The Republic of Estonia gained its independence from the Russian Empire on 24 February 1918 and established diplomatic relations with many countries via membership of the League of Nations. The forcible incorporation of Estonia into the Soviet Union in 1940 was not generally recognised by the international community and the Estonian diplomatic service continued to operate in some countries. Following the restoration of independence from the Soviet Union, Russia was one of the first nations to re-recognize Estonia's independence. Estonia's immediate priority after regaining its independence was the withdrawal of Russian forces from Estonian territory. In August 1994, this was completed. However, relations with Moscow have remained strained primarily because Russia decided not to ratify the border treaty it had signed with Estonia in 1999.

The United States, Venezuela, Cuba, and the People's Republic of China have embassies in Grenada. Grenada has been recognized by most members of the United Nations and maintains diplomatic missions in the United Kingdom, the United States, Venezuela, and Canada.

The foreign relations of the Russian Federation is the policy arm of the government of Russia which guides its interactions with other nations, their citizens, and foreign organizations. This article covers the foreign policy of the Russian Federation since the dissolution of the Soviet Union in late 1991. At present, Russia has no diplomatic relations with Ukraine due to its ongoing invasion of Ukraine. Other than Ukraine, Russia also has no diplomatic relations with Georgia, Bhutan, Federated States of Micronesia or Solomon Islands.

Vanuatu maintains diplomatic relations with many countries, and it has a small network of diplomatic missions. Australia, France, Japan, New Zealand, the People's Republic of China, South Korea and the United Kingdom maintain embassies, High Commissions, or missions in Port Vila. The British High Commission maintained a continued presence for almost a century, though closed from 2005 until reopening in 2019.

Tonga, by a modification of its treaty of friendship with the United Kingdom in July 1970, is responsible for its own external affairs. It maintains cordial relations with most countries and has close relations with its Pacific neighbours and the United Kingdom. In 1998, it recognized the People's Republic of China and broke relations with Taiwan.

The United States and Vanuatu established diplomatic relations on September 30, 1986 – three months to the day after Vanuatu had established diplomatic relations with the Soviet Union. Relations were often tense in the 1980s, under the prime ministership of Father Walter Lini in Vanuatu, but eased after that. At present, bilateral relations consist primarily in US aid to Vanuatu, and are cordial.
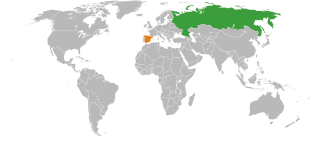
The Russian Federation and the Kingdom of Spain, a member state of the European Union, have bilateral foreign relations. Spain and the Grand Duchy of Moscow first exchanged envoys in 1520s; regular embassies were established in 1722. The two countries share a long history of relations, characterized at times by close cooperation and at other times by deep hostility. Soviet-Spanish relations, once terminated after the Spanish Civil War, were gradually reestablished starting in 1963 and were fully established by 1977. Trade between the two countries amounted to two billion euros in 2008. In March 2009, the two countries signed an energy agreement providing national energy companies access to other party's domestic markets.

The Embassy of Australia in Moscow is the diplomatic mission of Australia to the Russian Federation. The current head of post and Ambassador of Australia to the Russian Federation is John Geering. The embassy serves as the diplomatic mission for Australia to the Russian Federation, Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan. The chancery is located at 10A/2 Podkolokolny Lane in the Tagansky District of Moscow.

Monaco–Russia relations is the bilateral relationship between the Principality of Monaco and the Russian Federation.

Diplomatic relations between the Soviet Union and Trinidad and Tobago were established on June 6, 1974. Russia is represented in Trinidad and Tobago through a non-resident embassy in Georgetown, Guyana.

The Soviet Union and Vanuatu established official diplomatic relations on 30 June 1986, three months to the day before Vanuatu established diplomatic relations with the United States.

Tonga and the Soviet Union established formal diplomatic relations in April 1976. Tonga was the first Pacific Island country to establish relations with the USSR.

The Republic of Vanuatu and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics established official diplomatic relations on June 30, 1986 - three months to the day before Vanuatu established diplomatic relations with the United States. With the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, the Russian Federation emerged as its successor state in 1991.

Russia–Zambia relations are the bilateral relations between Russia and Zambia.

Diplomatic relations were established between Eswatini and Russia in 1999.
















