Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing and storage. Folate is required for the body to make DNA and RNA and metabolise amino acids necessary for cell division. As the human body cannot make folate, it is required in the diet, making it an essential nutrient. It occurs naturally in many foods. The recommended adult daily intake of folate in the U.S. is 400 micrograms from foods or dietary supplements.

Anemia or anaemia is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. The name is derived from Ancient Greek: ἀναιμία anaimia, meaning 'lack of blood', from ἀν- an-, 'not' and αἷμα haima, 'blood'. When anemia comes on slowly, the symptoms are often vague, such as tiredness, weakness, shortness of breath, headaches, and a reduced ability to exercise. When anemia is acute, symptoms may include confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out, loss of consciousness, and increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Symptoms of anemia depend on how quickly hemoglobin decreases. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause. Preoperative anemia can increase the risk of needing a blood transfusion following surgery. Anemia can be temporary or long term and can range from mild to severe.

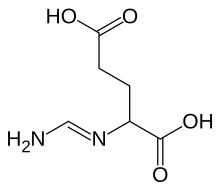
Homocysteine or Hcy: is a non-proteinogenic α-amino acid. It is a homologue of the amino acid cysteine, differing by an additional methylene bridge (-CH2-). It is biosynthesized from methionine by the removal of its terminal Cε methyl group. In the body, homocysteine can be recycled into methionine or converted into cysteine with the aid of vitamin B6, B9, and B12.
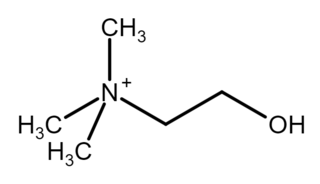
Choline is a cation with the chemical formula [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+. Choline forms various salts, for example choline chloride and choline bitartrate.

Pernicious anemia is a disease in which not enough red blood cells are produced due to a deficiency of vitamin B12. Those affected often have a gradual onset. The most common initial symptoms are feeling tired and weak. Other symptoms of anemia may include shortness of breath, lightheadedness, headaches, sore red tongue, cold hands and feet, pale or yellow skin, chest pain, and an irregular heartbeat. The digestive tract may also be disturbed giving symptoms that can include nausea and vomiting, heartburn, upset stomach and loss of appetite. Symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency may include decreased ability to think, numbness in the hands and feet, memory problems, blurred vision, trouble walking, poor balance, muscle weakness, decreased smell and taste, poor reflexes, clumsiness, depression, and confusion. Without treatment, some of these problems may become permanent.
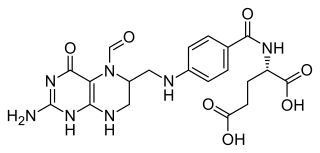
Folinic acid, also known as leucovorin, is a medication used to decrease the toxic effects of methotrexate and pyrimethamine. It is also used in combination with 5-fluorouracil to treat colorectal cancer and pancreatic cancer, may be used to treat folate deficiency that results in anemia, and methanol poisoning. It is taken by mouth, injection into a muscle, or injection into a vein.

Methylenetetrahydrofolatereductase (MTHFR) is the rate-limiting enzyme in the methyl cycle, and it is encoded by the MTHFR gene. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase catalyzes the conversion of 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, a cosubstrate for homocysteine remethylation to methionine. Natural variation in this gene is common in otherwise healthy people. Although some variants have been reported to influence susceptibility to occlusive vascular disease, neural tube defects, Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia, colon cancer, and acute leukemia, findings from small early studies have not been reproduced. Some mutations in this gene are associated with methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency. Complex I deficiency with recessive spastic paraparesis has also been linked to MTHFR variants. In addition, the aberrant promoter hypermethylation of this gene is associated with male infertility and recurrent spontaneous abortion.

Megaloblastic anemia is a type of macrocytic anemia. An anemia is a red blood cell defect that can lead to an undersupply of oxygen. Megaloblastic anemia results from inhibition of DNA synthesis during red blood cell production. When DNA synthesis is impaired, the cell cycle cannot progress from the G2 growth stage to the mitosis (M) stage. This leads to continuing cell growth without division, which presents as macrocytosis. Megaloblastic anemia has a rather slow onset, especially when compared to that of other anemias. The defect in red cell DNA synthesis is most often due to hypovitaminosis, specifically vitamin B12 deficiency or folate deficiency. Loss of micronutrients may also be a cause.

