Related Research Articles

Ore is natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals concentrated above background levels, typically containing metals, that can be mined, treated and sold at a profit. The grade of ore refers to the concentration of the desired material it contains. The value of the metals or minerals a rock contains must be weighed against the cost of extraction to determine whether it is of sufficiently high grade to be worth mining, and is therefore considered an ore. A complex ore is one containing more than one valuable mineral.

Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is the use of computers to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. Designs made through CAD software help protect products and inventions when used in patent applications. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The terms computer-aided drafting (CAD) and computer-aided design and drafting (CADD) are also used.
Geostatistics is a branch of statistics focusing on spatial or spatiotemporal datasets. Developed originally to predict probability distributions of ore grades for mining operations, it is currently applied in diverse disciplines including petroleum geology, hydrogeology, hydrology, meteorology, oceanography, geochemistry, geometallurgy, geography, forestry, environmental control, landscape ecology, soil science, and agriculture. Geostatistics is applied in varied branches of geography, particularly those involving the spread of diseases (epidemiology), the practice of commerce and military planning (logistics), and the development of efficient spatial networks. Geostatistical algorithms are incorporated in many places, including geographic information systems (GIS).

Economic geology is concerned with earth materials that can be used for economic and industrial purposes. These materials include precious and base metals, nonmetallic minerals and construction-grade stone. Economic geology is a subdiscipline of the geosciences; according to Lindgren (1933) it is “the application of geology”. It may be called the scientific study of the Earth's sources of mineral raw materials and the practical application of the acquired knowledge.

In statistics, originally in geostatistics, kriging or Kriging, also known as Gaussian process regression, is a method of interpolation based on Gaussian process governed by prior covariances. Under suitable assumptions of the prior, kriging gives the best linear unbiased prediction (BLUP) at unsampled locations. Interpolating methods based on other criteria such as smoothness may not yield the BLUP. The method is widely used in the domain of spatial analysis and computer experiments. The technique is also known as Wiener–Kolmogorov prediction, after Norbert Wiener and Andrey Kolmogorov.
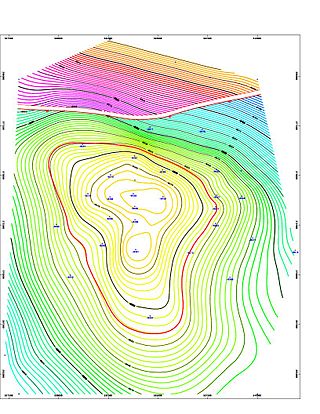
Geologic modelling,geological modelling or geomodelling is the applied science of creating computerized representations of portions of the Earth's crust based on geophysical and geological observations made on and below the Earth surface. A geomodel is the numerical equivalent of a three-dimensional geological map complemented by a description of physical quantities in the domain of interest. Geomodelling is related to the concept of Shared Earth Model; which is a multidisciplinary, interoperable and updatable knowledge base about the subsurface.
There are several classification systems for the economic evaluation of mineral deposits worldwide. The most commonly used schemes base on the International Reporting Template, developed by the CRIRSCO - Committee for Mineral Reserves International Reporting Standards, like the Australian Joint Ore Reserves Committee - JORC Code 2012, the Pan-European Reserves & Resources Reporting Committee' – PERC Reporting Standard from 2021, the Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum - CIM classification and the South African Code for the Reporting of Mineral Resources and Mineral Reserves (SAMREC). A more detailed description of the historical development concerning reporting about mineral deposits can be found on the PERC web site.
National Instrument 43-101 is a national instrument for the Standards of Disclosure for Mineral Projects within Canada. The Instrument is a codified set of rules and guidelines for reporting and displaying information related to mineral properties owned by, or explored by, companies which report these results on stock exchanges within Canada. This includes foreign-owned mining entities who trade on stock exchanges overseen by the Canadian Securities Administrators, even if they only trade on Over The Counter (OTC) derivatives or other instrumented securities.

The Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum (CIM) is a not-for-profit technical society of professionals in the Canadian minerals, metals, materials and energy industries. CIM's members are convened from industry, academia and government.
First developed in 1985 by RockWare Inc, RockWorks is used by the mining, petroleum, and environmental industry for subsurface visualization, borehole database management as well as the creation of grids, solid models, calculating volumetric analysis, etc.

Natural resource economics deals with the supply, demand, and allocation of the Earth's natural resources. One main objective of natural resource economics is to better understand the role of natural resources in the economy in order to develop more sustainable methods of managing those resources to ensure their availability for future generations. Resource economists study interactions between economic and natural systems, with the goal of developing a sustainable and efficient economy.

Hathor Exploration Limited is a uranium exploration company based in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. Its exploration office is located in Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada. Hathor's exploration projects concentrate on properties within the Athabasca Basin of Northern Saskatchewan, Canada.

Orex Exploration is a former Canadian gold mining company that conducted exploration work on mining properties it owned in the Goldboro and Guysborough County areas of Nova Scotia. The properties owned by Orex were the sites of the former Boston Richardson Mine, Dolliver Mountain Mine, West Goldbrook Mine, and East Goldbrook Mine which operated between 1892 and 1912. Headquartered in Rouyn-Noranda, Quebec, the company was founded in 1987 and raised funds for exploration work, in part, by issuing stocks traded on the Montreal Stock Exchange and then the TSX Venture Exchange. It became a subsidiary of Anaconda Mining Inc. after Anaconda acquired the company in a stock swap deal in 2017.

