Related Research Articles

Mercury is the first planet from the Sun and the smallest in the Solar System. In English, it is named after the ancient Roman god Mercurius (Mercury), god of commerce and communication, and the messenger of the gods. Mercury is classified as a terrestrial planet, with roughly the same surface gravity as Mars. The surface of Mercury is heavily cratered, as a result of countless impact events that have accumulated over billions of years. Its largest crater, Caloris Planitia, has a diameter of 1,550 km (960 mi), which is about one-third the diameter of the planet. Similarly to the Earth's Moon, Mercury's surface displays an expansive rupes system generated from thrust faults and bright ray systems formed by impact event remnants.

A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets by the most restrictive definition of the term: the terrestrial planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, and the giant planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a young protostar orbited by a protoplanetary disk. Planets grow in this disk by the gradual accumulation of material driven by gravity, a process called accretion.

Terraforming or terraformation ("Earth-shaping") is the hypothetical process of deliberately modifying the atmosphere, temperature, surface topography or ecology of a planet, moon, or other body to be similar to the environment of Earth to make it habitable for humans to live on.

Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is a terrestrial planet and is the closest in mass and size to its orbital neighbour Earth. Venus has by far the densest atmosphere of the terrestrial planets, composed mostly of carbon dioxide with a thick, global sulfuric acid cloud cover. At the surface it has a mean temperature of 737 K and a pressure 92 times that of Earth's at sea level. These extreme conditions compress carbon dioxide into a supercritical state at Venus's surface.

In astronomy, a conjunction occurs when two astronomical objects or spacecraft appear to be close to each other in the sky. This means they have either the same right ascension or the same ecliptic longitude, usually as observed from Earth.
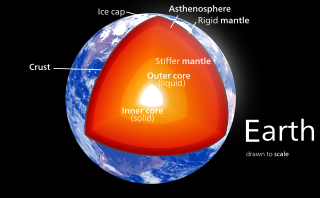
In geology, the crust is the outermost solid shell of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. It is usually distinguished from the underlying mantle by its chemical makeup; however, in the case of icy satellites, it may be distinguished based on its phase.

Radar astronomy is a technique of observing nearby astronomical objects by reflecting radio waves or microwaves off target objects and analyzing their reflections. Radar astronomy differs from radio astronomy in that the latter is a passive observation and the former an active one. Radar systems have been conducted for six decades applied to a wide range of Solar System studies. The radar transmission may either be pulsed or continuous. The strength of the radar return signal is proportional to the inverse fourth-power of the distance. Upgraded facilities, increased transceiver power, and improved apparatus have increased observational opportunities.

The Discovery Program is a series of Solar System exploration missions funded by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) through its Planetary Missions Program Office. The cost of each mission is capped at a lower level than missions from NASA's New Frontiers or Flagship Programs. As a result, Discovery missions tend to be more focused on a specific scientific goal rather than serving a general purpose.
A classical planet is an astronomical object that is visible to the naked eye and moves across the sky and its backdrop of fixed stars. Visible to humans on Earth there are seven classical planets. They are from brightest to dimmest: the Sun, the Moon, Venus, Jupiter, Mars, Mercury and Saturn.

A transit of Mercury across the Sun as seen from Mars takes place when the planet Mercury passes directly between the Sun and Mars, obscuring a small part of the Sun's disc for an observer on Mars. During a transit, Mercury can be seen from Mars as a small black disc moving across the face of the Sun.

Rille is typically used to describe any of the long, narrow depressions in the surface of the Moon that resemble channels. The Latin term is rima, plural rimae. Typically, a rille can be several kilometers wide and hundreds of kilometers in length. However, the term has also been used loosely to describe similar structures on a number of planets in the Solar System, including Mars, Venus, and on a number of moons. All bear a structural resemblance to each other.

Verona Rupes is the tallest known cliff on Miranda, a moon of Uranus, and plausibly holds the record for the highest cliff in the Solar System. It was discovered by the Voyager 2 space probe in January 1986. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1988, named after the city of Verona, which is the setting for Romeo and Juliet, written by William Shakespeare. It may have been created by a major impact that caused the moon to disrupt and reassemble, or by the crust rifting. Given Miranda's low gravity, it would take about 12 minutes to fall from the top, reaching the bottom at a speed of about 200 km/h.

A crater chain is a line of craters along the surface of an astronomical body. The descriptor term for crater chains is catena, plural catenae, as specified by the International Astronomical Union's rules on planetary nomenclature.
Planetary symbols are used in astrology and traditionally in astronomy to represent a classical planet or one of the modern planets. The classical symbols were also used in alchemy for the seven metals known to the ancients, which were associated with the planets, and in calendars for the seven days of the week associated with the seven planets. The original symbols date to Greco-Roman astronomy; their modern forms developed in the 16th century, and additional symbols would be created later for newly discovered planets.

Sobkou Planitia is a large basin on the planet Mercury. It is named after the ancient Egyptian messenger deity Sobkou. He was associated by the Egyptians with the planet Mercury.

Santa María Rupes is a prominent lobate escarpment and fault line on Mercury. According to data from Arecibo, it has a relief of roughly 700m. The formation was named after the ship Santa María, used by Christopher Columbus. The escarpment was probably created as Mercury cooled and thus contracted.

Rousillon Rupes is a scarp on the surface of the Uranian moon Titania named after "Bertram, count of Rousillon" in William Shakespeare's comedy All's Well That Ends Well. The 402 km long feature is a normal fault situated near the equator and running perpendicular to it. The scarp cuts impact craters, which probably means that it was formed at a relatively late stage of moon's evolution, when the interior of Titania expanded and its ice crust cracked as a result. Rousillon Rupes has only few crater superimposed on it, which also implies its relatively young age. The scarp was first imaged by Voyager 2 spacecraft in January 1986.
In astrology, planets have a meaning different from the astronomical understanding of what a planet is. Before the age of telescopes, the night sky was thought to consist of two similar components: fixed stars, which remained motionless in relation to each other, and moving objects/"wandering stars", which moved relative to the fixed stars over the course of the year(s).

Mons is a mountain on a celestial body. The term is used in planetary nomenclature: it is a part of the international names of such features. It is capitalized and usually stands after the proper given name, but stands before it in the case of lunar mountains.

A crater is a landform consisting of a hole or depression on a planetary surface, usually caused either by an object hitting the surface, or by geological activity on the planet. A crater has classically been described as: "a bowl-shaped pit that is formed by a volcano, an explosion, or a meteorite impact". On Earth, craters are "generally the result of volcanic eruptions", while "meteorite impact craters are common on the Moon, but are rare on Earth".
References
- ↑ The two Latin forms, singular rūpes with a short 'e' and plural rūpēs with a long 'e', are spelled the same in English.
- ↑ USGS Astrogeology: Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature - Feature Types
- ↑ "APOD: 21 January 1996 - Mercury's Faults". APOD (Astronomy Picture of the Day). 1996-01-21. Retrieved 2008-04-16.