Related Research Articles
The mesopelagiczone, also known as the middle pelagic or twilight zone, is the part of the pelagic zone that lies between the photic epipelagic and the aphotic bathypelagic zones. It is defined by light, and begins at the depth where only 1% of incident light reaches and ends where there is no light; the depths of this zone are between approximately 200 to 1,000 meters below the ocean surface.

In oceanography, a gyre is any large system of circulating ocean currents, particularly those involved with large wind movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis effect; planetary vorticity, horizontal friction and vertical friction determine the circulatory patterns from the wind stress curl (torque).

Marine debris, also known as marine litter, is human-created waste that has deliberately or accidentally been released in a sea or ocean. Floating oceanic debris tends to accumulate at the center of gyres and on coastlines, frequently washing aground, when it is known as beach litter or tidewrack. Deliberate disposal of wastes at sea is called ocean dumping. Naturally occurring debris, such as driftwood and drift seeds, are also present. With the increasing use of plastic, human influence has become an issue as many types of (petrochemical) plastics do not biodegrade quickly, as would natural or organic materials. The largest single type of plastic pollution (~10 %) and majority of large plastic in the oceans is discarded and lost nets from the fishing industry. Waterborne plastic poses a serious threat to fish, seabirds, marine reptiles, and marine mammals, as well as to boats and coasts.

The North Atlantic Gyre of the Atlantic Ocean is one of five great oceanic gyres. It is a circular ocean current, with offshoot eddies and sub-gyres, across the North Atlantic from the Intertropical Convergence Zone to the part south of Iceland, and from the east coasts of North America to the west coasts of Europe and Africa.

The Great Pacific garbage patch is a garbage patch, a gyre of marine debris particles, in the central North Pacific Ocean. It is located roughly from 135°W to 155°W and 35°N to 42°N. The collection of plastic and floating trash originates from the Pacific Rim, including countries in Asia, North America, and South America.
A garbage patch is a gyre of marine debris particles caused by the effects of ocean currents and increasing plastic pollution by human populations. These human-caused collections of plastic and other debris, cause ecosystem and environmental problems that affect marine life, contaminate oceans with toxic chemicals, and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Once waterborne, marine debris becomes mobile. Flotsam can be blown by the wind, or follow the flow of ocean currents, often ending up in the middle of oceanic gyres where currents are weakest. Garbage patches grow because of widespread loss of plastic from human trash collection systems.
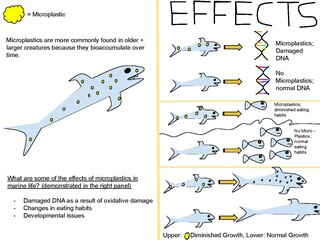
Marine plastic pollution is a type of marine pollution by plastics, ranging in size from large original material such as bottles and bags, down to microplastics formed from the fragmentation of plastic material. Marine debris is mainly discarded human rubbish which floats on, or is suspended in the ocean. Eighty percent of marine debris is plastic. Microplastics and nanoplastics result from the breakdown or photodegradation of plastic waste in surface waters, rivers or oceans. Recently, scientists have uncovered nanoplastics in heavy snow, more specifically about 3,000 tons that cover Switzerland yearly.

In the deep ocean, marine snow is a continuous shower of mostly organic detritus falling from the upper layers of the water column. It is a significant means of exporting energy from the light-rich photic zone to the aphotic zone below, which is referred to as the biological pump. Export production is the amount of organic matter produced in the ocean by primary production that is not recycled (remineralised) before it sinks into the aphotic zone. Because of the role of export production in the ocean's biological pump, it is typically measured in units of carbon. The term was coined by explorer William Beebe as observed from his bathysphere. As the origin of marine snow lies in activities within the productive photic zone, the prevalence of marine snow changes with seasonal fluctuations in photosynthetic activity and ocean currents. Marine snow can be an important food source for organisms living in the aphotic zone, particularly for organisms that live very deep in the water column.
The Center for Microbial Oceanography (C-MORE) is a research and education organization established in 2006 as a National Science Foundation funded Science and Technology Center.

Charles J. Moore is an oceanographer and boat captain known for articles that recently brought attention to the 'Great Pacific Garbage Patch', an area of the Pacific Ocean strewn with floating plastic debris caught in a gyre.
The Hawaii Ocean Time-series (HOT) program is a long-term oceanographic study based at the University of Hawaii at Manoa. In 2015, the American Society for Microbiology designated the HOT Program's field site Station ALOHA a "Milestone in Microbiology", for playing "a key role in defining the discipline of microbial oceanography and educating the public about the vital role of marine microbes in global ecosystems."