Antonio Nieto is an Earth Systems and Mining Engineer.
The Lac Otelnuk mine is Quebec's largest iron mine project with NI 43–101 compliant estimated reserves of 23.74 billion tonnes of ore grading 29.65% iron metal. In 2005 Bedford Resource Partners staked 129 claims over the deposit and optioned it to Adriana Resources. In 2012, 60% ownership of the iron deposit was sold to Wuhnan Iron and Steel Co. (WISCO). More than $150 million in expenditures have been invested in the exploration, all studies, the 2015 NI 43-101 compliant feasibility study and the formation of the Lac Otelnuk mining Company between Adriana Resources Inc and WISCO.
André Georges Journel is a French American engineer who excelled in formulating and promoting geostatistics in the earth sciences and engineering, first from the Centre of Mathematical Morphology in Fontainebleau, France and later from Stanford University.
Mineral resource estimation is used to determine and define the ore tonnage and grade of a geological deposit, from the developed block model. There are different estimation methods used for different scenarios dependent upon the ore boundaries, geological deposit geometry, grade variability and the amount of time and money available. A typical resource estimation involves the construction of a geological and resource model with data from various sources. Depending on the nature of the information and whether the data is hard copy or computerized, the principal steps of computer resource estimation are:
- Creation, standardization and validation of the database.
- Section plotting and interactive geological modeling.
- Geostatistical analysis.
- Block modeling and block estimation.
Quantitative mineral-resource assessments are defined as the numerical estimate of the amount, quality, and in some cases, value of undiscovered minerals present within a specified area (tract). Their purpose is to provide a framework for making decisions by governments or institutions concerning mineral resources under conditions of uncertainty. Due to the uncertainty inherent in assessment of unknown resources, the results are presented probabilistically. The resources are in undiscovered mineral deposits whose existence is postulated based on indirect geologic evidence. The mineral deposits are believed to exist within a specified distance from the surface of the ground, or an incompletely explored mineral occurrence or prospect that could have sufficient size and grade to be classed a deposit. A mineral concentration of sufficient size and grade richness that it might, under the most favorable of circumstances, be considered to have potential for economic development is a mineral deposit (Ore).

Oil and gas reserves denote discovered quantities of crude oil and natural gas that can be profitably produced/recovered from an approved development. Oil and gas reserves tied to approved operational plans filed on the day of reserves reporting are also sensitive to fluctuating global market pricing. The remaining resource estimates are likely sub-commercial and may still be under appraisal with the potential to be technically recoverable once commercially established. Natural gas is frequently associated with oil directly and gas reserves are commonly quoted in barrels of oil equivalent (BoE). Consequently, both oil and gas reserves, as well as resource estimates, follow the same reporting guidelines, and are referred to collectively hereinafter as oil & gas.

The Kubi gold mine is an abandoned open pit mine located 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) northeast of Dunkwa-on-Offin and 22 kilometres (14 mi) south of Obuasi, in Central Region, southern Ghana. It is 180 kilometres (110 mi) northwest of the national capital, Accra.
References
- ↑ Estimation of Mineral Resource and Mineral Reserve Best Practices Guidelines (PDF) (Report). 2003.
- ↑ Dimitrakopoulos, Roussos; Dagbert, Michel (2001). "Obituary: Farewell to Michel David (1945–2000)". Mathematical Geology. 33 (2): 241–244. doi: 10.1023/A:1007543603786 . S2CID 117556995.
- Claude Duplessis (2013). NI 43-101 Technical Report Joyce Lake DSO Iron Project NewfoundLand & Labrador (PDF) (Report). Labec Century Iron.
- Claude Duplessis; Jeffrey Cassoff; Stéphane Rivard; Michel L. Bilodeau; Mary Jean Buchanan; Nicolas Skiadasrédéric Côté; Alex Topalovic; Benoît Turgeon; Pascal Vallée; Michael Verreault; Ewan Wingate (2013). NI 43-101 Technical Report - Feasibility Study to Produce 3Mtpy of High Purity Apatite Concentrate at the Lac a Paul Project, Québec, Canada (PDF) (Report). Arianne Phosphate.
- Claude Duplessis; Jeffrey Cassoff; Stéphane Rivard; Michel L. Bilodeau; Mary Jean Buchanan; Nicolas Skiadas (2012). NI 43-101 TECHNICAL REPORT ON THE PRE-FEASIBILITY STUDY UPDATE (50 ktpd milling rate) LAC À PAUL APATITE PROJECT (PDF) (Report). Ressources d'Arianne.
- Claude Duplessis; Gilbert Rousseau (2011). Technical Report Preliminary Economic Assessment on the Bissett Creek Graphite Property of Industrial Minerals & Northern Graphite Corporation (PDF) (Report). Industrial Minerals & Northern Graphite Corporation.
- Guy Desharnais; Claude Duplessis (2011). Montviel Core Zone REE Mineral Resource Estimate Technical Report, Quebec (PDF) (Report). Geomega Resources.
- Yann Camus; André Laferrière (2010). NI 43 101 Technical Report Mineral Resource Estimation Kipawa Deposit, Zeus Project (PDF) (Report). Quebec Matamec Explorations.
- Claude Duplessis; Yann Camus (2010). NI 43 101 Technical Report Mineral Resource Estimation 2010 Update Barry Deposit, Barry Property Metanor Resources Inc (PDF) (Report). Metanor Resources.
- Michel Dagbert; Jean-François Couture; Philippe Giaro; Mohammed Rachek Jr (2008). RAPPORT TECHNIQUE NI 43-101 PROJET BAKOUDOU Région du Haut-Ogooué Gabon (PDF) (Report). Ressources Searchgold.