
The franc is any of various units of currency. One franc is typically divided into 100 centimes. The name is said to derive from the Latin inscription francorum rex used on early French coins and until the 18th century, or from the French franc, meaning "frank".

Saarland is a state of Germany in the southwest of the country. With an area of 2,570 km2 (990 sq mi) and population of 990,509 in 2018, it is the smallest German state in area apart from the city-states of Berlin, Bremen, and Hamburg, and the smallest in population apart from Bremen. Saarbrücken is the state capital and largest city; other cities include Neunkirchen and Saarlouis. Saarland is mainly surrounded by the department of Moselle in France to the west and south and the neighboring state of Rhineland-Palatinate in Germany to the north and east; it also shares a small border about 8 kilometres long with the canton of Remich in Luxembourg to the northwest.

The Hallstein Doctrine, named after Walter Hallstein, was a key principle in the foreign policy of the Federal Republic of Germany from 1955 to 1970. As usually presented, it prescribed that the Federal Republic would not establish or maintain diplomatic relations with any state that recognized the German Democratic Republic. In fact it was more nuanced. There was no public official text of the "doctrine", but its main architect, Wilhelm Grewe, explained it publicly in a radio interview. Konrad Adenauer, who served as Chancellor of Germany from 1949 to 1963, explained the outlines of the policy in a statement to the German parliament on 22 September 1955. It meant that the Federal German government would regard it as an unfriendly act if third countries were to recognize the "German Democratic Republic" or to maintain diplomatic relations with it – with the exception of the Soviet Union. The West German response to such could mean breaking off diplomatic relations, though this was not stated as an automatic response under the policy and in fact remained the ultima ratio.

Walter Hallstein was a German academic, diplomat and statesman who was the first president of the Commission of the European Economic Community and one of the founding fathers of the European Union.

The European Union (EU) has expanded a number of times throughout its history by way of the accession of new member states to the Union. To join the EU, a state needs to fulfil economic and political conditions called the Copenhagen criteria, which require a stable democratic government that respects the rule of law, and its corresponding freedoms and institutions. According to the Maastricht Treaty, each current member state and the European Parliament must agree to any enlargement. The process of enlargement is sometimes referred to as European integration. This term is also used to refer to the intensification of co-operation between EU member states as national governments allow for the gradual harmonisation of national laws.
The Saar Protectorate, officially Saarland, was a French protectorate and a disputed territory separated from Germany. On joining the Federal Republic of Germany in 1957, it became the smallest "federal state", the Saarland, not counting the "city states" of Berlin, Hamburg, and Bremen. It is named after the Saar River.

The National Olympic Committee (NOC) of the Saarland was founded in the spring of 1950 in the Saar Protectorate, which existed from 1947 to 1956, a region of Western Germany that was occupied in 1945 by France. As a separate team, Saar took part in its sole Olympic Games at the 1952 Summer Olympics before being allowed to rejoin the German team in 1956. Thirty-six competitors, 31 men and five women, took part in 32 events in nine sports.

The entirety of Germany was occupied and administered by the Allies of World War II from the Berlin Declaration on 5 June 1945 to the establishment of West Germany on 23 May 1949. Unlike occupied Japan, Germany was stripped of its sovereignty and former state: after Nazi Germany surrendered on 8 May 1945, four countries representing the Allies asserted joint authority and sovereignty through the Allied Control Council (ACC). At first, Allied-occupied Germany was defined as all territories of Germany before the 1938 Nazi annexation of Austria; the Potsdam Agreement on 2 August 1945 defined the new eastern German border by giving Poland and the Soviet Union all regions of Germany east of the Oder–Neisse line and divided the remaining "Germany as a whole" into four occupation zones, each administered by one of the Allies.

The Saar franc was the French franc used as the official currency of the Saar during the times that the Saar territory was economically split off from Germany, in 1920–1935 as the Territory of the Saar Basin, in 1947–1957 as the Saar Protectorate and 1957–1959 as the state of Saarland in West Germany. Local notes and coins were issued during both periods, but the Saar franc was never legally an independent currency.