The North Pacific Subtropical Gyre (NPSG) is the largest contiguous ecosystem on earth. In oceanography, a subtropical gyre is a ring-like system of ocean currents rotating clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere caused by the Coriolis Effect. They generally form in large open ocean areas that lie between land masses.

Project Kaisei is a scientific and commercial mission to study and clean up the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, a large body of floating debris trapped in the Pacific Ocean by the currents of the North Pacific Gyre. Discovered by NOAA, the patch is estimated to contain 20 times the density of floating debris compared to the global average. The project aims to study the extent and nature of the debris with a view to capturing, detoxifying, and recycling the material, and is organised by the Ocean Voyages Institute, a California-based 501c3 non-profit organisation dealing with marine preservation. The project is based in San Francisco and Hong Kong.
The Southern Pacific Gyre is part of the Earth's system of rotating ocean currents, bounded by the Equator to the north, Australia to the west, the Antarctic Circumpolar Current to the south, and South America to the east. The center of the South Pacific Gyre is the oceanic pole of inaccessibility, the site on Earth farthest from any continents and productive ocean regions and is regarded as Earth's largest oceanic desert. With an area of 37 million square kilometres it makes up ~10 % of the Earth's ocean surface. The gyre, as with Earth's other four gyres, contains an area with elevated concentrations of pelagic plastics, chemical sludge, and other debris known as the South Pacific garbage patch.

The Indian Ocean gyre, located in the Indian Ocean, is one of the five major oceanic gyres, large systems of rotating ocean currents, which together form the backbone of the global conveyor belt. The Indian Ocean gyre is composed of two major currents: the South Equatorial Current, and the West Australian Current.

The North Atlantic garbage patch is a garbage patch of man-made marine debris found floating within the North Atlantic Gyre, originally documented in 1972. A 22-year research study conducted by the Sea Education Association estimates the patch to be hundreds of kilometers across, with a density of more than 200,000 pieces of debris per square kilometer. The garbage originates from human-created waste traveling from rivers into the ocean and mainly consists of microplastics. The garbage patch is a large risk to wildlife through plastic consumption and entanglement. There have only been a few awareness and clean-up efforts for the North Atlantic garbage patch, such as The Garbage Patch State at UNESCO and The Ocean Cleanup, as most of the research and cleanup efforts have been focused on the Great Pacific garbage patch, a similar garbage patch in the north Pacific.

The Indian Ocean garbage patch, discovered in 2010, is a marine garbage patch, a gyre of marine litter, suspended in the upper water column of the central Indian Ocean, specifically the Indian Ocean Gyre, one of the five major oceanic gyres. The patch does not appear as a continuous debris field. As with other patches in each of the five oceanic gyres, the plastics in it break down to ever smaller particles, and to constituent polymers. As with the other patches, the field constitutes an elevated level of pelagic plastics, chemical sludge, and other debris; primarily particles that are invisible to the naked eye. The concentration of particle debris has been estimated to be approximately 10,000 particles per square kilometer.

The plastisphere consists of ecosystems that have evolved to live in human-made plastic environments. All plastic accumulated in marine ecosystems serves as a habitat for various types of microorganisms, with the most notable contaminant being microplastics. There are an estimate of about 51 trillion microplastics floating in the oceans. Relating to the plastisphere, over 1,000 different species of microbes are able to inhabit just one of these 5mm pieces of plastic.

The South Pacific garbage patch is an area of ocean with increased levels of marine debris and plastic particle pollution, within the ocean's pelagic zone. This area is in the South Pacific Gyre, which itself spans from waters east of Australia to the South American continent, as far north as the Equator, and south until reaching the Antarctic Circumpolar Current. The degradation of plastics in the ocean also leads to a rise in the level of toxics in the area. The garbage patch was confirmed in mid-2017, and has been compared to the Great Pacific garbage patch's state in 2007, making the former ten years younger. The South Pacific garbage patch is not visible on satellites, and is not a landmass. Most particles are smaller than a grain of rice. A researcher said: "This cloud of microplastics extends both vertically and horizontally. It's more like smog than a patch".

Human activities affect marine life and marine habitats through overfishing, habitat loss, the introduction of invasive species, ocean pollution, ocean acidification and ocean warming. These impact marine ecosystems and food webs and may result in consequences as yet unrecognised for the biodiversity and continuation of marine life forms.
References
- ↑ Altonn, Helen ."Marine garbage: UH TEAM researches effects of trash", Honolulu Star-Bulletin, August 24, 2008
- ↑ "Researching the Garbage Patch" [ permanent dead link ], News at UH, August 25, 2008
- ↑ Bialik, Carl. "How Big Is That Widening Gyre of Floating Plastic? ", The Wall Street Journal, March 25, 2009