 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
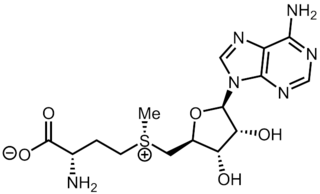
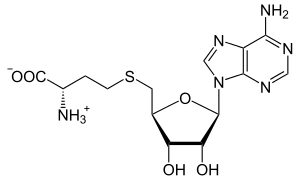
| IUPAC name S-(5′-Deoxyadenos-5′-yl)-L-homocysteine | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (2S)-2-Amino-4-({[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl}sulfanyl)butanoic acid | |
| Other names AdoHcy, 2-S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine, 5′-S-(3-Amino-3-carboxypropyl)-5′-thioadenosine S-adenosylhomocysteine, SAH | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.328 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | S-Adenosylhomocysteine |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H20N6O5S | |
| Molar mass | 384.41 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
S-Adenosyl-L-homocysteine (SAH) is the biosynthetic precursor to homocysteine. [1] SAH is formed by the demethylation of S-adenosyl-L-methionine. [2] [3] Adenosylhomocysteinase converts SAH into homocysteine and adenosine.