
In molecular biology, a riboswitch is a regulatory segment of a messenger RNA molecule that binds a small molecule, resulting in a change in production of the proteins encoded by the mRNA. Thus, an mRNA that contains a riboswitch is directly involved in regulating its own activity, in response to the concentrations of its effector molecule. The discovery that modern organisms use RNA to bind small molecules, and discriminate against closely related analogs, expanded the known natural capabilities of RNA beyond its ability to code for proteins, catalyze reactions, or to bind other RNA or protein macromolecules.
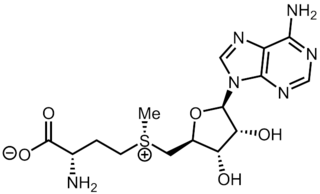
S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM), also known under the commercial names of SAMe, SAM-e, or AdoMet, is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation. Although these anabolic reactions occur throughout the body, most SAM is produced and consumed in the liver. More than 40 methyl transfers from SAM are known, to various substrates such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and secondary metabolites. It is made from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and methionine by methionine adenosyltransferase. SAM was first discovered by Giulio Cantoni in 1952.

In molecular genetics, a repressor is a DNA- or RNA-binding protein that inhibits the expression of one or more genes by binding to the operator or associated silencers. A DNA-binding repressor blocks the attachment of RNA polymerase to the promoter, thus preventing transcription of the genes into messenger RNA. An RNA-binding repressor binds to the mRNA and prevents translation of the mRNA into protein. This blocking or reducing of expression is called repression.

Amino acid synthesis is the set of biochemical processes by which the amino acids are produced. The substrates for these processes are various compounds in the organism's diet or growth media. Not all organisms are able to synthesize all amino acids. For example, humans can synthesize 11 of the 20 standard amino acids. These 11 are called the non-essential amino acids).

The SAM-II riboswitch is an RNA element found predominantly in Alphaproteobacteria that binds S-adenosyl methionine (SAM). Its structure and sequence appear to be unrelated to the SAM riboswitch found in Gram-positive bacteria. This SAM riboswitch is located upstream of the metA and metC genes in Agrobacterium tumefaciens, and other methionine and SAM biosynthesis genes in other alpha-proteobacteria. Like the other SAM riboswitch, it probably functions to turn off expression of these genes in response to elevated SAM levels. A significant variant of SAM-II riboswitches was found in Pelagibacter ubique and related marine bacteria and called SAM-V. Also, like many structured RNAs, SAM-II riboswitches can tolerate long loops between their stems.

The SAM riboswitch is found upstream of a number of genes which code for proteins involved in methionine or cysteine biosynthesis in Gram-positive bacteria. Two SAM riboswitches in Bacillus subtilis that were experimentally studied act at the level of transcription termination control. The predicted secondary structure consists of a complex stem-loop region followed by a single stem-loop terminator region. An alternative and mutually exclusive form involves bases in the 3' segment of helix 1 with those in the 5' region of helix 5 to form a structure termed the anti-terminator form. When SAM is unbound, the anti-terminator sequence sequesters the terminator sequence so the terminator is unable to form, allowing the polymerase to read-through the downstream gene. When S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM) is bound to the aptamer, the anti-terminator is sequestered by an anti-anti-terminator; the terminator forms and terminates the transcription. However, many SAM riboswitches are likely to regulate gene expression at the level of translation.

The SMKbox riboswitch is an RNA element that regulates gene expression in bacteria. The SMK box riboswitch is found in the 5' UTR of the MetK gene in lactic acid bacteria. The structure of this element changes upon binding to S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) to a conformation that blocks the shine-dalgarno sequence and blocks translation of the gene.

