
Paramahansa Yogananda was an Indian Hindu monk, yogi and guru who introduced millions to the teachings of meditation and Kriya Yoga through his organization Self-Realization Fellowship (SRF) / Yogoda Satsanga Society (YSS) of India. A chief disciple of the yoga guru Swami Sri Yukteswar Giri, he was sent by his lineage to spread the teachings of yoga to the West. He immigrated to America at the age of 27 to prove the unity between Eastern and Western religions and to preach a balance between Western material growth and Indian spirituality. His long-standing influence in the American yoga movement, and especially the yoga culture of Los Angeles, led him to be considered by yoga experts as the "Father of Yoga in the West". He lived his last 32 years in America.

The National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory (NSCL), located on the campus of Michigan State University was a rare isotope research facility in the United States. Established in 1963, the cyclotron laboratory has been succeeded by the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams, a linear accelerator providing beam to the same detector halls.
A supercentenarian is a person who has reached the age of 110 years. This age is achieved by about one in 1,000 centenarians. Supercentenarians typically live a life free of major age-related diseases until shortly before the maximum human lifespan is reached.

Self-Realization Fellowship (SRF) is a worldwide, spiritual organization founded by Paramahansa Yogananda in 1920. Before coming to the United States, Yogananda began his spiritual work in India in 1917 and named it Yogoda Satsanga Society of India (YSS). He founded SRF in 1920 and in 1925 the Mount Washington property became the international headquarters for SRF and YSS, located in Los Angeles, California. Before his return visit to India in 1935, he legally incorporated SRF in the United States as a non-profit religious organization.
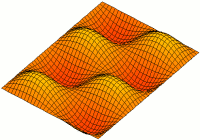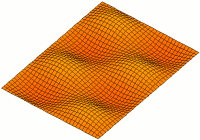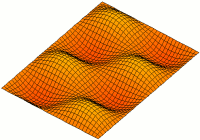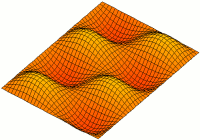
A resonator is a device or system that exhibits resonance or resonant behavior. That is, it naturally oscillates with greater amplitude at some frequencies, called resonant frequencies, than at other frequencies. The oscillations in a resonator can be either electromagnetic or mechanical. Resonators are used to either generate waves of specific frequencies or to select specific frequencies from a signal. Musical instruments use acoustic resonators that produce sound waves of specific tones. Another example is quartz crystals used in electronic devices such as radio transmitters and quartz watches to produce oscillations of very precise frequency.
An elf is a mythological creature, originally from Germanic mythology.

Kriyananda was an American Hindu religious leader, yoga guru, meditation teacher, musician, and author. He was a direct disciple of Paramahansa Yogananda, and founder of the spiritual movement named "Ananda". He authored over 150 books, and composed about 400 pieces of music. In 1998, he was found guilty of "constructive fraud", with a finding of "malice" and "fraudulent conduct" in a sexual harassment lawsuit.
Guggenheim Foundation or Guggenheim Fund may refer to:

Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility (TJNAF), commonly called Jefferson Lab or JLab, is a US National Laboratory located in Newport News, Virginia. Its stated mission is "to provide forefront scientific facilities, opportunities and leadership essential for discovering the fundamental structure of nuclear matter; to partner in industry to apply its advanced technology; and to serve the nation and its communities through education and public outreach."
A cryomodule is a section of a modern particle accelerator composed of superconducting RF (SRF) acceleration cavities, which need very low operating temperatures, often around 2 Kelvin). The cryomodule is a complex, state-of-the-art supercooled component in which particle beams are accelerated for scientific research. The superconducting cavities are cooled with liquid helium.
Winlink, or formally, Winlink Global Radio Email, also known as the Winlink 2000 Network, is a worldwide radio messaging system that uses amateur-band radio frequencies and government frequencies to provide radio interconnection services that include email with attachments, position reporting, weather bulletins, emergency and relief communications, and message relay. The system is built and administered by volunteers and is financially supported by the Amateur Radio Safety Foundation.

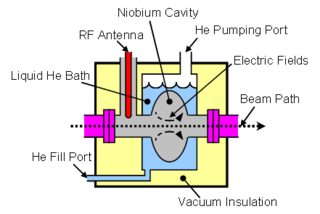
Superconducting radio frequency (SRF) science and technology involves the application of electrical superconductors to radio frequency devices. The ultra-low electrical resistivity of a superconducting material allows an RF resonator to obtain an extremely high quality factor, Q. For example, it is commonplace for a 1.3 GHz niobium SRF resonant cavity at 1.8 kelvins to obtain a quality factor of Q=5×1010. Such a very high Q resonator stores energy with very low loss and narrow bandwidth. These properties can be exploited for a variety of applications, including the construction of high-performance particle accelerator structures.
A research fellow is an academic research position at a university or a similar research institution, usually for academic staff or faculty members. A research fellow may act either as an independent investigator or under the supervision of a principal investigator.

The Methuselah Foundation is an American-based global non-profit organization based in Springfield, Virginia, with a declared mission to "make 90 the new 50 by 2030" by supporting tissue engineering and regenerative medicine therapies. The organization was originally incorporated by David Gobel in 2001 as the Performance Prize Society, a name inspired by the British governments Longitude Act, which offered monetary rewards for anyone who could devise a portable, practical solution for determining a ship's longitude.
The Institute of International Education Scholar Rescue Fund (IIE-SRF) provides fellowships for established scholars whose lives and work are threatened in their home countries. These fellowships permit professors, researchers and other senior academics to find temporary refuge at host universities and colleges anywhere in the world, enabling them to pursue their academic work. In some cases, conditions may improve, but if the scholar is unable to return home, the scholar may use the fellowship period to identify a longer-term opportunity.

The Syrian Revolutionaries Front is an alliance of 14 relatively moderate religious and some secular armed groups fighting under the banner of the Free Syrian Army, formed in December 2013, thus according to Arutz Sheva further sidelining the FSA and its leadership Supreme Military Council. It was established as a response to the merger of Islamist Syrian rebels into the Islamic Front.

Anna Grassellino is an Italian and American physicist, Senior Scientist and, since 2020, Director of the SQMS Center at Fermilab. In 2017 she was awarded the Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers by Barack Obama.
The Sudanese peace process consists of meetings, written agreements and actions that aim to resolve the War in Darfur, the Sudanese conflict in South Kordofan and Blue Nile, and armed conflicts in central, northern and eastern Sudan.
Leslie Mareike Schoop is a German materials chemist who is an associate professor at Princeton University. Her research considers the realization of new materials for quantum technologies. She has identified several new topological materials, including the non-toxic, air-stable topological semi-metal ZrSiS.









