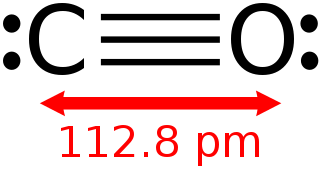Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a transcontinental country spanning South America and an insular region in North America. It is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuela to the east, Brazil to the southeast, Ecuador and Peru to the south, the Pacific Ocean to the west, and Panama to the northwest. Colombia comprises 32 departments and the Capital District of Bogotá, the country's largest city. It covers an area of 1,141,748 square kilometers (440,831 sq mi), with a population of 50 million. Colombia's rich cultural heritage reflects influences by various Amerindian civilizations, European settlement, African slaves, and immigration from Europe and the Middle East. Spanish is the nation's official language, besides which over 70 languages are spoken.

Capcom Co., Ltd. is a Japanese video game developer and publisher. It has created a number of multi-million-selling game franchises, with its most commercially successful being Resident Evil, Monster Hunter, Street Fighter, Mega Man, Devil May Cry, Dead Rising, and Marvel vs. Capcom. Established in 1979, it has become an international enterprise with subsidiaries in Asia, Europe, and North America.

Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound occurring as an acidic colorless gas with a density about 53% higher than that of dry air. Carbon dioxide molecules consist of a carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It occurs naturally in Earth's atmosphere as a trace gas. The current concentration is about 0.04% (412 ppm) by volume, having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Natural sources include volcanoes, forest fires, hot springs, geysers, and it is freed from carbonate rocks by dissolution in water and acids. Because carbon dioxide is soluble in water, it occurs naturally in groundwater, rivers and lakes, ice caps, glaciers and seawater. It is present in deposits of petroleum and natural gas. Carbon dioxide has a sharp and acidic odor and generates the taste of soda water in the mouth, but at normally encountered concentrations it is odorless.
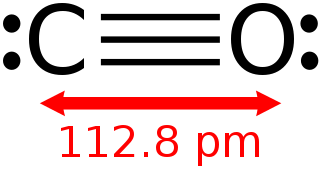
Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest molecule of the oxocarbon family. In coordination complexes the carbon monoxide ligand is called carbonyl. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry.

The citric acid cycle (CAC) – also known as the TCA cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The Krebs cycle is used by organisms that respire to generate energy, either by anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration. In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent NADH, that are used in numerous other reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest components of metabolism and may have originated abiogenically. Even though it is branded as a 'cycle', it is not necessary for metabolites to follow only one specific route; at least three alternative segments of the citric acid cycle have been recognized.

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars and starches, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek phōs, "light", and sunthesis, "putting together". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product that stores three times more chemical energy than the carbohydrates. Most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis is largely responsible for producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and supplies most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.

Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the formula CaCO3. It is a common substance found in rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite (most notably as limestone, which is a type of sedimentary rock consisting mainly of calcite) and is the main component of eggshells, gastropod shells, shellfish skeletons and pearls. Calcium carbonate is the active ingredient in agricultural lime and is created when calcium ions in hard water react with carbonate ions to create limescale. It has medical use as a calcium supplement or as an antacid, but excessive consumption can be hazardous and cause hypercalcemia and digestive issues.

Sodium bicarbonate (IUPAC name: sodium hydrogencarbonate), commonly known as baking soda or bicarbonate of soda, is a chemical compound with the formula NaHCO3. It is a salt composed of a sodium cation (Na+) and a bicarbonate anion (HCO3−). Sodium bicarbonate is a white solid that is crystalline, but often appears as a fine powder. It has a slightly salty, alkaline taste resembling that of washing soda (sodium carbonate). The natural mineral form is nahcolite. It is a component of the mineral natron and is found dissolved in many mineral springs.

Sodium carbonate, Na2CO3·10H2O, (also known as washing soda, soda ash and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield moderately alkaline solutions in water. Historically, it was extracted from the ashes of plants growing in sodium-rich soils. Because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood (once used to produce potash), sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash". It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process.