The asd RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure found in certain lactic acid bacteria. The asd motif was detected by bioinformatics and an individual asd RNA in Streptococcus pyogenes was detected by microarray and northern hybridization experiments as a 170-nucleotide molecule called "SR914400". The transcription start site determined for SR914400 corresponds to the 5′-end of the molecule shown in the consensus diagram.
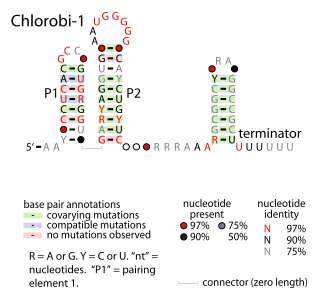
The Chlorobi-1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA secondary structure identified by bioinformatics. It is predicted to be used only by Chlorobiota, a phylum of bacteria. The motif consists of two stem-loops that are followed by an apparent rho-independent transcription terminator. The motif is presumed to function as an independently transcribed non-coding RNA.
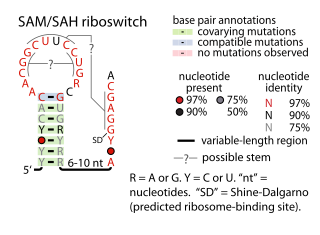
The SAM–SAH riboswitch is a conserved RNA structure in certain bacteria that binds S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) and S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) and is therefore presumed to be a riboswitch. SAM–SAH riboswitches do not share any apparent structural resemblance to known riboswitches that bind SAM or SAH. The binding affinities for both compounds are similar, but binding for SAH is at least somewhat stronger. SAM–SAH riboswitches are exclusively found in Rhodobacterales, an order of alphaproteobacteria. They are always found in the apparent 5' untranslated regions of metK genes, which encode the enzyme that synthesizes SAM.
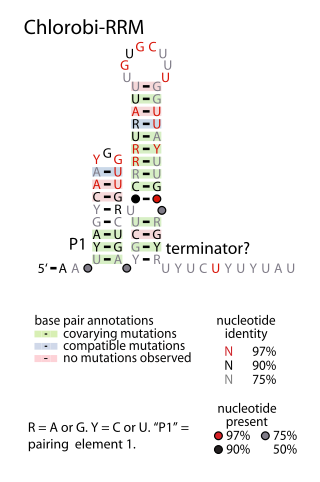
The Chlorobi-RRM RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics. It is found within bacteria in the phylum Chlorobiota, and is exclusively detected in the presumed 5' untranslated regions of genes that encode putative RNA-binding proteins. Since many RNA-binding proteins regulate their own expression in a feedback mechanism by binding or acting up their 5' UTR, it was proposed that the Chlorobi-RRM is a component in an analogous feedback mechanism. Structurally, the motif consists of two stem-loops, the second of which might function as a rho-independent transcription terminator.
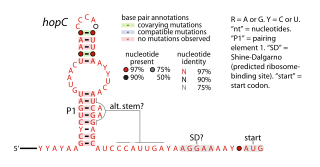
The hopC RNA motif is a predicted cis-regulatory element identified by a bioinformatic screen for conserved RNA secondary structures. hopC RNAs are exclusively found within bacteria classified within the genus Helicobacter, some of which are human pathogens that infect the stomach and can cause ulcers.

The JUMPstart RNA motif describes a conserved RNA-based secondary structure associated with JUMPstart elements. The 39-base-pair JUMPstart sequence describes a conserved element upstream of genes that participate in polysaccharide synthesis. The JUMPstart element has been shown to function as an RNA, and is present in the 5' untranslated regions of the genes it regulates.
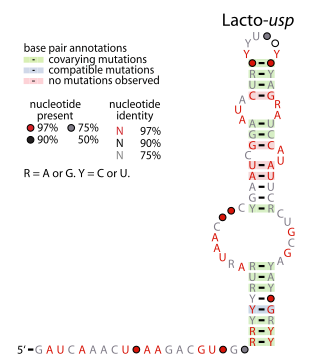
The Lacto-usp RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified in bacteria by bioinformatics. Lacto-usp RNAs are found exclusively in lactic acid bacteria, and exclusively in the possible 5′ untranslated regions of operons that contain a hypothetical gene and a usp gene. The usp gene encodes the universal stress protein. It was proposed that the Lacto-usp might correspond to the 6S RNA of the relevant species, because four of five of these species lack a predicted 6S RNA, and 6S RNAs commonly occur in 5′ UTRs of usp genes. However, given that the Lacto-usp RNA motif is much shorter than the standard 6S RNA structure, the function of Lacto-usp RNAs remains unclear.
The Lnt RNA motif refers to a conserved RNA structure found in certain bacteria. Specifically, Lnt RNAs are known only in species within the phylum Chlorobiota, and are located in the possible 5' untranslated regions of genes that are annotated as encoding apolipoprotein N-acyltransferase enzymes. There is some doubt as to whether the indicated motif is transcribed as RNA, or whether its reverse complement is transcribed. If the reverse complement is transcribed it would potentially in 5' UTRs of genes encoding bacteriochlorophyll A, and would be close to the start codon of those genes.

The mraW RNA motif is a conserved, structured RNA found in certain bacteria. Specifically, it is predicted in many, though not all, species of actinobacteria, and especially within the genus Mycobacterium. Structurally, the motif consists of a hairpin with a highly conserved terminal loop sequence. mraW RNAs are consistently in the presumed 5' untranslated regions of mraW genes. These mraW genes likely form operons with immediately downstream ftsI genes, and multiple types of mur genes. These genes are associated with peptidoglycan synthesis, and it was hypothesized that the mraW RNA motif might regulate these genes.

The psaA RNA motif describes a class of RNAs with a common secondary structure. psaA RNAs are exclusively found in locations that presumably correspond to the 5' untranslated regions of operons formed of psaA and psaB genes. For this reason, it was hypothesized that psaA RNAs function as cis-regulatory elements of these genes. The psaAB genes encode proteins that form subunits in the photosystem I structure used for photosynthesis. psaA RNAs have been detected only in cyanobacteria, which is consistent with their association with photosynthesis.

The yjdF RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified using bioinformatics. Most yjdF RNAs are located in bacteria classified within the phylum Bacillota. A yjdF RNA is found in the presumed 5' untranslated region of the yjdF gene in Bacillus subtilis, and almost all yjdF RNAs are found in the 5' UTRs of homologs of this gene. The function of the yjdF gene is unknown, but the protein that it is predicted to encode is classified by the Pfam Database as DUF2992.

S-Adenosylmethionine synthetase, also known as methionine adenosyltransferase (MAT), is an enzyme that creates S-adenosylmethionine by reacting methionine and ATP.

The uup RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. uup motif RNAs are found in Bacillota and Gammaproteobacteria.



