The Luxembourg Crisis was a diplomatic dispute and confrontation in 1867 between France and Prussia over the political status of Luxembourg.
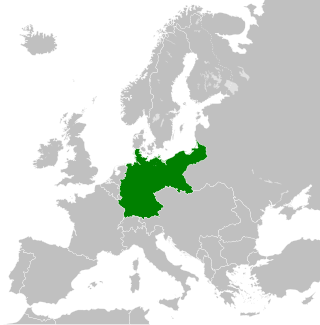
The territorial evolution of Germany in this article include all changes in the modern territory of Germany from its unification making it a country on 1 January 1871 to the present although the history of "Germany" as a territorial polity concept and the history of the ethnic Germans are much longer and much more complex. Modern Germany was formed when the Kingdom of Prussia unified most of the German states, with the exception of multi-ethnic Austria, into the German Empire. After the First World War, on 10 January 1920, Germany lost about 13% of its territory to its neighbours, and the Weimar Republic was formed two days before this war was over. This republic included territories to the east of today's German borders.

The year 1948 marked the beginning of the institutionalised modern European integration. With the start of the Cold War, the Treaty of Brussels was signed in 1948 establishing the Western Union (WU) as the first organisation. In the same year, the International Authority for the Ruhr and the Organization for European Economic Co-operation, the predecessor of the OECD, were also founded, followed in 1949 by the Council of Europe, and in 1951 by the European Coal and Steel Community, with the ensuing moves to create further communities leading to the Treaty of Rome (1957).

This is a timeline of European Union history and its previous development.

The Greater Region, formerly also known as SaarLorLux, is a euroregion of eleven regional authorities located in four European states. The term has also been applied to cooperations of several of these authorities or of their subdivisions, administrations, organisations, clubs and people. Member regions represent different political structures: the Walloon region, comprising the French and German-speaking Communities of Belgium; the former Lorraine part of Grand Est, a region of France, including the French departments Meurthe-et-Moselle, Meuse, Moselle and Vosges; the German federated states of Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland; and the sovereign state of Luxembourg.

The London and Paris Conferences were two related conferences held in London and Paris during September–October 1954 to determine the status of West Germany. The talks concluded with the signing of the Paris Agreements, which granted West Germany some sovereignty, ended the occupation, and allowed its admittance to NATO. Furthermore, both West Germany and Italy joined the Brussels Treaty on 23 October 1954. The Agreements went into force on 5 May 1955. The participating powers included France, the United Kingdom, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, West Germany, Italy, Canada, the United States, and remaining NATO members.

The International Authority for the Ruhr (IAR) was an international body established in 1949 by the Western Allies to regulate the coal and steel industries of the Ruhr area in West Germany. Its seat was in Düsseldorf.
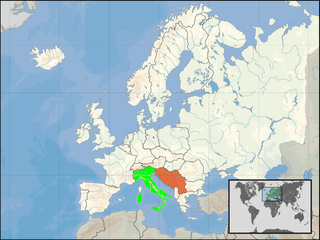
Italy–Yugoslavia relations are the cultural and political relations between Italy and Yugoslavia in the 20th century, since the creation of Yugoslavia in 1918 until its dissolution in 1992. Relations during the interwar years were hostile because of Italian irredentist demands to Yugoslav territory, leading to Fascist Italy and the Axis Powers invading Yugoslavia during World War II. After lingering tensions after the war over the status of the Free Territory of Trieste, relations improved during the Cold War.
The Saar Treaty, or Treaty of Luxembourg is an agreement between West Germany and France concerning the return of the Saar Protectorate to West Germany. The treaty was signed in Luxembourg on October 27, 1956, by foreign ministers Heinrich von Brentano of West Germany and Christian Pineau of France, following the Saar Statute referendum on October 23, 1955, which resulted in a majority vote against the Saar Statute.
A referendum on the Saar statute was held in the Saar Protectorate on 23 October 1955. The statute would have made the territory an independent polity under the auspices of a European Commissioner, to be appointed by the Council of Ministers of the Western European Union, while remaining in the economic union with France.

Johann Viktor, known professionally as Johannes "Joho" Hoffmann, was a German politician. A founding member and chairman of the Christian People's Party of Saarland, Hoffman served as Minister-President of the French Saar Protectorate from 1947 to 1955.