Neural tube defects (NTDs) are a group of birth defects in which an opening in the spine or cranium remains from early in human development. In the third week of pregnancy called gastrulation, specialized cells on the dorsal side of the embryo begin to change shape and form the neural tube. When the neural tube does not close completely, an NTD develops.

Hyperhomocysteinemia is a medical condition characterized by an abnormally high level of total homocysteine in the blood, conventionally described as above 15 μmol/L.

Folate deficiency, also known as vitamin B9 deficiency, is a low level of folate and derivatives in the body. Signs of folate deficiency are often subtle. A low number of red blood cells (anemia) is a late finding in folate deficiency and folate deficiency anemia is the term given for this medical condition. It is characterized by the appearance of large-sized, abnormal red blood cells (megaloblasts), which form when there are inadequate stores of folic acid within the body.
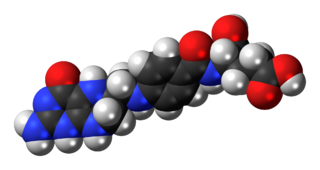
Tetrahydrofolic acid (THFA), or tetrahydrofolate, is a folic acid derivative.

Vitamin B12 deficiency, also known as cobalamin deficiency, is the medical condition in which the blood and tissue have a lower than normal level of vitamin B12. Symptoms can vary from none to severe. Mild deficiency may have few or absent symptoms. In moderate deficiency, feeling tired, anemia, soreness of the tongue, mouth ulcers, breathlessness, feeling faint, rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure, pallor, hair loss, decreased ability to think and severe joint pain and the beginning of neurological symptoms, including abnormal sensations such as pins and needles, numbness and tinnitus may occur. Severe deficiency may include symptoms of reduced heart function as well as more severe neurological symptoms, including changes in reflexes, poor muscle function, memory problems, blurred vision, irritability, ataxia, decreased smell and taste, decreased level of consciousness, depression, anxiety, guilt and psychosis. If left untreated, some of these changes can become permanent. Temporary infertility reversible with treatment, may occur. In exclusively breastfed infants of vegetarian mothers who don't take B12 supplements as advised, undetected and untreated deficiency can lead to poor growth, poor development, and difficulties with movement.

Antifolates are a class of antimetabolite medications that antagonise (that is, block) the actions of folic acid (vitamin B9). Folic acid's primary function in the body is as a cofactor to various methyltransferases involved in serine, methionine, thymidine and purine biosynthesis. Consequently, antifolates inhibit cell division, DNA/RNA synthesis and repair and protein synthesis. Some such as proguanil, pyrimethamine and trimethoprim selectively inhibit folate's actions in microbial organisms such as bacteria, protozoa and fungi. The majority of antifolates work by inhibiting dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR).

Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. It is one of eight B vitamins. It is required by animals, which use it as a cofactor in DNA synthesis, and in both fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It is important in the normal functioning of the nervous system via its role in the synthesis of myelin, and in the circulatory system in the maturation of red blood cells in the bone marrow. Plants do not need cobalamin and carry out the reactions with enzymes that are not dependent on it.
Vitamins occur in a variety of related forms known as vitamers. A vitamer of a particular vitamin is one of several related compounds that performs the functions of said vitamin and prevents the symptoms of deficiency of said vitamin.

Nutritional neuroscience is the scientific discipline that studies the effects various components of the diet such as minerals, vitamins, protein, carbohydrates, fats, dietary supplements, synthetic hormones, and food additives have on neurochemistry, neurobiology, behavior, and cognition.
Relatively speaking, the brain consumes an immense amount of energy in comparison to the rest of the body. The mechanisms involved in the transfer of energy from foods to neurons are likely to be fundamental to the control of brain function. Human bodily processes, including the brain, all require both macronutrients, as well as micronutrients.

Cerebral folate deficiency is a condition in which concentrations of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate are low in the brain as measured in the cerebral spinal fluid despite being normal in the blood. Symptoms typically appear at about 5 to 24 months of age. Without treatment there may be poor muscle tone, trouble with coordination, trouble talking, and seizures.
Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency is the most common genetic cause of elevated serum levels of homocysteine (hyperhomocysteinemia). It is caused by genetic defects in MTHFR, which is an important enzyme in the methyl cycle.