EFnet or Eris-Free network is a major Internet Relay Chat (IRC) network, with more than 35,000 users. It is the modern-day descendant of the original IRC network.

The Undernet is the third largest publicly monitored Internet Relay Chat (IRC) network, c. 2022, with about 36 client servers serving 47,444 users in ~6000 channels at any given time.
DALnet is an Internet Relay Chat (IRC) network made up of 39 servers, with a stable population of approximately 10,000 users in about 4,000 channels.
DALnet is accessible by connecting with an IRC client to an active DALnet server on ports 6660 through 6669, and 7000. SSL users can connect on port 6697 as well. The generic round-robin address is irc.dal.net.

Internet Relay Chat (IRC) is a text-based chat system for instant messaging. IRC is designed for group communication in discussion forums, called channels, but also allows one-on-one communication via private messages as well as chat and data transfer, including file sharing.
ICQ New is a cross-platform instant messaging (IM) and VoIP client. The name ICQ derives from the English phrase "I Seek You". Originally developed by the Israeli company Mirabilis in 1996, the client was bought by AOL in 1998, and then by Mail.Ru Group in 2010.

QuakeNet is an Internet Relay Chat (IRC) network, and was one of the largest IRC networks. The network was founded in 1997 by Garfield and Oli as a new home for their respective countries' Quake channels. At its peak on February 8, 2005, the network recorded 243,394 simultaneous connections. As of 2020, there are 9 servers and about 12,000 users remaining.
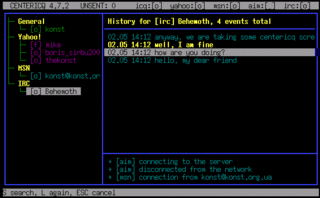
Centericq is a text mode menu- and window-driven instant messaging interface that supports the ICQ, Yahoo!, AIM, MSN, IRC, XMPP, LiveJournal, and Gadu-Gadu protocols.
IRCnet is currently the third largest IRC network with around 25,000 users using it daily. An early 2005 record had approximately 123,110 users simultaneously connected to the network.
Internet Relay Chat services is a name for a set of features implemented on many modern Internet Relay Chat networks. Services are automated bots with special status which are generally used to provide users with access with certain privileges and protection. They usually implement some sort of login system so that only people on the access control list can obtain these services.
GameSurge is a popular Internet Relay Chat network devoted to the online multiplayer gaming community. Games commonly seen referenced on GameSurge include many first person shooters and MMORPGs.
An IRC bot is a set of scripts or an independent program that connects to Internet Relay Chat as a client, and so appears to other IRC users as another user. An IRC bot differs from a regular client in that instead of providing interactive access to IRC for a human user, it performs automated functions.
An IRCd, short for Internet Relay Chat daemon, is server software that implements the IRC protocol, enabling people to talk to each other via the Internet. It is distinct from an IRC bot that connects outbound to an IRC channel.
A BNC is a piece of software that is used to relay traffic and connections in computer networks, much like a proxy. Using a BNC allows a user to hide the original source of the user's connection, providing privacy as well as the ability to route traffic through a specific location. A BNC can also be used to hide the true target to which a user connects.
SlashNET is a medium-sized, independently operated Internet Relay Chat (IRC) network. Originally sponsored by Slashdot and founded in 1998, in 1999 SlashNET split off to become its own entity. A few well-known communities and projects maintain an IRC presence at SlashNET, including #g7, #totse (Totse), #idiots-club, #mefi, various Penny Arcade-related communities, #Twitterponies, and #rags. As of 2012 it is ranked in the top 40 networks by IRC.Netsplit.de, with an estimated relatively constant 1700 users, and #25/737 by SearchIRC.com.
Rizon is a large Internet Relay Chat (IRC) network with an average of around 20,000 users. The IRC network itself ranks number 5 among the largest IRC networks. Rizon is popular with many anime fansubbing groups who work online, many of whom provide their content through XDCC via IRC bots in their distribution channels. It is also used by many users of eRepublik as a means of communication. File sharing of other copyrighted material such as Warez is also common in some channels on the network.
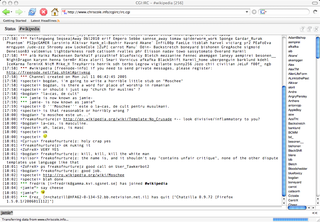
CGI:IRC is a CGI program written in Perl that allows access to IRC via a web browser. It is designed to be flexible and has many uses such as an IRC gateway for an IRC network, a chat-room for a website or to access IRC when stuck behind a restrictive firewall.

Mibbit is a web-based client for web browsers that supports Internet Relay Chat (IRC), Yahoo! Messenger, and Twitter. It is developed by Jimmy Moore and is designed around the Ajax model with a user interface written in JavaScript. It is the IRC application setup by default on Firefox.
Freenode, stylized as freenode and formerly known as Open Projects Network, is an IRC network which was previously used to discuss peer-directed projects. Their servers are accessible from the hostname chat.freenode.net, which load balances connections by using round-robin DNS.

Konversation is an Internet Relay Chat (IRC) client built on the KDE Platform and is free software released under the terms of the GNU GPL-2.0-or-later. Konversation is currently maintained in the KDE Extragear Network module, which means that it has its own release cycle which is independent from the main KDE applications. It is the default IRC client in many prominent Linux distributions, such as openSUSE, the KDE spin of Fedora, and Kubuntu.