Brentford Football Club is a professional football club based in Brentford, West London, England. They currently compete in the Premier League, the highest tier of English football, having gained promotion via the playoffs at the end of the 2020–21 Championship season. Nicknamed "the Bees", the club was founded in 1889 and played home matches at Griffin Park from 1904 before moving to Brentford Community Stadium in 2020. Their main rivals are fellow West London based clubs Fulham and Queens Park Rangers.

Ronald Antonio O'Sullivan is an English professional snooker player who is the current world champion and world number one. Widely recognised as one of the most talented and accomplished players in the history of the sport, he has won the World Snooker Championship seven times, a modern era record he holds jointly with Stephen Hendry. He has also won a record seven Masters and record seven UK Championship titles for a total of 21 Triple Crown titles, the most won by any player. He holds the record for the most ranking titles in professional snooker, with 39, and has held the world number one ranking on multiple occasions. Along with John Higgins and Mark Williams, O'Sullivan is one of a triad of players known as the Class of '92, all of whom were born in 1975, turned professional in 1992, and have won a combined 14 world titles.

PepsiCo, Inc. is an American multinational food, snack, and beverage corporation headquartered in Harrison, New York, in the hamlet of Purchase. PepsiCo's business encompasses all aspects of the food and beverage market. It oversees the manufacturing, distribution, and marketing of its products. PepsiCo was formed in 1965 with the merger of the Pepsi-Cola Company and Frito-Lay, Inc. PepsiCo has since expanded from its namesake product Pepsi Cola to an immensely diversified range of food and beverage brands. The largest and most recent acquisition was Pioneer Foods in 2020 for $1.7bn and before that it was the Quaker Oats Company in 2001, which added the Gatorade brand to the Pepsi portfolio and Tropicana Products in 1998.

Contemporary climate change includes both global warming and its impacts on Earth's weather patterns. There have been previous periods of climate change, but the current changes are distinctly more rapid and not due to natural causes. Instead, they are caused by the emission of greenhouse gases, mostly carbon dioxide and methane. Burning fossil fuels for energy use creates most of these emissions. Certain agricultural practices, industrial processes, and forest loss are additional sources. Greenhouse gases are transparent to sunlight, allowing it through to heat the Earth's surface. When the Earth emits that heat as infrared radiation the gases absorb it, trapping the heat near the Earth's surface. As the planet heats up it causes changes like the loss of sunlight-reflecting snow cover, amplifying global warming.

James Kimberley Corden is an English actor, comedian, singer, writer, producer, and television host. In the United States, he is best known as the host of The Late Late Show with James Corden, a late-night talk show that has been on CBS since 2015. In the United Kingdom, he is best known for co-writing and starring in the critically acclaimed BBC sitcom Gavin & Stacey.
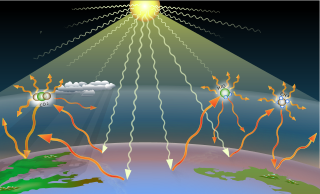
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and ozone (O3). Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth's surface would be about −18 °C (0 °F), rather than the present average of 15 °C (59 °F). The atmospheres of Venus, Mars and Titan also contain greenhouse gases.

Cobalt is a chemical element with the symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal.

The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identified from an outbreak in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. Attempts to contain it there failed, allowing the virus to spread worldwide. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared a Public Health Emergency of International Concern on 30 January 2020 and a pandemic on 11 March 2020. As of 6 May 2022, the pandemic had caused more than 516 million cases and 6.24 million deaths, making it one of the deadliest in history.

Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had a provisional name, 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), and has also been called human coronavirus 2019. First identified in the city of Wuhan, Hubei, China, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak a Public Health Emergency of International Concern on 30 January 2020, and a pandemic on 11 March 2020. SARS‑CoV‑2 is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus that is contagious in humans.

Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease spread worldwide, leading to the COVID-19 pandemic.