
In primates, and specifically in humans, the labia majora, also known as the outer lips or outer labia, are two prominent longitudinal skin folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum. Together with the labia minora, they form the labia of the vulva.

The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the gastric phase of digestion, following the cephalic phase in which the sight and smell of food and the act of chewing are stimuli. In the stomach a chemical breakdown of food takes place by means of secreted digestive enzymes and gastric acid.

The gastrointestinal tract is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. Gastrointestinal is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines.

The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the pancreatic duct to aid in digestion. The small intestine is about 5.5 metres long and folds many times to fit in the abdomen. Although it is longer than the large intestine, it is called the small intestine because it is narrower in diameter.

The esophagus, oesophagus, or œsophagus all ; pl.: ( e)(œ)sophagi or (œ)sophaguses), colloquially known also as the food pipe, food tube, or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the stomach. The esophagus is a fibromuscular tube, about 25 cm (10 in) long in adults, that travels behind the trachea and heart, passes through the diaphragm, and empties into the uppermost region of the stomach. During swallowing, the epiglottis tilts backwards to prevent food from going down the larynx and lungs. The word oesophagus is from Ancient Greek οἰσοφάγος (oisophágos), from οἴσω (oísō), future form of φέρω + ἔφαγον.

The pylorus connects the stomach to the duodenum. The pylorus is considered as having two parts, the pyloric antrum and the pyloric canal. The pyloric canal ends as the pyloric orifice, which marks the junction between the stomach and the duodenum. The orifice is surrounded by a sphincter, a band of muscle, called the pyloric sphincter. The word pylorus comes from Greek πυλωρός, via Latin. The word pylorus in Greek means "gatekeeper", related to "gate" and is thus linguistically related to the word "pylon".

The human female reproductive system is made up of the internal and external sex organs that function in the reproduction of new offspring. The reproductive system is immature at birth and develops at puberty to be able to release matured ova from the ovaries, facilitate their fertilization, and create a protective environment for the developing fetus during pregnancy. The female reproductive tract is made of several connected internal sex organs—the vagina, uterus, and fallopian tubes—and is prone to infections. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse, and is connected to the uterus at the cervix. The uterus accommodates the embryo by developing the uterine lining.

Fetal pigs are unborn pigs used in elementary as well as advanced biology classes as objects for dissection. Pigs, as a mammalian species, provide a good specimen for the study of physiological systems and processes due to the similarities between many pig and human organs.

The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that play a role in the process of human reproduction. These organs are located on the outside of the body, and within the pelvis.

Gastric glands are glands in the lining of the stomach that play an essential role in the process of digestion. Their secretions make up the digestive gastric juice. The gastric glands open into gastric pits in the mucosa. The gastric mucosa is covered in surface mucous cells that produce the mucus necessary to protect the stomach's epithelial lining from gastric acid secreted by parietal cells in the glands, and from pepsin, a secreted digestive enzyme. Surface mucous cells follow the indentations and partly line the gastric pits. Other mucus secreting cells are found in the necks of the glands. These are mucous neck cells that produce a different kind of mucus.

The circular folds are large valvular flaps projecting into the lumen of the small intestine.

Equine anatomy encompasses the gross and microscopic anatomy of horses, ponies and other equids, including donkeys, mules and zebras. While all anatomical features of equids are described in the same terms as for other animals by the International Committee on Veterinary Gross Anatomical Nomenclature in the book Nomina Anatomica Veterinaria, there are many horse-specific colloquial terms used by equestrians.

The gastric mucosa is the mucous membrane layer of the stomach, which contains the gastric pits, to which the gastric glands empty. In humans, it is about one mm thick, and its surface is smooth, soft, and velvety. It consists of simple secretory columnar epithelium, an underlying supportive layer of loose connective tissue called the lamina propria, and the muscularis mucosae, a thin layer of muscle that separates the mucosa from the underlying submucosa.
The development of the reproductive system is the part of embryonic growth that results in the sex organs and contributes to sexual differentiation. Due to its large overlap with development of the urinary system, the two systems are typically described together as the genitourinary system.
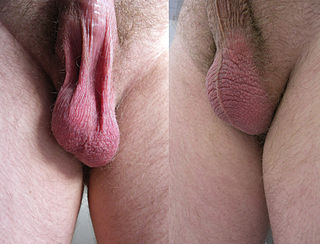
In most terrestrial mammals, the scrotum or scrotal sac is a part of the external male genitalia located at the base of the penis. It consists of a sac of skin containing the external spermatic fascia, testicles, epididymides, and vasa deferentia. The scrotum will usually tighten when exposed to cold temperatures.

The gastric folds are coiled sections of tissue that exist in the mucosal and submucosal layers of the stomach. They provide elasticity by allowing the stomach to expand when a bolus enters it. These folds stretch outward through the action of mechanoreceptors, which respond to the increase in pressure. This allows the stomach to expand, therefore increasing the volume of the stomach without increasing pressure. They also provide the stomach with an increased surface area for nutrient absorption during digestion. Gastric folds may be seen during esophagogastroduodenoscopy or in radiological studies.

The gastrointestinal wall of the gastrointestinal tract is made up of four layers of specialised tissue. From the inner cavity of the gut outwards, these are the mucosa, the submucosa, the muscular layer and the serosa or adventitia.

The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion. Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has three stages: the cephalic phase, the gastric phase, and the intestinal phase.
Vaginal rugae are structures of the vagina that are transverse ridges formed out of the supporting tissues and vaginal epithelium in females. Some conditions can cause the disappearance of vaginal rugae and are usually associated with childbirth and prolapse of pelvic structures. The rugae contribute to the resiliency and elasticity of the vagina and its ability to distend and return to its previous state. These structures not only allow expansions and an increase in surface area of the vaginal epithelium, they provide the space necessary for the vaginal microbiota. The shape and structure of the rugae are supported and maintained by the lamina propria of the vagina and the anterior and posterior rugae.


















