The Direct Rendering Manager (DRM) is a subsystem of the Linux kernel responsible for interfacing with GPUs of modern video cards. DRM exposes an API that user space programs can use to send commands and data to the GPU, and perform operations such as configuring the mode setting of the display. DRM was first developed as the kernel space component of the X Server's Direct Rendering Infrastructure, but since then it has been used by other graphic stack alternatives such as Wayland.
Mesa, also called Mesa3D and The Mesa 3D Graphics Library, is an open source software implementation of OpenGL, Vulkan, and other graphics API specifications. Mesa translates these specifications to vendor-specific graphics hardware drivers.

A free and open-source graphics device driver is a software stack which controls computer-graphics hardware and supports graphics-rendering application programming interfaces (APIs) and is released under a free and open-source software license. Graphics device drivers are written for specific hardware to work within a specific operating system kernel and to support a range of APIs used by applications to access the graphics hardware. They may also control output to the display if the display driver is part of the graphics hardware. Most free and open-source graphics device drivers are developed by the Mesa project. The driver is made up of a compiler, a rendering API, and software which manages access to the graphics hardware.

The Intel Graphics Media Accelerator, or GMA, is a series of integrated graphics processors introduced in 2004 by Intel, replacing the earlier Intel Extreme Graphics series and being succeeded by the Intel HD and Iris Graphics series.
Unified Video Decoder (UVD), previously called Universal Video Decoder, is the name given to AMD's dedicated video decoding ASIC. There are multiple versions implementing a multitude of video codecs, such as H.264 and VC-1.
Video Acceleration API is a royalty-free API as well as its implementation as free and open-source library (libVA) distributed under the MIT License.

Phoronix Test Suite (PTS) is a free and open-source benchmark software for Linux and other operating systems which is developed by Michael Larabel and Matthew Tippett. The Phoronix Test Suite has been endorsed by sites such as Linux.com, LinuxPlanet and has been called "the best benchmarking platform" by Softpedia. The Phoronix Test Suite is also used by Tom's Hardware, ASELabs and other review sites.
X-Video Bitstream Acceleration (XvBA), designed by AMD Graphics for its Radeon GPU and Fusion APU, is an arbitrary extension of the X video extension (Xv) for the X Window System on Linux operating-systems. XvBA API allows video programs to offload portions of the video decoding process to the GPU video-hardware. Currently, the portions designed to be offloaded by XvBA onto the GPU are currently motion compensation (MC) and inverse discrete cosine transform (IDCT), and variable-length decoding (VLD) for MPEG-2, MPEG-4 ASP, MPEG-4 AVC (H.264), WMV3, and VC-1 encoded video.
Video Decode and Presentation API for Unix (VDPAU) is a royalty-free application programming interface (API) as well as its implementation as free and open-source library (libvdpau) distributed under the MIT License. VDPAU is also supported by Nvidia.
System Controller Hub (SCH) is a family of Intel microchips employed in chipsets for low-power Atom-based platforms. Its architecture is consistent with the Intel Hub Architecture but combines the traditional northbridge and southbridge functions into a single microchip.

Mode setting is a software operation that activates a display mode for a computer's display controller.

Intel Graphics Technology (GT) is the collective name for a series of integrated graphics processors (IGPs) produced by Intel that are manufactured on the same package or die as the central processing unit (CPU). It was first introduced in 2010 as Intel HD Graphics.

Oil Rush is a tower defense real-time strategy game developed by Unigine Corp using their Unigine engine technology. Set in a flooded, post-apocalyptic world, the game consists of players fighting over control of the world's last remaining oil reserves. The game was released as a digital download for Microsoft Windows, Linux, and OS X.
Mir is a computer display server and, recently, a Wayland compositor for the Linux operating system that is under development by Canonical Ltd. It was planned to replace the currently used X Window System for Ubuntu, however the plan changed and Mutter was adopted as part of GNOME Shell.
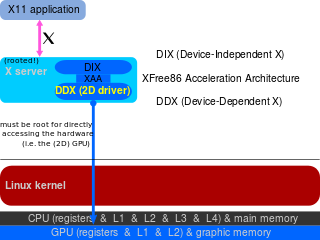
In computing, SNA is a graphics acceleration architecture for the X.Org Server developed by Intel as a replacement for UXA.
Vulkan is a low-overhead, cross-platform 3D graphics and computing API. Vulkan targets high-performance realtime 3D graphics applications such as video games and interactive media across all platforms. Compared to OpenGL and Direct3D 11, and like Direct3D 12 and Metal, Vulkan is intended to offer higher performance and more balanced CPU/GPU usage. Other major differences from Direct3D 11 and OpenGL are Vulkan being a considerably lower level API and offering parallel tasking. Vulkan also has the ability to render 2D graphics applications. In addition to its lower CPU usage, Vulkan is also able to better distribute work among multiple CPU cores.

LunarG is a software company specializing in device driver development for video cards.










