
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Santa Clara, California and Austin, Texas that develops computer processors and related technologies for business and consumer markets. While initially it manufactured its own processors, the company later outsourced its manufacturing, a practice known as fabless, after GlobalFoundries was spun off in 2009. AMD's main products include microprocessors, motherboard chipsets, embedded processors and graphics processors for servers, workstations and personal computers, and embedded systems applications.

A coprocessor is a computer processor used to supplement the functions of the primary processor. Operations performed by the coprocessor may be floating point arithmetic, graphics, signal processing, string processing, cryptography or I/O interfacing with peripheral devices. By offloading processor-intensive tasks from the main processor, coprocessors can accelerate system performance. Coprocessors allow a line of computers to be customized, so that customers who do not need the extra performance do not need to pay for it.
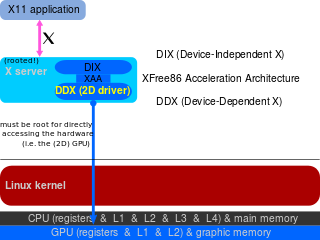
In computing, EXA is a graphics acceleration architecture of the X.Org Server designed to replace XAA and to make the XRender extension more usable, with only minor changes needed to adapt XFree86 video drivers written to use XAA; it was designed by Zack Rusin and announced at LinuxTag 2005 and first released with X.Org Server version 6.9/7.0.
Indeo Video is a video codec developed by Intel in 1992. It was sold to Ligos Corporation in 2000. While its original version was related to Intel's DVI video stream format, a hardware-only codec for the compression of television-quality video onto compact discs, Indeo was distinguished by being one of the first codecs allowing full-speed video playback without using hardware acceleration. Also unlike Cinepak and TrueMotion S, the compression used the same Y'CbCr 4:2:0 colorspace as the ITU's H.261 and ISO's MPEG-1.
The P6 microarchitecture is the sixth-generation Intel x86 microarchitecture, implemented by the Pentium Pro microprocessor that was introduced in November 1995. It is frequently referred to as i686. It was succeeded by the NetBurst microarchitecture in 2000, but eventually revived in the Pentium M line of microprocessors. The successor to the Pentium M variant of the P6 microarchitecture is the Core microarchitecture which in turn is also derived from the P6 microarchitecture.
The Intel Performance Acceleration Technology (PAT) is technology built onto Intel i875 Canterwood mainboards and other Pentium 4 based motherboards that based on the Intel D875PBZ reference board. Performance Acceleration Technology delivers additional system-level performance by optimizing memory access between CPU and system memory, allowing increased performance to be exhibited at standard operating specification.

Pentium is a brand used for a series of x86 architecture-compatible microprocessors produced by Intel since 1993. In their form as of November 2011, Pentium processors are considered entry-level products that Intel rates as "two stars", meaning that they are above the low-end Atom and Celeron series, but below the faster Core i3, i5, i7, i9, and high-end Xeon series.
Video Acceleration API is a royalty-free API as well as its implementation as free and open-source library (libVA) distributed under the MIT License.
Scalable Networking Pack (SNP) is a set of additions that adds new features to Microsoft's Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 or later with architectural enhancements and APIs to support the new capabilities of network acceleration and hardware-based offload technologies.

In computing, UMA Acceleration Architecture (UXA) is the reimplementation of the EXA graphics acceleration architecture of the X.Org Server developed by Intel. Its major difference with EXA is the use of GEM, replacing Translation Table Maps. In February 2009 it became clear that UXA would not be merged back into EXA.
System Controller Hub (SCH) is a family of Intel microchips employed in chipsets for low-power Atom-based platforms. Its architecture is consistent with the Intel Hub Architecture but combines the traditional northbridge and southbridge functions into a single microchip.
An Advanced Encryption Standard instruction set is now integrated into many processors. The purpose of the instruction set is to improve the speed of applications performing encryption and decryption using Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). They are often implemented as instructions implementing a single round of AES along with a special version for the last round which has a slightly different method.
Intel Turbo Boost is Intel's trade name for a feature that automatically raises certain of its processors' operating frequency, and thus performance, when demanding tasks are running. Turbo-Boost-enabled processors are the Core i5, Core i7, Core i9 and Xeon series manufactured since 2008, more particularly, those based on the Nehalem, Sandy Bridge, and later microarchitectures. The frequency is accelerated when the operating system requests the highest performance state of the processor. Processor performance states are defined by the Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) specification, an open standard supported by all major operating systems; no additional software or drivers are required to support the technology. The design concept behind Turbo Boost is commonly referred to as "dynamic overclocking".

Skylake is the codename used by Intel for a processor microarchitecture that was launched in August 2015 succeeding the Broadwell microarchitecture. Skylake is a microarchitecture redesign using the same 14 nm manufacturing process technology as its predecessor, serving as a "tock" in Intel's "tick–tock" manufacturing and design model. According to Intel, the redesign brings greater CPU and GPU performance and reduced power consumption. Skylake CPUs share its microarchitecture with Kaby Lake, Coffee Lake and Cannon Lake CPUs.

Android-x86 is an unofficial initiative to port Google's Android mobile operating system to run on devices powered by AMD and Intel x86 processors, rather than RISC-based ARM chips.
Intel SHA Extensions are set of extensions to the x86 instruction set architecture which support hardware acceleration of Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) family. Introduced on Intel Goldmont microarchitecture.
The Intel Cache Acceleration Software (CAS) is a computer data storage product for solid-state drive (SSD) caching.
The Xeon D is a brand of x86 system on a chip designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the microserver market. It was announced in 2014, with the first products released in 2015. Related to the Xeon brand of workstation and server processors are based on the same architecture as server-grade CPUs, with support for ECC memory, higher core counts, support for larger amounts of RAM, larger cache memory. Unique to the Xeon D line, emphasis was also made on low power consumption, and integrated hardware blocks such as a network interface controllers, a PCI express root complex, and USB and SATA controllers.









