucasus mainly occurred between 1800 and 1864. The Russian Empire sought to control the region between the Black Sea and Caspian Sea. South of the mountains was the territory that is modern Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Iran and Turkey. North of the mountains was the North Caucasus region of modern Russia. The difficult conquest of the intervening mountains is known as the Caucasian War. Multiple wars were fought against the local rulers of the regions, as well as the dominant powers, the Ottoman Empire and Qajar Iran, for control. By 1864 the last regions were brought under Russian control.

Qalaqayın is a village and the most populous municipality, except for the capital Sabirabad, in the Sabirabad Rayon of Azerbaijan. It has a population of 7,658.
The fortress of the historic Javad Khanate and the center of the Mughan district.

The Derbent Khanate was a Caucasian khanate that was established in Afsharid Iran. It corresponded to southern Dagestan and its center was at Derbent.
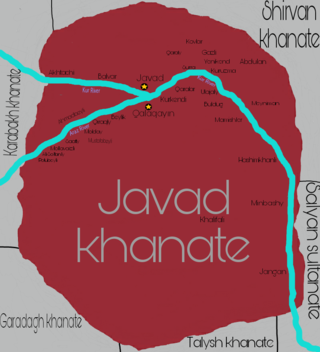
Javad Khanate was a Caucasian khanate with its capital in the town of Javad. It extended from Javad on the Kura River southwest along the east side of the Aras River. It was bordered by the Shamakhy (north), Karabakh (west), Karadagh (southwest) and Talysh khanates (south), and the Salyan Sultanate (east), its territory lays within modern Azerbaijan.

The Sultanate of Elisu, also known as Elisou or Ilisu, was a sultanate in the 18th and 19th centuries.
Mostafa Khan was the last khan of Shirvan, until 1820.

Otuzikilar district or mahal of Otuzikilar was one of the mahals of the Karabakh khanate. Today, the territory of the Otuziki mahal, being historically small in area, corresponds to the territory of the Aghdam region of modern Azerbaijan.
Serious historians and geographers agree that after the fall of the Safavids, and especially from the mid-eighteenth century, the territory of the South Caucasus was composed of the khanates of Ganja, Kuba, Shirvan, Baku, Talesh, Sheki, Karabagh, Nakhichivan and Yerevan, all of which were under Iranian suzerainty.